Abstract
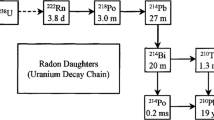
In this study, the radon gas and radium concentration in the bottled mineral water samples was measured. A total of sixty samples were collected from bottled mineral water sold in the markets in Kahramanmaraş. DURRIDGE Rad7 electronic radon detector was used for measurements. Radon and radium activity amounts range from 33.50 ± 1.30 mBq/L to 51.70 ± 2.20 mBq/L, and 2.92 ± 0.15 mBq/L to 4.51 ± 0.26 mBq/L, respectively. Average radon and radium active amounts are 41.67 ± 1.54 mBq/L and 3.63 ± 0.18 mBq/L, respectively. Total annual effective dose values were calculated for these mineral waters according to three different scenarios. In the first of these, it was assumed that natural mineral water was consumed annually instead of 730 L of drinking water (S1). In the second case, 150 L which was the annual average amount of natural mineral water consumed in European Union member countries was used for the annual average amount of natural mineral water consumed by adults (S2). Finally, the annual average amount of natural mineral water consumed in Turkey, 14 L, was used for adults (S3). For scenarios (S1, S2, S3), the total (ingestion + inhalation) annual average dose values ranged from 6.83E−04 mSv/y to 1.05E−03 mSv/y, 1.40E−04 mSv/y to 2.17E−04, and 1.32E−05 mSv/y to 2.03E−05 mSv/y, their average values were 8.49E−04 mSv/y, 1.75E−04 mSv/y, and 1.64E−05 mSv/y, respectively. The total effective dose values calculated within the scope of the current study were below the limit value announced by WHO.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altıkulaç, A., Kurnaz, A., Turhan, S., & Kutucu, M. (2022). Natural radionuclides in bottled mineral waters consumed in Turkey and their contribution to radiation dose. ACS Omega, 7(38), 34428–34435.
Durridge (2023). Rad7 electronic radon detector user manual. Revision 2023–03–27,2023. ( access date:15 July 2023). https://durridge.com/documentation/RAD7%20Manual.pdf
Erden, P. E., Dirican, A., Seferinoğlu, M., Yeltepe, E., & Şahin, N. K. (2014). 238 U, 234 U and 226 Ra concentrations in mineral waters and their contribution to the annual committed effective dose in Turkey. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 301, 159–166.
EU (2001). European Commission, Commission recommendation of 20th December 2001 on the protection of the public against exposure to radon in drinking water. 2001/982/Euratom, L344/85
IAEA (1996). International atomic energy agency. International basic safety standards for protection against ionizing radiation and for the safety of radiation sources. Safety Report Series No: 115. https://gnssn.iaea.org/Superseded%20Safety%20Standards/Safety_Series_115_1996_Pub996_EN.pdf
Jabbari, S., Salimi, B., Bahrami Samani, A., & Shirvani Arani, S. (2022). Assessment of radon-222 and radium-226 radioactivity concentration in the mineral and drinking water of Sareyn city. Radiation Safety and Measurement, 7(1), 11–20.
Jackson, P. C. (1996). AgE−dependent doses to members of the public from intake of radionuclides: Part 5 compilation of ingestion and inhalation dose coefficients (ICRP Publication 72). Physics in Medicine & Biology, 41(12), 2807–2807.
Khandaker, M. U., Nasir, N. L. M., Zakirin, N. S., Kassim, H. A., Asaduzzaman, K., Bradley, D. A., & Hayyan, A. (2017). Radiation dose to the Malaysian populace via the consumption of bottled mineral water. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 140, 173–179.
Komosa, A., Madej, E., & Piekarz, M. (2008). Determination of a supported radon activity concentration in bottled mineral waters. Chemia Analityczna, 53, 835–843.
Kovacs, T., Bodrogi, E., Dombovari, P., Somlai, J., Németh, C., Capote, A., & Tarjan, S. (2004). 238U, 226Ra, 210Po concentrations of bottled mineral waters in Hungary and their committed effective dose. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 108(2), 175–181.
Kozłowska, B., Walencik, A., Dorda, J., & Przylibski, T. A. (2007). Uranium, radium and 40K isotopes in bottled mineral waters from Outer Carpathians. Poland. Radiation Measurements, 42(8), 1380–1386.
Küçükönder, E., & Gümbür, S. (2023). Health risk assessment, and seasonal radon-thoron concentrations of water samples in Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam University, Turkey. Mapan, 1–10.
Küçükönder, E., & Gümbür, S. (2022). Radon gas measurement in water samples in Kahramanmaras province of Turkey. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 233(5), 175.
Labidi, S., & Gharbi, S. (2018). Dose assessment to members of the pulic in Tunisia from intakes of some naturally occurring radionuclides in bottled mineral water. International Journal of Radiation Research, 16(3), 371–381.
Le, C. H., Huynh, N. P. T., & Le, Q. B. (2015). Radon and radium concentrations in drinkable water supplies of the Thu Duc region in Ho Chi Minh City Vietnam. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 105, 219–224.
MASUDER (2023). Mineral Water producers association. http://www.masuder.org.tr/MasuderHakk%C4%B1nda/tabid/1095/Default.aspx
Oudah, O. N., & Al-Hamzawi, A. A. (2020). Measurement of radon concentrations in mineral water of Iraqi local markets using RAD7 technique. Nature Environment and Pollution Technology, 19(5), 1973–1976.
Şahin, M., Dirican, A., & Şahin, N. K. (2017). Radiochemical separation and determination of radium-228 in bottled mineral waters by low level gamma spectrometry and its committed effective dose. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76, 1–7.
Seid, A. M. A., Turhan, Ş, Kurnaz, A., Bakır, T. K., & Hançerlioğulları, A. (2022). Radon concentration of different brands of bottled natural mineral water commercially sold in Turkey and radiological risk assessment. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 102(19), 7469–7481.
Silva, C. R. E., Machado, D. V., & da Silva-Filho, E. V. (2019). Determination of the natural radioactivity in the mineral water distributed in the Salutaris Park, Paraíba do Sul, Brazil. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78, 1–9.
Sola, P., Srisuksawad, K., Loaharojanaphand, S., O-Manee, A., Permnamtip, V., Issarapan, P., & Thummagarun, L. (2013). Radon concentration in air, hot spring water, and bottled mineral water in one hot spring area in Thailand. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 297(2), 183–187.
Tabar, E., & Yakut, H. (2014). Determination of 226Ra concentration in bottled mineral water and assessment of effective doses, a survey in Turkey.
TAEA (2012). Turkish atomic energy authority. Natural mineral waters in Turkey and total alpha/beta of drinking water, 226ra, 234u, 238u, determination of 210po and 228ra activities and total calculation of indicator doses. Technical Report. Retrieved 19 Sep 2023. https://kurumsalarsiv.tenmak.gov.tr/bitstream/20.500.12878/311/4/9997.pdf
TUIK (2023). Turkish statistical ınstitute, Population of Türkiye Provincial District neighborhood village population. Retrieved 19 Sep 2023. https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Search/Search?text=n%C3%BCfus&dil=2
UNSCEAR (2000). United Nations scientific committee on the effects of atomic radiation. Report to the general assembly with scientific annexes. United Nations Publication, New York, USA.
USEPA (1991). National primary drinking water regulations for radionuclides. EPA/570/9–91/700. US, Governmental printing office.
Wätjen, U., Benedik, L., Spasova, Y., Vasile, M., Altzitzoglou, T., & Beyermann, M. (2010). EC comparison on the determination of 226Ra, 228Ra, 234U and 238U in water among European monitoring laboratories. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 68(7–8), 1200–1206.
WHO (2004). (World Health Organization). Guidelines for third edition recommendations drinking‐water quality, vol.1, Geneva.
WHO (2011). (World Health Organization). Guidelines for drinking water quality (4th ed.p. 1). Recommendations.
Yousef, H. A. (2018). Assessment of the annual effective dose of bottled mineral waters using closed can technique. Journal of Advances in Physics, 14(3).
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Assistant Professor Doctor Erdal KÜÇÜKÖNDER for his support.
Funding
This research was not supported by any organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Serdar Gümbür wrote the main manuscript text and prepared figure.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The author declares that they have no competing interests.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gümbür, S. Measurement of radium and radon gas in bottled mineral waters. Environ Geochem Health 46, 9 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01792-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01792-5