Abstract
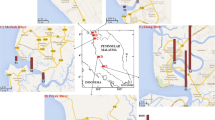
The levels, spatial distribution, and sources of petroleum hydrocarbons and phthalates were assessed in surface sediment samples from the urban lagoon of Obhur near Jeddah, the largest city on the Red Sea coast of Saudi Arabia. The lagoon was divided into the inner zone, middle zone, and outer zone based on its geomorphological features and developmental activities. n-Alkanes, hopane and sterane biomarkers, and unresolved complex mixture were the major petroleum hydrocarbon compounds of the total extractable organic matter. Phthalates were also measured in the sediment samples. In the three zones, n-alkanes ranged from 89.3 ± 88.5 to 103.2 ± 114.9 ng/g, whereas the hopane and sterane biomarkers varied from 69.4 ± 75.3 to 77.7 ± 69.9 ng/g and 72.5 ± 77.9–89.5 ± 82.2 ng/g, respectively. The UCM concentrations ranged from 821 ± 1119 to 1297 ± 1684 ng/g and phthalates from 37.4 ± 34.5 65 ± 68 ng/g. The primary origins of these anthropogenic hydrocarbons in the lagoon sediments were petroleum products (boat engine discharges, boat washing, lubricants, and wastewater flows) and plasticizers (plastic waste and litter). The proportions of anthropogenic hydrocarbons derived from petroleum products in the sediment’s TEOM ranged from 43 ± 33 to 62 ± 15%, while the percentages for plasticizers varied from 2.9 ± 1.2 to 4.0 ± 1.6%. The presence and inputs of these contaminants from petroleum and plastic wastes in the lagoon’s sediments will eventually have an impact on its habitats, including the benthic nursery and spawning areas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abas, M. R. B., & Simoneit, B. R. T. (1996). Composition of extractable organic matter of air particles from Malaysia: Initial studies. Atmospheric Environment, 15, 2779–2793.
Abdallah, R. I., Khalil, N. M., & Roushdie, M. I. (2015). Monitoring of pollution in Egyptian Red Sea. Egypt J Petroleum, 24(1), 59–70.
Abdulla, C. P., & Al-Subhi, A. M. (2020). Sea level variability in the Red Sea: A persistent east-west pattern. Remote Sensing, 12(13), 2090.
Aboul-Kassim, T. A. T., & Simoneit, B. R. T. (1996). Lipid geochemistry of surficial sediments from coastal environment of Egypt I. Aliphatic hydrocarbons - characterization and sources. Marine Chemistry, 54, 135–158.
Alamri, D. A., Al-Solaimani, S. G., Abohassan, R. A., Rinklebe, J., & Shaheen, S. M. (2021). Assessment of water contamination by potentially toxic elements in mangrove lagoons of the Red Sea. Saudi Arabia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43(11), 4819–4830.
Albaiges, J., & Cuberes, M. R. (1980). On the degradation of petroleum residues in the marine environment. Chemosphere, 9, 539–545.
Albarakati, A., Ahmad, F. (2019). Red Sea Coastal Lagoons: Their dynamics and future challenges. In: Oceanographic and Biological Aspects of the Red Sea, (pp. 123–131). Springer, Cham
Albarakati, A. (2009). Water exchange of Sharm Obhur, Jeddah. Red Sea. JKAU: Marine Scienes, 20, 49–58.
Alhudhodi, A. H., Alduwais, A. K., Aldhafeeri, Z. M., Al-Shamsi, M. A. S., & Alharbi, B. H. (2022). Contamination assessment of mangrove ecosystems in the Red Sea coast by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(9), 5474.
Ali, A. M., Rønning, H. T., Al Arif, W. M., Kallenborn, R., & Al-Lihaibi, S. S. (2017). Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in effluent-dominated Saudi Arabian coastal waters of the Red Sea. Chemosphere, 175, 505–513.
Aljahdali, M. O., Munawar, S., & Khan, W. R. (2021). Monitoring mangrove forest degradation and regeneration: Landsat time series analysis of moisture and vegetation indices at Rabigh Lagoon, Red Sea. Forests, 12(1), 52.
Al-Khion, D. D., Al-Ali, B. S., Al-Saad, H. T., & Rushdi, A. I. (2021). Levels and source of aliphatic hydrocarbons in marine fishes from coast of Iraq based on biomarkers and biogeochemical indices. Indian Journal of Ecology, 48(2), 536–544.
Al-Lihaibi, S., Al-Mehmadi, A., Alarif, W. M., Bawakid, N. O., Kallenborn, R., & Ali, A. M. (2019). Microplastics in sediments and fish from the Red Sea coast at Jeddah (Saudi Arabia). Environmental Chemistry, 16(8), 641–650.
Alsaafani, M. A., Alraddadi, T. M., & Albarakati, A. M. (2017). Seasonal variability of hydrographic structure in Sharm Obhur and water exchange with the Red Sea. Arabian Journal Geoscience, 10(14), 315.
Alsharhan, A. S. (2003). Petroleum geology and potential hydrocarbon plays in the Gulf of Suez rift basin. Egypt Bulletin Am Assoc Petrol Geol, 87(1), 143–180.
Ameen, F., Moslem, M., Hadi, S., & Al-Sabri, A. E. (2016). Biodegradation of diesel fuel hydrocarbons by mangrove fungi from Red Sea Coast of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Journal Biological Sciences, 23(2), 211–218.
Andrady, A. L. (2011). Microplastics in the marine environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(8), 1596–1605.
Arfaeinia, H., Fazlzadeh, M., Taghizadeh, F., Saeedi, R., Spitz, J., & Dobaradaran, S. (2019). Phthalate acid esters (PAEs) accumulation in coastal sediments from regions with different land use configuration along the Persian Gulf. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 169, 496–506.
Badr, N. B., El-Fiky, A. A., Mostafa, A. R., & Al-Mur, B. A. (2009). Metal pollution records in core sediments of some Red Sea coastal areas, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Environ Monitoring Assessment, 155(1), 509–526.
Barboza, L.G.A., C ́ozar, A., Gimenez, B.C.G., Barros, T.L., Kershaw, P.J., Guilhermino, L. (2019). Macroplastics pollution in the marine environment. In: World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation. Elsevier, pp. 305–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-805052-1.00019-X
Basaham, A. S., El-Sayed, M. A. (2006). Sharm Obhur: environmental consequences of 20 years of uncontrolled coastal urbanization. Marine Scienes, 17(1)
Basaham, A. S., & El-Shater, A. (1994). Textural and mineralogical characteristics of the surficial sediments of Sharm Obhur, Red Sea coast of Saudi Arabia. Marine Scienes, 5(1), 51–71.
Basaham, A. S., Ghandour, I. M., & Haredy, R. (2019). Controlling factors on the geochemistry of Al-Shuaiba and Al-Mejarma coastal lagoons, Red Sea Saudi Arabia. Open Geosciences, 11(1), 426–439.
Batang, Z. B., Alikunhi, N., Gochfeld, M., Burger, J., Al-Jahdali, R., Al-Jahdali, H., Aziz, M. A., Al-Jebreen, D., & Al-Suwailem, A. (2016). Congener-specific levels and patterns of polychlorinated biphenyls in edible fish tissue from the central Red Sea coast of Saudi Arabia. Sci Total Environment, 572, 915–925.
Bellar, H., Barrick, R. C., Becker, S. (1986). Development of sediment quality values for Puget Sound. Prepared by Tetra Tech, Inc. for Resource Planning Associates/U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Seattle District for the Puget Sound Dredged Disposal Analysis Program. Tetra Tech Inc. Bellevue, Washington
Bellou, N., Gambardella, C., Karantzalos, K., Monteiro, J. G., Canning-Clode, J., Kemna, S., Arrieta-Giron, C. A., & Lemmen, C. (2021). Global assessment of innovative solutions to tackle marine litter. Nature Sustainability, 4, 516–524. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-021-00726-2
Boonyatumanond, R., Wattayakorn, G., Togo, A., & Takada, H. (2006). Distribution and origins of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in riverine, estuarine, and marine sediments in Thailand. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52(8), 942–956.
Bouloubassi, I., Fillaux, J., & Saliot, A. (2001). Hydrocarbons in surface sediments from the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary, East China Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42, 1335–1346.
Bourbonniere, R. A., & Meyers, P. A. (1996). Sedimentary geolipid records of historical changes in the watersheds and productivities of Lakes Ontario and Erie. Limnology and Oceanography, 41(2), 352–359.
Bray, E. E., & Evans, E. D. (1961). Distribution of n-paraffins as a clue to recognition of source beds. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 22(1), 2–15.
Bryan, G. T. (1976). Heavy metal contamination in the sea. Marine Pollution, 3, 185–302.
Cesar, A., Lia, L. R. B., Pereira, C. D. S., Santos, A. R., Cortez, F. S., Choueri, R. B., & Rachid, B. R. F. (2014). Environmental assessment of dredged sediment in the major Latin American seaport (Santos, São Paulo—Brazil): An integrated approach. Science of the Total Environment, 497, 679–687.
Colombo, J. C., Pelletier, E., Brochu, C., Khalil, M., & Catoggio, J. A. (1989). Determination of hydrocarbon sources using n-alkane and polyaromatic hydrocarbon distribution indexes. Case study: Rio de la Plata estuary Argentina. Environmental Science & Technology, 23(7), 888–894.
Commendatore, M. G., & Esteves, J. L. (2004). Natural and anthropogenic hydrocarbons in sediments from the Chubut river (Patagonia, Argentina). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 48, 910–918.
Derraik, J. G. B. (2002). The pollution of the marine environment by plastic debris: A review. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 44(9), 842–852.
Dicks, B. (1987). Pollution. In A. Edwards & S. M. Head (Eds.), Key Environments: The Red Sea (pp. 383–404). Pergamon Press.
Diefendorf, A. F., Freeman, K. H., & Wing, S. L. (2014). A comparison of terpenoid and leaf fossil vegetation proxies in Paleocene and Eocene Bighorn Basin sediments. Organic Geochemistry, 71, 30–42.
Diem, A., Tesfaldet, Y. T., Hocherman, T., Hoon, V., & Zijlemans, K. (2023). Marine litter in the Red Sea: Status and policy implications. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 187, 114495.
Dong, C. D., Huang, C. P., Nguyen, T. B., Hsiung, C. F., Wu, C. H., Lin, Y. L., & Hung, C. M. (2019). The degradation of phthalate esters in marine sediments by persulfate over iron–cerium oxide catalyst. Science of the Total Environment, 696, 133973.
DouAbul, A. A., Heba, H. M., & Fareed, K. H. (1997). Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in fish from the Red Sea Coast of Yemen. Asia-Pacific Conference on Science and Management of Coastal Environment (pp. 251–262). Springer.
Durmuş, K. A. Y. A. (2019). Sustainable domestic solid waste management in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Journal of International Environmental Application and Science, 14(4), 193–198.
Eerkes-Medrano, D., Thompson, R. C., & Aldridge, D. C. (2015). Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Research, 75, 63–82.
Eglinton, G., & Hamilton, R. J. (1967). Leaf epicuticular waxes. Science, 156, 1322–1335.
El Nemr, A., El-Sadaawy, M. M., Khaled, A., & El-Sikaily, A. (2014). Distribution patterns and risks posed of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated in the surface sediment of the Red Sea coast (Egypt). Desalination and Water Treatment, 52(40–42), 7964–7982.
El Nemr, A., El-Sikaily, A., Khaled, A., Said, T. O., & Abd-Alla, A. M. (2004). Determination of hydrocarbons in mussels from the Egyptian Red Sea coast. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 96(1–3), 251–261.
El Sayed, M. A. (2002a). Distribution and behavior of dissolved species of nitrogen and phosphorus in two coastal Red Sea lagoons receiving domestic sewage. Marine Sciences, 13, 47–73.
El Sayed, M. A. (2002b). Nitrogen and phosphorus in the effluent of a sewage treatment station on the eastern Red Sea coast: Daily cycle, flux and impact on the coastal area. International Journal Environmental Studies, 59(1), 73–94.
El-Rayis, O. A., & Eid, F. M. (1997). Hydrography and water budget of Obhur creek, Red Sea. Marine Scienes, 8, 29–45.
El-Sikaily, A., Khaled, A., El Nemr, A., Said, T. O., & Abd-Alla, A. M. A. (2003). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and aliphatics in the coral reef skeleton of the Egyptian Red Sea Coast. Bulletin Environment Contamination Toxicology, 71(6), 1252–1259.
Eriksen, M., Mason, S., Wilson, S., Box, C., Zellers, A., Edwards, W., Farley, H., & Amato, S. (2013). Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 77(1–2), 177–182.
Fan, S., Yan, Z., Qiao, L., Gui, F., Li, T., Yang, Q., & Ren, C. (2023). Biological effects on the migration and transformation of microplastics in the marine environment. Marine Environmental Research, 185, 105875.
Ficken, K. J., Li, B., Swain, D. E., & Eglinton, G. (2000). An n-alkanes proxy for the sedimentary input of submerged/floating fresh water aquatic macrophytes. Organic Geochemistry, 31, 745–759.
Frysinger, G. S., Gaines, R. B., Xu, L., & Reddy, C. M. (2003). Resolving the unresolved complex mixture in petroleum-contaminated sediments. Environmental Sci Technol, 37(8), 1653–1662.
Gao, L., Wang, Z., Peng, X., Su, Y., Fu, P., Ge, C., & Peng, L. (2022). Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics, and their correlation with petroleum in coastal waters of Hainan Island China. Environmental Pollution, 294, 118636.
Gao, Y., Han, Y., Xia, J., Tan, J., Wang, Y. P., & Wang, S. (2021). Composition and distribution of aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds and biomarkers in seafloor sediments from offshore of the Leizhou Peninsula (South China). ACS Omega, 6(50), 34286–34293.
Garcia, M. R., Cattani, A. P., da Cunha Lana, P., Figueira, R. C. L., & Martins, C. C. (2019). Petroleum biomarkers as tracers of low-level chronic oil contamination of coastal environments: A systematic approach in a subtropical mangrove. Environmental Pollution, 249, 1060–1070.
Gough, M. A., & Rowland, S. J. (1990). Characterization of unresolved complex mixtures of hydrocarbons in petroleum. Nature, 344, 648–650.
Harji, R. R., Yvenat, A., & Bhosle, N. B. (2008). Sources of hydrocarbons in sediments of the Mandovi estuary and the Marmugoa harbour, west coast of India. Environment International, 34(7), 959–965.
Hees, W. (1977). Sewage discharges from ships transiting coastal salt waters. J Am Water Resources Assoc, 13(2), 215–230.
Isobe, A., & Iwasaki, S. (2022). The fate of missing ocean plastics: Are they just a marine environmental problem? Science of the Total Environment, 825, 153935.
Jafarabadi, A. R., Dashtbozorg, M., Bakhtiari, A. R., Maisano, M., & Cappello, T. (2019). Geochemical imprints of occurrence, vertical distribution and sources of aliphatic hydrocarbons, aliphatic ketones, hopanes and steranes in sediment cores from ten Iranian Coral Islands, Persian Gulf. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 144, 287–298.
Jamoussi, B., Chakroun, R., & Al-Mur, B. (2022). Assessment of total petroleum hydrocarbon contamination of the red sea with endemic fish from Jeddah (Saudi Arabia) as bioindicator of Aquatic environmental pollution. Water, 14(11), 1706.
Jang, M., Shim, W. J., Han, G. M., Cho, Y., & Hong, S. H. (2023). Plastic debris as a mobile source of additive chemicals in marine environments: In-situ evidence. Science of the Total Environment, 856, 158893.
Keshavarzifard, M., Zakaria, M. P., Sharifinia, M., Grathwohl, P., Keshavarzifard, S., Sharifi, R., & Mehr, M. R. (2022). Determination of hydrocarbon sources in major rivers and estuaries of peninsular Malaysia using aliphatic hydrocarbons and hopanes as biomarkers. Environmental Forensics, 23(3–4), 255–268.
Killops, S. D., & Al-Juboori, M. A. H. A. (1990). Characterisation of the unresolved complex mixture (UCM) in the gas chromatograms of biodegraded petroleums. Organic Geochem, 15(2), 147–160.
Kingsley, O., & Witthayawirasak, B. (2020). Deterministic assessment of the risk of phthalate esters in sediments of U-Tapao Canal Southern Thailand. Toxics, 8(4), 93.
Kjerfve, B. (1994). Coastal lagoons. In: Elsevier oceanography series (Vol. 60, pp. 1–8). Elsevier
Knoppers, B., Kjerfve, B., & Carmouze, J. P. (1991). Trophic state and water turn-over time in six choked coastal lagoons in Brazil. Biogeochemistry, 14(2), 149–166.
Kostianaia, E. A., Kostianoy, A., Lavrova, O. Y., Soloviev, D. M. (2020). Oil pollution in the Northern Red Sea: A threat to the marine environment and tourism development. In: Environmental Remote Sensing in Egypt (pp. 329–362). Springer, Cham
Kvenvolden, K. A., Rapp, J. B., & Hostettler, F. D. (1990). Hydrocarbon geochemistry of hydrothermal generated petroleum from Escanaba Trough, offshore California, U.S.A. Applied Geochemistry, 5, 83–91.
Laws, E. A. (1993). Oil Pollution. Aquatic Pollution: An Introductory Text (2nd ed., pp. 417–458). Wiley.
Long, E. R., & Morgan, L. G. (1990). The potential for biological effects of sediment-sorbed contaminants tested in the National Status and Trends Program. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS OMA 52 (p. 175). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Seattle.
Long, E. R., MacDonald, D. D., Smith, S. L., & Calder, F. D. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Management, 19, 81–97.
Loya, Y. (1975). Possible effects of water pollution on the community structure of Red Sea corals. Marine Biology, 29, 177–185.
Malins, D. C. (1977). Metabolism of aromatic hydrocarbons in marine organisms. Annals New York Acad Sci, 298(1), 482–496.
Mandura, A. S. (1997). A mangrove stand under sewage pollution stress: Red Sea. Mangroves Salt Marshes, 1(4), 255–262.
Mazurek, M. A., & Simoneit, B. R. T. (1984). Characterization of biogenic and petroleum derived organic matter in aerosols over remote, rural and urban areas. In L. H. Kieth (Ed.), Identification and Analysis of Organic Pollutants in Air (pp. 353–370). Ann Arbor Science/Butterworth Publishers.
Medeiros, P. M., Bicego, M. C., Castelao, R. M., Rosso, D. C., Fillmann, G., & Zamboni, A. T. (2005). Natural and anthropogenic hydrocarbon inputs to sediments of Patos Lagoon estuary, Brazil. Environment International, 31, 77–87.
Moldowan, J. M., Seifert, W. K., & Gallegos, E. J. (1985). Relationship between petroleum composition and depositional environment of petroleum source rocks. Bulletin - American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 69(8), 1255–1268.
Ndungu, K., Beylich, B. A., Staalstrøm, A., Øxnevad, S., Berge, J. A., Braaten, H. F. V., & Bergstrøm, R. (2017). Petroleum oil and mercury pollution from shipwrecks in Norwegian coastal waters. Science of the Total Environment, 593, 624–633.
Neves, P. A., Costa, P. G., Portz, L. C., Garcia, M. R., & Fillmann, G. (2023). Levels and sources of hydrocarbons in the Patos Lagoon estuary and Cassino Beach mud bank (South Atlantic, Brazil): Evidence of transference between environments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(4), 484.
Nilsen, O. G., Haugen, O. A., Zahlsen, K., Halgunset, J., Helseth, A., Aarset, H., & Eide, I. (1988). Toxicity of n-C9 to n-C13 alkanes in the rat on short term inhalation. Pharmacology & Toxicology, 62(5), 259–266.
Peng, L., Fu, D., Qi, H., Lan, C. Q., Yu, H., & Ge, C. (2020). Micro-and nano-plastics in marine environment: Source, distribution and threats—A review. Science of the Total Environment, 698, 134254.
Periáñez, R. (2020). A Lagrangian oil spill transport model for the Red Sea. Ocean Engineering, 217, 107953.
Perkins, S. (2015). Nearly every seabird may be eating plastic by 2050. Retrieved from: http://www.sciencemag.org/news/2015/08/nearly-every-seabird-may-be-eating-plastic-2050
Peters, K. E., & Moldowan, J. M. (1993). The Biomarker Guide: Interpreting Molecular Fossils in Petroleum and Ancient Sediments. Prentice-Hall.
Por, F. D. (2012). Lessepsian migration: The influx of Red Sea biota into the Mediterranean by way of the Suez Canal. Springer.
PTI (PTI Environmental Services; Barrick R, Becker S, Brown L, Beller H, Pastorok R). (1988). Sediment quality values refinement: 1988 update and evaluation of Puget Sound AET. Volume 1. PTI Environmental Services. Bellevue, Washington. Pp. 173
Ramirez, M. M. B., Caamal, R. D., & von Osten, J. R. (2019). Occurrence and seasonal distribution of microplastics and phthalates in sediments from the urban channel of the Ria and coast of Campeche, Mexico. Science of the Total Environment, 672, 97–105.
Rasul, N. M. A. (2015). Lagoon sediments of the Eastern Red Sea: Distribution processes, pathways and patterns. In N. M. A. Rasul & I. C. F. Stewart (Eds.), The Red Sea: The Formation, Morphology, Oceanography and Environment of a Young Ocean Basin (pp. 281–316). Springer.
Rinkevich, B., & Loya, Y. (1979). Laboratory experiments on the effects of crude oil on the Red Sea coral Stylophora pistillate. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 10, 328–330.
Rushdi, A. I., Abubakr. M. M., Hebba, H. (1994). Marine habitats of Alurj-Alsalif and Dubab-Yakhtul areas: Ecology, environment and management. Final Report, Department of Oceanography, Sana'a University, pp. 117
Rushdi, A. I., Simoneit, B. R., Lijotra, L., Bazeyad, A. Y., Dumenden, R., El-Mubarak, A. H., & Al-Mutlaq, K. F. (2022b). Phthalates, non-phthalates, polychlorinated biphenyls, and phenyl phosphates in atmospheric suspended particulate matter of Dhahran City, Saudi Arabia: levels and seasonal variation. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 20(4), 1–16.
Rushdi, A. I., Al-Mutlaq, K. F., Simoneit, B. R. T., Al-Azri, A., DouAbul, A. A. Z., Al-Zarban, S., & Al-Yamani, F. (2010). Characteristics of lipid tracers to the Arabian Gulf by run-off from rivers and atmospheric dust transport. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 3, 113–131.
Rushdi, A. I., Al-Shaikh, I., El-Mubarak, A. H., Alnaimi, H. A., Al-Shamary, N., Hassan, H. M., & Abou Assali, M. (2017b). Characteristics and sources of anthropogenic and biogenic hydrocarbons in sediments from the coast of Qatar. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 124(1), 56–66.
Rushdi, A. I., Al-Shaikh, I., El-Mubarak, A. H., Alnaimi, H. A., Al-Shamary, N., Hassan, H. M., & Assali, M. A. (2017a). Characteristics and sources of anthropogenic and biogenic hydrocarbons in sediments from the coast of Qatar. Marine Pollut Bull, 124(1), 56–66.
Rushdi, A. I., DouAboul, A. A., Mohammed, S. S., & Simoneit, B. R. T. (2006). Distribution and sources of extractable organic matter in the Mesopotamian wetland marsh sediments of Iraq: I - aliphatic lipids. Environmental Geology, 50, 857–866.
Rushdi, A. I., DouAbul, A. A., Al-Maarofi, S. S., & Simoneit, B. R. (2018). Impacts of Mesopotamian wetland re-flooding on the lipid biomarker distributions in sediments. Journal of Hydrology, 558, 20–28.
Rushdi, A. I., DouAbul, A. A., Simoneit, B. R., El-Mubarak, A. H., Al-Mutlaq, K. F., Qurban, M. A., & Goni, M. A. (2014b). Nonpolar lipid tracers in sediments from the Shatt al-Arab River of Iraq and the northwestern Arabian Gulf. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 7, 5495–5508.
Rushdi, A. I., El-Mubarak, A. H., Simoneit, B. R., Goni, M. A., Qurban, M. A., Bazeyad, A. Y., & Al-Mutlaq, K. F. (2022a). Natural and anthropogenic sources of extractable organic matter in sediments from the coastal zone of the Arabian Gulf in Saudi Arabia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 15(17), 1–17.
Rushdi, A. I., Kassim, T. A. T. A., & Simoneit, B. R. T. (2009). Sources of organic tracers in sediments from the coastal zone of Ras Abu el-Darag, Gulf of Suez. Environmental Geology, 58, 1675–1687.
Rushdi, A. I., & Simoneit, B. R. T. (2002a). Hydrothermal alteration of organic matter in sediments of the northeastern Pacific Ocean: Part 1. Middle Valley. Juan De Fuca Ridge. Appl Geochem, 17, 1401–1428.
Rushdi, A. I., & Simoneit, B. R. T. (2002b). Hydrothermal alteration of organic matter in sediments of the northeastern Pacific Ocean: Part 2. Gorda Ridge. Escanaba Trough. Appl Geochem, 17, 1467–1494.
Rushdi, A. I., Simoneit, B. R. T., DouAbul, A. A. Z., Al-Mutlaq, K. F., El-Mubarak, A. H., Qurban, M., & Goni, M. A. (2014a). Occurrence, distribution and sources of polar lipid tracers in sediments from the Shatt al-Arab River, Iraq – Polar compounds. Sci Tot Environ, 470–471, 180–192.
Ryan, P.G., (2015). A brief history of marine litter research. In: Marine Anthropogenic Litter. Springer, pp. 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16510-3_1
Salem, D. M. A., Morsy, F. A. E. M., El Nemr, A., El-Sikaily, A., & Khaled, A. (2014). The monitoring and risk assessment of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of the Red Sea. Egypt. Egypt Journal Aquatic Research, 40(4), 333–348.
Shetaia, Y. M., Mohamed, T. M., Farahat, L. A., & ElMekawy, A. (2016). Potential biodegradation of crude petroleum oil by newly isolated halotolerant microbial strains from polluted Red Sea area. Marine Pollution Bull, 111(1), 435–442.
Shirneshan, G., Bakhtiari, A. R., & Memariani, M. (2016). Distribution and origins of n-alkanes, hopanes, and steranes in rivers and marine sediments from Southwest Caspian coast, Iran: Implications for identifying petroleum hydrocarbon inputs. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 17484–17495.
Simoneit, B. R. T. (1977a). Diterpenoid compounds and other lipids in deep-sea sediments and their geochemical significance. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 41, 463–476.
Simoneit, B. R. T. (1977b). Organic matter in eolian dusts over the Atlantic Ocean. Marine Chemistry, 5, 443–464.
Simoneit, B. R. T. (1978). The organic chemistry of marine sediments. In J. P. Riley & R. Chester (Eds.), Chemical Oceanography (2nd ed., pp. 233–311). Academic Press.
Simoneit, B. R. T. (1984). Organic matter of the troposphere - III. Characterization and sources of petroleum and pyrogenic residues in aerosols over the western United States. Atmospheric Environment, 18, 51–67.
Simoneit, B. R. T. (1985). Application of molecular marker analysis to vehicular exhaust for source reconciliation. Int J Environ Analyt Chem, 22, 203–233.
Simoneit, B. R. T. (1989). Organic matter of troposphere – V: Application of molecular analysis to biogenic emissions into troposphere for source reconciliations. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 8, 251–275.
Simoneit, B. R. T., Crisp, P. T., Mazurek, M. A., & Standley, L. J. (1991a). Composition of extractable organic matter of aerosols from the Blue Mountains and southeast coast of Australia. Environment International, 17, 405–419.
Simoneit, B. R. T., & Mazurek, M. A. (1982). Organic matter of the troposphere - II. Natural background of biogenic lipid matter in aerosols over the rural western United States. Atmospheric Environment, 16, 2139–2159.
Simoneit, B. R. T., Sheng, G., Chen, X., Fu, J., Zhang, J., & Xu, Y. (1991b). Molecular marker study of extractable organic matter in aerosols from urban areas of China. Atmospheric Environment, 25A, 2111–2129.
Sivadas, S. K., Mishra, P., Kaviarasan, T., Sambandam, M., Dhineka, K., Murthy, M. R., & Hoehn, D. (2022). Litter and plastic monitoring in the Indian marine environment: A review of current research, policies, waste management, and a roadmap for multidisciplinary action. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 176, 113424.
Squillante, J., Scivicco, M., Ariano, A., Nolasco, A., Esposito, F., Cacciola, N. A., & Cirillo, T. (2023). Occurrence of phthalate esters and preliminary data on microplastics in fish from the Tyrrhenian sea (Italy) and impact on human health. Environmental Pollution, 316, 120664.
Surhoff, T. J., & Scholz-Bottcher, B. M. (2016). Qualitative impact of salinity, UV radiation and turbulence on leaching of organic plastic additives from four common plastics - a lab experiment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 102(1), 84–94.
Ten Haven, H. L., De Leeuw, J. W., Damsté, J. S., Schenck, P. A., Palmer, S. E., & Zumberge, J. E. (1988). Application of biological markers in the recognition of palaeohypersaline environments. Special Publication of the Geological Society of London, 40(1), 123–130.
Tolosa, I., De Mora, S. J., Fowler, S. W., Villeneuve, J. P., Bartocci, J., & Cattini, C. (2005). Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons in marine biota and coastal sediments from the Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50(12), 1619–1633.
Tolosa, I., de Mora, S., Sheikholeslami, M. R., Villeneuve, J. P., Bartocci, J., & Cattini, C. (2004). Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons in coastal Caspian Sea sediments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 48(1–2), 44–60.
Tranganida, A., Hall, A. J., Armstrong, H. C., Moss, S. E., & Bennett, K. A. (2023). Consequences of in vitro benzyl butyl phthalate exposure for blubber gene expression and insulin-induced Akt activation in juvenile grey seals. Environmental Pollution, 316, 120688.
Tsapakis, M., Dakanali, E., Stephanou, E. G., & Karakassis, I. (2010). PAHs and n-alkanes in Mediterranean coastal marine sediments: Aquaculture as a significant point source. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 12(4), 958–963.
Uddin, S., Fowler, S. W., Saeed, T., Jupp, B., & Faizuddin, M. (2021). Petroleum hydrocarbon pollution in sediments from the Gulf and Omani waters: Status and review. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 173, 112913.
UNEP. (1985). The management and conservation of renewable marine resources in the Indian Ocean Region in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden region. UNEP Regional Seas Reports & Studies, No. 64
van Wezel, A. P., van Vlaardingen, P., Posthumus, R., Grommentijn, G. H., & Sijm, D. T. H. (2000). Environmental risk limits for two phthalates with special emphasis on endocrine disruptive properties. Ecotox Environment Safe, 46, 305–321.
Vegter, A. C., Barletta, M., Beck, C., Borrero, J., Burton, H., Campbell, M. L., Costa, M. F., Eriksen, M., Eriksson, C., Estrades, A., & Gilardi, K. V. (2014). Global research priorities to mitigate plastic pollution impacts on marine wildlife. Endanger Species Res, 25, 225–247.
Walker, T. R., Grant, J., & Archambault, M. C. (2006). Accumulation of marine debris on an intertidal beach in an urban park (Halifax Harbour, Nova Scotia). Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 41, 256–262.
Walker, T. R., Reid, K., Arnould, J. P. Y., & Croxall, J. P. (1997). Marine debris surveys at Bird Island, South Georgia 1990–1995. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 34, 61–65.
Wang, S., Liu, G., Yuan, Z., & Da, C. (2018). n-Alkanes in sediments from the Yellow River Estuary, China: Occurrence, sources and historical sedimentary record. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 150, 199–206.
Wang, X. C., Sun, S., Ma, H. Q., & Liu, Y. (2006). Sources and distribution of aliphatic and polyaromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao. China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52(2), 129–138.
Wilson, J. J., Al-Sofyani, A. A., & Marimuthu, N. (2017). Current biodiversity and ecological status of scleractinian corals of Sharm Obhur, Jeddah, Saudi Arabian coast of the Red Sea. Marine Biodiversity. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-017-0784-2
WPR (World Population Review). (2023). https://worldpopulationreview.com/
Xanthos, D., & Walker, T. R. (2017). International policies to reduce plastic marine pollution from single-use plastics (plastic bags and microbeads): A review. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 118(1–2), 17–26.
Zhang, H., Zhao, C., & Na, H. (2021). Stability Enhancement of a Plastic Additive (dimethyl Phthalate, dMP) with Environment-Friendly Based on 3d-QSAR Model. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 30(4), 3885–3896.
Zhang, Z., Zhao, M., Eglinton, G., Lu, H., & HuangC-Y,. (2006). Leaf wax lipids as paleovegetational and paleoenvironmental proxies for the Chinese Loess Plateau over the last 170 kyr. Quaternary Science Reviews, 25(5–6), 575–594.
Ziegler, M., Roik, A., Porter, A., Zubier, K., Mudarris, M. S., Ormond, R., & Voolstra, C. R. (2016). Coral microbial community dynamics in response to anthropogenic impacts near a major city in the central Red Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 105(2), 629–640.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Plan for Science, Technology, and Innovation (MAARIFAH), King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Award Number (NPST 13-ENV2233-02-R).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HA contributed to conceptualization, methodology, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft, visualization, project administration, and funding acquisition. AR contributed to Methodology, investigation, formal data analysis, and writing—review & editing. NR contributed to Methodology, investigation, data curation, and writing—review & editing. AB contributed to methodology, investigation, and writing—review & editing. KA contributed to investigation and writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alharbi, H.A., Rushdi, A.I., Rasul, N. et al. Levels, spatial distributions, and provision of petroleum hydrocarbons and phthalates in sediments from Obhur lagoon, Red Sea coast of Saudi Arabia. Environ Geochem Health 46, 22 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01793-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01793-4