Abstract
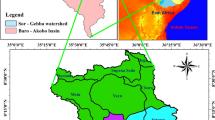
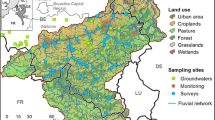
East China is a highly aggregated coal–grain composite area where coal mining and agricultural production activities are both flourishing. At present, the geochemical characteristics of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) in groundwater in coal mining areas are still unclear. This study combined hydrochemical and carbon isotope methods to explore the sources and factors influencing DIC in the groundwater of different active areas in coal mining areas. Moreover, the 13C isotope method was used to calculate the contribution rates of various sources to DIC in groundwater. The results showed that the hydrochemical types of groundwater were HCO3-Ca·Na and HCO3-Na. The main water‒rock interactions were silicate and carbonate rock weathering. Agricultural areas were mainly affected by the participation of HNO3 produced by chemical fertilizer in the weathering of carbonate rocks. Soil CO2 and carbonate rock weathering were the major sources of DIC in the groundwater. Groundwater in residential areas was primarily affected by CO2 from the degradation of organic matter from anthropogenic inputs. Sulfate produced by gypsum dissolution, coal gangue accumulation leaching and mine drainage participated in carbonate weathering under acidic conditions, which was an important factor controlling the DIC and isotopic composition of groundwater in coal production areas. The contribution rates of groundwater carbonate weathering to groundwater DIC in agricultural areas and coal production areas ranged from 57.46 to 66.18% and from 54.29 to 62.16%, respectively. In residential areas, the contribution rates of soil CO2 to groundwater DIC ranged from 51.48 to 61.84%. The results will help clarify the sources and circulation of DIC in groundwater under the influence of anthropogenic activities and provide a theoretical reference for water resource management.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abongwa, P. T., Den, W., & Teague, A. (2022). Chemical and carbon isotopic characterization of a Karst-Dominated urbanized watershed: Case of the upper San Antonio river. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 82(3), 439–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-022-00921-y
Akondi, R. N., Atekwana, E. A., & Molwalefhe, L. (2019). Origin and chemical and isotopic evolution of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) in groundwater of the Okavango Delta, Botswana. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 64(1), 105–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2018.1560447
An, S., Jiang, C., Zhang, W., Chen, X., & Zheng, L. (2020). Influencing factors of the hydrochemical characteristics of surface water and shallow groundwater in the subsidence area of the Huainan Coalfield. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13(4), 191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5140-3
Brown, K. A., Mclaughlin, F., Tortell, P. D., Yamamoto-Kawai, M., & Francois, R. (2016). Sources of dissolved inorganic carbon to the Canada Basin halocline: A multitracer study. Journal of Geophysical Research-Ocean, 121(5), 2918–2936. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JC011535
Cao, X., Wu, P., Han, Z., Tu, H., & Zhang, S. (2016). Factors controlling the isotope composition of dissolved inorganic carbon in a karst-dominated wetland catchment, Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(14), 1103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5899-4
Chandrasekar, T., Sabarathinam, C., Viswanathan, P. M., Viswanathan, P. M., Rajendiran, T., Mathivanan, M., Natesan, D., & Samayamanthula, D. R. (2021). Potential interplay of Uranium with geochemical variables and mineral saturation states in groundwater. Applied Water Science, 11(4), 75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01396-3
Chen, K., Liu, Q., Yang, T., Ju, Q., & Feng, Y. (2022). Statistical analyses of hydrochemistry in multi-aquifers of the Pansan coalmine, Huainan coalfield, China: implications for water-rock interaction and hydraulic connection. Heliyon, 8(9), e10690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10690
Chen, Q., Jia, C., Wei, J., Dong, F., Yang, W., Hao, D., Jia, Z., & Ji, Y. (2020a). Geochemical process of groundwater fluoride evolution along global coastal plains: Evidence from the comparison in seawater intrusion area and soil salinization area. Chemical Geology, 552, 119779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119779
Chen, X., Jiang, C., Zheng, L., Dong, X., Chen, Y., & Li, C. (2020b). Identification of nitrate sources and transformations in basin using dual isotopes and hydrochemistry combined with a Bayesian mixing model: Application in a typical mining city. Environmental Pollution, 267, 115651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115651
Chen, X., Zheng, L., Dong, X., Jiang, C., & Wei, X. (2020c). Sources and mixing of sulfate contamination in the water environment of a typical coal mining city, China: Evidence from stable isotope characteristics. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(9), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00525-2
Chen, X., Jiang, C., Zheng, L., Zhang, L., Fu, X., Chen, S., Chen, Y., & Hu, J. (2021). Evaluating the genesis and dominant processes of groundwater salinization by using hydrochemistry and multiple isotopes in a mining city. Environmental Pollution, 283, 117381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117381
Chen, Y., Song, R., Li, P., Wang, Y., Tan, Y., Ma, Y., Yang, L., Wu, L., Du, Z., Qi, X., & Zhang, Z. (2023). Spatiotemporal distribution, sources apportionment and ecological risks of PAHs: a study in the Wuhan section of the Yangtze River. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01500-3
Fang, T., Liu, G., Zhou, C., & Lu, L. (2015). Lead in soil and agricultural products in the Huainan Coal Mining Area, Anhui, China: Levels, distribution, and health implications. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(3), 152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4368-y
Ge, L., Tan, H., Chen, X., Rao, W., & Fan, M. (2021). Dissolved inorganic carbon isotopes of a typical alpine river on the Tibetan Plateau revealing carbon sources, wetland effect and river recharge. Hydrological Processes, 35(10), 14402. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.14402
Godfrey, L. V., Herrera, C., Burr, G. S., Houston, J., Aguirre, I., & Jordan, T. E. (2021). Delta C-13 and C-14 activity of groundwater DOC and DIC in the volcanically active and arid Loa Basin of northern Chile. Journal of Hydrology, 595, 125987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.125987
Gopinathan, P., Jha, M., Singh, A. K., Mahato, A., Subramani, T., Singh, P. K., & Singh, V. (2022a). Geochemical characteristics, origin and forms of sulphur distribution in the Talcher coalfield, India. Fuel, 316, 123376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.123376
Gopinathan, P., Santosh, M. S., Dileepkumar, V. G., Subramani, T., Reddy, R., Masto, R. E., & Maity, S. (2022b). Geochemical, mineralogical and toxicological characteristics of coal fly ash and its environmental impacts. Chemosphere, 307, 135710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135710
Gopinathan, P., Singh, A. K., Singh, P. K., & Jha, M. (2022c). Sulphur in Jharia and Raniganj coalfields: Chemical fractionation and its environmental implications. Environmental Research, 204, 112382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112382
Gui, H., & Chen, S. (2016). Isotopic geochemical characteristics of groundwater and its geological significance in Sunan mining area. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(3), 133–139. in Chines with English abstract.
Guo, Y., Song, C., Wan, Z., Tan, W., Lu, Y., & Qiao, T. (2014). Effects of long-term land use change on dissolved carbon characteristics in the permafrost streams of northeast China. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 16(11), 2496–2506. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4em00283k
Han, X., Cheng, X., Li, S., Yuan, J., & Zhang, Q. (2019). Carbon concentrations and their stable isotopic signatures in the upper Han River, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(14), 14116–14127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04568-6
Hu, J., Chen, X., Chen, Y., Li, C., Ren, M., Jiang, C., Chen, Y., An, S., Xu, Y., & Zheng, L. (2021). Nitrate sources and transformations in surface water of a mining area due to intensive mining activities: Emphasis on effects on distinct subsidence waters. Journal of Environmental Management, 298, 113451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113451
Hu, W., Hu, F., Guo, H., Wu, T., Jia, Q., Hu, E., Wang, H., Lei, Z., & Wang, Q. (2022). Rapid oxidative removal of Fe2+ and Mn2+ from acidic mining wastewater by a new-type biofilter system: Application and mechanism. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01461-z
Huang, F., Zhang, C., Xie, Y., Li, L., & Cao, J. (2015). Inorganic carbon flux and its source in the karst catchment of Maocun, Guilin, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(2), 1079–1089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4478-4
Huang, J., Li, Q., Wu, P., Wang, S., Guo, M., & Liu, K. (2022). The effects of weathering of coal-bearing stratum on the transport and transformation of DIC in karst watershed. Science of the Total Environment, 838, 156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156436
Huang, Q., Qin, X., Liu, P., Zhang, L., & Su, C. (2017). Impact of sulfuric and nitric acids on carbonate dissolution, and the associated deficit of CO2 uptake in the upper–middle reaches of the Wujiang River, China. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 203, 18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2017.05.006
Huang, W., Jiang, C., Chen, X., Fu, X., Chen, S., & Zheng, L. (2020). Chemical characteristics and genesis of deep groundwater in the Xinji mining area. Earth and Environment, 48(4), 432–442. in Chinese with English abstract.
Huang, X., Wang, G., Liang, X., Cui, L., Ma, L., & Xu, Q. (2018). Hydrochemical and stable isotope (delta D and delta O-18) characteristics of groundwater and hydrogeochemical processes in the Ningtiaota coalfield, northwest China. Mine Water and the Environment, 37(1), 119–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0477-x
Humphrey, V., Zscheischler, J., Ciais, P., Gudmundsson, L., Sitch, S., & Seneviratne, S. I. (2018). Sensitivity of atmospheric CO2 growth rate to observed changes in terrestrial water storage. Nature, 560(7720), 628–631. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0424-4
Jiang, C., Jiang, C., Zha, J., Liu, H., Liu, D., & Zheng, L. (2023). Water chemistry and stable isotope characteristics of subsidence lakes in coal mining areas, Eastern China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(15), 43152–43167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25285-1
Jiang, C., Zhu, S., Hu, H., An, S., Su, W., Chen, X., Li, C., & Zheng, L. (2022). Deep learning model based on big data for water source discrimination in an underground multiaquifer coal mine. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02535-5
Jiang, Y. (2013). The contribution of human activities to dissolved inorganic carbon fluxes in a karst underground river system: Evidence from major elements and delta C-13(DIC) in Nandong, Southwest China. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 152, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2013.05.010
Khazaei, E., & Milne-Home, W. (2017). Applicability of geochemical techniques and artificial sweeteners in discriminating the anthropogenic sources of chloride in shallow groundwater north of Toronto, Canada. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(5), 218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5927-1
Li, Q., Wu, P., Zha, X., Li, X., Wu, L., & Gu, S. (2018). Effects of mining activities on evolution of water chemistry in coal-bearing aquifers in karst region of Midwestern Guizhou, China: Evidences from delta C-13 of dissolved inorganic carbon and delta S-34 of sulfate. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(18), 18038–18048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1969-3
Li, S., Calmels, D., Han, G., Gaillardet, J., & Liu, C. (2008a). Sulfuric acid as an agent of carbonate weathering constrained by delta C-13(DIC): Examples from Southwest China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 270, 189–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2008.02.039
Li, S., Liu, C., Lang, Y., Tao, F., Zhao, Z., & Zhou, Z. (2008b). Stable carbon isotope biogeochemistry and anthropogenic impacts on karst ground water, Zunyi, southwest China. Aquatic Geochemistry, 14(3), 211–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-008-9033-4
Li, S., Liu, C., Li, J., Lang, Y., Ding, H., & Li, L. (2010a). Geochemistry of dissolved inorganic carbon and carbonate weathering in a small typical karstic catchment of Southwest China: Isotopic and chemical constraints. Chemical Geology, 277(3–4), 301–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.08.013
Li, X., Han, G., Liu, M., Song, C., Zhang, Q., Yang, K., & Liu, J. (2019a). Hydrochemistry and dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) cycling in a tropical agricultural river, Mun river basin, northeast Thailand. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(18), 3410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16183410
Li, X., Liu, C., Harue, M., & Li, S. (2010b). The use of environmental isotopic (C, Sr, S) and hydrochemical tracers to characterize anthropogenic effects on karst groundwater quality: A case study of the Shuicheng Basin, SW China. Applied Geochemistry, 25(12), 1924–1936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.10.008
Li, X., Huang, X., & Zhang, Y. (2021a). Spatio-temporal analysis of groundwater chemistry, quality and potential human health risks in the Pinggu basin of North China Plain: Evidence from high-resolution monitoring dataset of 2015–2017. Science of the Total Environment, 800, 149568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149568
Li, X., Ma, H., Ran, Y., Wang, X., Zhu, G., Liu, F., He, H., Zhang, Z., & Huang, C. (2021b). Terrestrial carbon cycle model-data fusion: Progress and challenges. Science China Earth Sciences, 64(10), 1645–1657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-020-9800-3
Li, Z., Xia, M., Dong, S., Liu, X., Wang, C., & Zhou, Y. (2019b). Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution characteristics of shallow groundwater in the Luoyang basin. Earth and Environment, 47(1), 57–63. in Chinese with English abstract.
Liu, H., Kang, B., Guan, Z., Song, Y., & Chai, Y. (2023). Hydrochemical characteristics and control factors of surface water and groundwater in Huainan coal mine area. Environmental Science, 1–14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, Z., Macpherson, G. L., Groves, C., Martin, J. B., Yuan, D., & Zeng, S. (2018). Large and active CO2 uptake by coupled carbonate weathering. Earth-Science Reviews, 182, 42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.05.007
Mathis, M., Logemann, K., Maerz, J., Lacroix, F., Hagemann, S., Chegini, F., Ramme, L., Ilyina, T., Korn, P., & Schrum, C. (2022). Seamless integration of the coastal ocean in global marine carbon cycle modeling. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021MS002789
Moya, C. E., Raiber, M., Taulis, M., & Cox, M. E. (2015). Hydrochemical evolution and groundwater flow processes in the Galilee and Eromanga basins, Great Artesian Basin, Australia: A multivariate statistical approach. Science of the Total Environment, 508, 411–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.11.099
Nakayama, T. (2019). Inter-annual simulation of global carbon cycle variations in a terrestrial–aquatic continuum. Hydrological Processes, 34(3), 662–678. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13616
Ni, M., & Li, S. (2022). Dynamics and internal links of dissolved carbon in a karst river system: Implications for composition, origin and fate. Water Research, 226, 119289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.119289
Porowska, D. (2015). Determination of the origin of dissolved inorganic carbon in groundwater around a reclaimed landfill in Otwock using stable carbon isotopes. Waste Management, 39, 216–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.01.044
Qian, J., Peng, Y., Zhao, W., Ma, L., He, X., & Lu, Y. (2018). Hydrochemical processes and evolution of karst groundwater in the northeastern Huaibei Plain, China. Hydrogeology Journal, 26(5), 1721–1729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1805-3
Qian, Y., Yuan, K., Wang, J., Xu, Z., Liang, H., & Tie, C. (2023). Parent and alkylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon emissions from coal seam fire at Wuda, Inner Mongolia, China: Characteristics, spatial distribution, sources, and health risk assessment. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01476-0
Ren, K., Pan, X., Zeng, J., Jiao, Y., Peng, C., & Liang, J. (2019). Geochemical characteristics and ecological significance of carbon isotopes in groundwater under the influence of different land use types in karst areas. Environment Science, 40(10), 4523–4531. in Chinese with English abstract.
Rosentreter, J. A., & Eyre, B. D. (2020). Alkalinity and dissolved inorganic carbon exports from tropical and subtropical river catchments discharging to the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Hydrological Processes, 34(7), 1530–1544. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13679
Santosh, M. S., Purushotham, S., Gopinathan, P., Guna, V., Dileepkumar, V. G., Kumar, M., & Reddy, N. (2023). Natural sub-bituminous coal as filler enhances mechanical, insulation and flame retardant properties of coir–polypropylene bio-composites. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01489-9
Schiavo, M. A., Hauser, S., & Povinec, P. P. (2007). Isotope distribution of dissolved carbonate species in southeastern coastal aquifers of Sicily (Italy). Hydrological Processes, 21(20), 2690–2697. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6498
Schulte, P., Van, G. R., Freitag, H., Karim, A., Negrel, P., Petelet-Giraud, E., Probst, A., Probast, J. L., Telmer, K., Veizer, J., & Barth, J. A. (2011). Applications of stable water and carbon isotopes in watershed research: Weathering, carbon cycling, and water balances. Earth-Science Reviews, 109(1), 20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2011.07.003
Shen, B., Wu, J., Zhan, S., Jin, M., Saparow, A. S., & Abuduwaili, J. (2021). Spatial variations and controls on the hydrochemistry of surface waters across the Ili-Balkhash Basin, arid Central Asia. Journal of Hydrology, 600, 126565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126565
Song, S., Peng, R., Wang, Y., Cheng, X., Niu, R., & Ruan, H. (2023). Spatial distribution characteristics and risk assessment of soil heavy metal pollution around typical coal gangue hill located in Fengfeng Mining area. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01530-x
Song, X., Lyu, S., Sun, K., Gao, Y., & Wen, X. (2021). Flux and source of dissolved inorganic carbon in a headwater stream in a subtropical plantation catchment. Journal of Hydrology, 600, 126511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126511
Vitoria, L., Soler, A., Canals, A., & Otero, N. (2008). Environmental isotopes (N, S, C, O, D) to determine natural attenuation processes in nitrate contaminated waters: Example of Osona (NE Spain). Applied Geochemistry, 23(12), 3597–3611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.07.018
Wachniew, P. (2006). Isotopic composition of dissolved inorganic carbon in a large polluted river: The Vistula, Poland. Chemical Geology, 233(3–4), 293–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.03.012
Wang, J., Lu, C., Sun, Q., Xiao, W., Cao, G., Li, H., Yan, L., & Zhang, B. (2017). Simulating the hydrologic cycle in coal mining subsidence areas with a distributed hydrologic model. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39983
Wu, C., Wu, X., Zhu, G., & Qian, C. (2019). Predicting mine water inflow and groundwater levels for coal mining operations in the Pangpangta coalfield, China. Environmetal Earth Sciences, 78(5), 130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8098-2
Wu, D., & Zhang, W. (2019). Geochemical characteristics of trace elements and carbon isotopes in Taiyuan Formation: A case study of Huainan Coalfield. Geosciences Journal, 23(6), 991–1003. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-018-0083-3
Xiao, M., Han, Z., Xu, S., & Wang, Z. (2020). Temporal variations of water chemistry in the wet season in a typical urban karst groundwater system in southwest China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(7), 2520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072520
Xie, K., Li, R., & Zhang, L. (2017). Chemical composition and source assessment of precipitation in Huainan. Environmental Monitoring in China, 33(3), 31–38. in Chinese with English abstract.
Xie, Y., Huang, F., Yang, H., & Yu, S. (2021). Role of anthropogenic sulfuric and nitric acids in carbonate weathering and associated carbon sink budget in a karst catchment (Guohua), southwestern China. Journal of Hydrology, 599, 126287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126287
Xu, J., Ling, H., Zhang, G., Yan, J., Deng, M., Wang, G., & Xu, S. (2021). Variations in the dissolved carbon concentrations of the shallow groundwater in a desert inland river basin. Journal of Hydrology, 602, 126774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126774
Xu, J., Wu, Y., Wang, S., Wang, Y., Dong, S., Chen, Z., & He, L. (2023). Source identification and health risk assessment of heavy metals with mineralogy: The case of soils from a Chinese industrial and mining city. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112382
Xu, S., Li, S., & Zhong, J. (2022). Effects of land use on riverine dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) and δ13CDIC in a karst river basin, southwestern China. Environmental Science, 43(2), 752–761. in Chinese with English abstract.
Xuan, Y., Cao, Y., Tang, C., & Li, M. (2020). Changes in dissolved inorganic carbon in river water due to urbanization revealed by hydrochemistry and carbon isotope in the Pearl River Delta, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(19), 24542–24557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08454-4
Yi, Y., Li, S., Zhong, J., Wang, W., Chen, S., Bao, H., & He, D. (2022). The influence of the deep subtropical reservoir on the karstic riverine carbon cycle and its regulatory factors: Insights from the seasonal and hydrological changes. Water Research, 226, 119267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.119267
Yin, X., Lin, Y., Liang, C., Tao, S., Wang, L., Xu, Y., & Li, Y. (2020). Source and fate of dissolved inorganic carbon in Jiulong River, southeastern China. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 246, 107031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2020.107031
Yue, F., Li, S., Liu, C., & Lang, Y. (2015). Sources and transport of nitrate constrained by the isotopic technique in a karst catchment: An example from Southwest China. Hydrology Processes, 29(8), 1883–1893. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10302
Zhang, C., Li, X., Ma, J., Wang, Z., & Hou, X. (2022a). Stable isotope and hydrochemical evolution of shallow groundwater in mining area of the Changzhi Basin, northern China. Environmental Earth Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10416-7
Zhang, H., Xu, G., Chen, X., Chen, X., & Mabaire, A. (2019). Hydrogeochemical evolution of multilayer aquifers in a massive coalfield. Environmental Earth Science, 78(24), 675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8694-1
Zhang, H., Xu, G., Zhan, H., Chen, X., Liu, M., & Wang, M. (2020). Identification of hydrogeochemical processes and transport paths of a multi-aquifer system in closed mining regions. Journal of Hydrology, 589, 125344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125344
Zhang, J., Chen, L., Hou, X., Lin, M., Ren, X., Li, J., Zhang, M., & Zheng, X. (2021). Multi-isotopes and hydrochemistry combined to reveal the major factors affecting Carboniferous groundwater evolution in the Huaibei coalfield, North China. Science of the Total Environment, 791, 148420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148420
Zhang, Y., Li, Q., Luo, Y., Yan, L., Peng, K., Liu, Z., & Wang, Y. (2022b). Groundwater salinization in a subtropical region, Beihai, southern China: Insights from hydrochemistry and multiple isotopes (H, O, S, Sr). Applied Geochemistry, 141, 105323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105323
Zhao, Y., Lyu, X., Xiao, W., Tian, S., Zhang, J., Hu, Z., & Fu, Y. (2021). Evaluation of the soil profile quality of subsided land in a coal mining area backfilled with river sediment based on monitoring wheat growth biomass with UAV systems. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09250-4
Zheng, L., Jiang, C., Chen, X., Li, Y., Li, C., & Zheng, L. (2022). Combining hydrochemistry and hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes to reveal the influence of human activities on surface water quality in Chaohu Lake Basin. Journal of Environmental Management, 312, 114933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114933
Zhong, J., Wallin, M. B., Wang, W., Li, S., Guo, L., Dong, K., Ellam, R. M., Liu, C., & Xu, S. (2021). Synchronous evaporation and aquatic primary production in tropical river networks. Water Research, 200, 117272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117272
Zhou, X., Zhang, C., Ma, J., Liu, M., Ma, L., & Qian, J. (2016). Characteristics of multiple aquifers groundwater system in hugely thick Cenozoic stratum in Huainan. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (natural Science), 39(12), 1693–1697. in Chinese with English abstract.
Acknowledgements
We are deeply grateful to the editors and anonymous reviewers for their careful work and thoughtful suggestions that helped improve this paper substantially. The authors also gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Natural Science Foundation of the Department of Education of Anhui Province (KJ2021A0085).
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of the Department of Education of Anhui Province (KJ2021A0085).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CJ: data curation, validation, writing—review & editing, resources, funding acquisition, supervision. ML: methodology, formal analysis, software, formal analysis, writing—original draft, visualization. CL: writing—review & editing. LZ: conceptualization, resources, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no confict of interest.
Consent to participate and consent to publish
Consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, C., Li, M., Li, C. et al. Combining hydrochemistry and 13C analysis to reveal the sources and contributions of dissolved inorganic carbon in the groundwater of coal mining areas, in East China. Environ Geochem Health 45, 7065–7080 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01726-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01726-1