Abstract
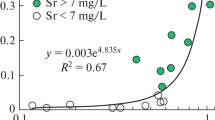
This paper confirms the regularities of the formation of increased concentrations of strontium (Sr) in fresh groundwater used for drinking water supply, depending on the time they are residen in the carbonate deposits of the aquifer. On average, every thousand years, the Sr concentration increases by 2.1–3.5 mg L−1. In addition, high strontium content is positively correlated with altitude and well depth and negatively correlated with redox conditions in the aquifer. Large relief elevations are associated with the development of marginal moraine deposits from the Last Glacial Period composed predominantly of clay, which contributes to a decrease in water exchange. The high Sr content is associated with the dissolution of significant formations of celestite and strontianite, up to their ore occurrences. For this reason, the saturation indices (SIs) for celestite and strontianite correlate with TDS and rise to − 1.42 and 2.05, respectively. Low Sr values do not correlate with the residence time of groundwater in the aquifer or the depth of wells and tend to depressions in the relief, with a virtual absence of overlying sediments and positive Eh values, which indicates an active water exchange. The low level of Sr is associated with the dissolution of gypsum, calcite, and dolomite containing strontium as an impurity. This causes the SIs for gypsum, calcite, and dolomite to correlate with TDS, while for celestite and strontianite, the SI drops to − 5.02 and − 0.92, respectively. The established patterns make it possible to more reasonably choose places for the construction of water wells to obtain drinking water of standard quality.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arslanov, Kh. A., Tertychnaya, T. V., & Chernov, S. B. (1993). Problems and methods of dating of low-activity samples by liquid scintillation counting. Radiocarbon, 35, 393–398.
Back, W., Hanshaw, B. B., Plummer, L. N., Rahn, P. H., Rightmere, C. T., & Rubin, M. (1983). Process and rate of dedolomitization: Mass transfer and 14C dating in a regional carbonate aquifer. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 94, 1415–1429. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1983)94%3c1415:PARODM%3e2.0.CO;2
Bartley, J. C., & Reber, E. F. (1961). Toxic effects of stable strontium in young pigs. Journal of Nutrition, 75, 21–28.
Bui, D. T., Khosravi, K., Karimi, M., Busico, G., Khozani, Z. S., Nguyen, H., Mastrocicco, M., Tedesco, D., Cuoco, E., & Kazakis, N. (2020). Enhancing nitrate and strontium concentration prediction in groundwater by using new data mining algorithm. Science of the Total Environment, 715, 136836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136836
Colvin, L. B., & Creger, C. R. (1967). Stable strontium and experimental bone anomalies. Federation Proceedings, Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 26, 416.
Colvin, L. B., Creger, C. R., Ferguson, T. M., & Crookshank, H. R. (1972). Experimental epiphyseal cartilage anomalies by dietary strontium. Poultry Science, 51, 576–581.
Curzon, M. E. J., & Spector, P. C. (1977). Enamel mottling in a high strontium area of the USA. Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology, 5, 243–247.
Devyatova, E. I. (1982). Late Pleistocene environment and its impact on human population in the Severnaya Dvina basin and in Karelia (p. 156). Karelia (in Russian).
Ding, D., Kong, L., Jiang, D., Wei, J., Cao, S., Li, X., Zheng, L., & Deng, S. (2022). Source apportionment and health risk assessment of chemicals of concern in soil, water and sediment at a large strontium slag pile area. Journal of Environmental Management, 304, 114228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114228
Ermakov, V., Bech, J., Gulyaeva, U., Tyutikov, S., Safonov, V., Danilova, V., & Roca, N. (2020). Relationship of the mobile forms of calcium and strontium in soils with their accumulation in meadow plants in the area of Kashin-Beck endemia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42, 159–171.
Ferronsky, V. I., & Polyakov, V. A. (2012). Isotopes of the earth’s hydrosphere. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-2856-1-1
Gad, S. C. (2014). Strontium. In P. H. Wexler (Ed.), Encyclopedia of toxicology (3rd ed., pp. 405–406). Acad. press.
Giménez-Forcada, E., & Vega-Alegre, M. (2015). Arsenic, barium, strontium and uranium geochemistry and their utility as tracers to characterize groundwaters from the Espadán-Calderona Triassic Domain, Spain. Science of the Total Environment, 512–513, 599–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.010
Han, L.-F., & Plummer, N. (2013). Revision of Fontes and Garnier’s model for the initial 14C content of dissolved inorganic carbon used in groundwater dating. Chemical Geology, 351, 105–114.
Han, L.-F., & Plummer, N. (2016). A review of single-sample-based models and other approaches for radiocarbon dating of dissolved inorganic carbon in groundwater. Earth Science Reviews, 152, 119–142.
Höllriegl, V., & München, H. Z. (2011). Strontium in the environment and possible human health effects. In Jerome Nriagu (Ed.), Encyclopedia environmental health (pp. 268–275). Germ. Res. Cent. Env. Health. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-52272-6.00638-3
Hubberten, H. W., Andreev, A., Astakhov, V. I., Demidov, I., Dowdeswell, J. A., Henriksen, M., Hjort, C., Houmark-Nielsen, M., Jakobsson, M., Kuzmina, S., Larsen, E., Lunkka, J. P., Lyså, A., Mangerud, J., Möller, P., Saarnisto, M., Schirrmeister, L., Sher, A. V., Siegert, C., … Svendsen, J. I. (2004). The periglacial climate and environment in northern Eurasia during the last glaciation. Quaternary Science Reviews, 23, 1333–1357.
Ingerson, E., & Pearson, F. J. (1964). Estimation of age and rate of motion of groundwater by the 14C method. In Recent researches in the fields of hydrosphere (pp. 263–283). Atm. and Nucl. Chem.
Inoue, S. (1981). Chemistry of strontium. In S. C. Skoryna (Ed.), Handbook of stable strontium (pp. 11–18). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-3698-3_2
Ivanova, N. I. (2014). Strontium distridution patterns in groundwater and aquifer host rocks in the southeastern part of the Severnaya Dvina artesian basin. Moscow University Geology Bulletin, 69–4, 258–266.
Keesari, T., Sabarathinam, C., Sinha, U. K., Pethaperumal, Thilagavathi, R., & Kamaraj, P. (2022). Fate and transport of strontium in groundwater from a layered sedimentary aquifer system. Chemosphere, 307, 136015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136015
Khandare, A. L., Validandi, V., Rajendran, A., Singh, T. G., Thingnganing, L., Kurella, S., Nagaraju, R., Dheeravath, S., Vaddi, N., Kommu, S., & Maddela, Y. (2020). Health risk assessment of heavy metals and strontium in groundwater used for drinking and cooking in 58 villages of Prakasam district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42, 3675–3701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00596-1
Krainov, S. R., Ryzhenko, B. N. & Shvets, V. M. (2012). Geochemistry of groundwater. In Fundamental, applied and environmental aspects (p. 672). CenterLitNefteGaz (In Russian).
Krainov, S. R., & Zakutin, V. A. (1994). Geochemical-ecological state of groundwater in Russia. Geochemistry, 3, 312–329.
Larsen, E., Lyså, A., Demidov, I., Funder, S., Houmark-Nielsen, M., Kjær, K. H., & Murray, A. S. (1999). Age and extent of the Scandinavian Ice Sheet in northwest Russia. Boreas, 28, 115–132
Levine, N. S., Roberts, S. J., & Aring, J. L. (2002). Geological controls on the distribution and origin of selected inorganic ions in Ohio groundwater. Environmental and Engineering Geoscience, 8–4, 319–328. https://doi.org/10.2113/8.4.319
Luczaj, J., & Masarik, K. (2015). Groundwater quantity and quality issues in a water-rich region: Examples from Wisconsin, USA. Resources, 4, 323–357. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources4020323
Lyså, A., Demidov, I., Houmark-Nielsen, M., & Larsen, E. (2001). Late Pleistocene stratigraphy and sedimentary environment of the Arkhangelsk area, northwest Russia. Global and Planetary Change, 31, 179–199.
Malaisse, F., & Mathieu, F. (Eds.). (2008). Big bone disease, a multidisciplinary approach of Kashin-Beck disease in Tibet Autonomous Region (PR China) (p. 148). Les presses universitaires de Gembloux.
Malov, A. I. (2003). Groundwater of the South-East White Sea: Formation, role in geological processes (p. 234). UB RAS (in Russian). https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=19474464
Malov, A. I. (2023). Features of a High Strontium Concentration in Drinking Groundwater near the Sea Coast. Doklady Earth Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1028334X23601098 (in print)
Malov, A. I. (2000). Formation of strontium-containing waters in the marginal part of the Mezen syneclise. In S. L. Shvartsev (Ed.), Fundamental problems of water and water resources at the turn of the 3rd millennium (pp. 233–235). Publ. house of sci. and tech. lit. (in Russian).
Malov, A. I., Sidkina, E. S., & Ryzhenko, B. N. (2017). Model of the Lomonosov diamond deposit as a water–rock system: Migration species, groundwater saturation with rock-forming and ore minerals, and ecological assessment of water quality. Geochemistry International, 55, 1118–1130. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702917090038
Malov, A. I., & Tokarev, I. V. (2019). Using stable isotopes to characterize the conditions of groundwater formation on the eastern slope of the Baltic Shield (NW Russia). Journal of hydrology, 578, 124130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124130
McCartan, L., Plummer, L. N., Hosterman, J. W., Busenberg, E., Dwornik, E. J., Duerr, A. D., Miller, R. L., Kiesler, J. L. (1988). Celestine (SrSO4) in Hardee and De Soto counties, Florida. In G. S. Gohn (Ed.), Proceedings of the 1988 U.S. geological survey workshop on the geology and geohydrology of the Atlantic coastal plain (vol. 1059, pp. 129–138). U.S. Geol. Surv. Circ. https://doi.org/10.3133/cir1059
Merzlyakov, G. A. (1979). Permian saline basins of Eurasia (p. 142). Science (in Russian).
Mook, W. G. (1972). On the reconstruction of the initial 14C content of groundwater from the chemical and isotopic composition. In Proc. of Eighth International Conference on radiocarbon dating (vol. 1, pp. 342–352). Royal Society of New Zealand.
Mook, W. G. (1976). The dissolution-exchange model for dating groundwater with 14C. Interpretation of environmental isotope and hydrochemical data in groundwater hydrology (pp. 213–225). IAEA.
Münnich, K. O. (1957). Messungen des 14C-Gehaltes von hartem Grundwasser. Naturwissenschaften, 44, 32–34.
Münnich, K. O. (1968). Isotopendatierung von Grundwasser. Naturwissenschaften, 55, 3–11.
Musgrove, M. (2021). The occurrence and distribution of strontium in U.S. groundwater. Applied Geochemistry, 126, 104867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104867
Musgrove, M., & Banner, J. L. (2004). Controls on the spatial and temporal variability of vadose dripwater geochemistry: Edwards aquifer, central Texas. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68, 1007–1020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2003.08.014
Nichols, M. S., & McNall, D. R. (1957). Strontium content of Wisconsin municipal waters. Journal American Water Works Association, 49, 1493–1498.
Norman, J. E., Toccalino, P. L., & Morman, S. A. (2018). In Health-based screening levels for evaluating water-quality data (2rd edn.) U.S. Geol. Surv. National Water-Quality Assessment Program web page. https://doi.org/10.5066/F71C1TWP
Odum, H. T. (1951). Strontium in Florida waters. In A. P. Black, E. Brown (Eds.), Chemical character of Florida waters. Florida State Board of Conservation, Division of Water Survey and Research Papers (vol. 6, pp. 20–21).
Özgür, S., Sümer, H., & Koҫoǧlu, G. (1996). Rickets and soil strontium. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 75, 524–526.
Partington, J. R. (1981). Early history of strontium. In S. C. Skoryna (Ed.), Handbook of stable strontium (pp. 1–9). Plenum. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-3698-3_1
Pearson, F. J., & Hanshaw Jr. (1970). Sources of dissolved carbonate species in groundwater and their effects on carbon-14 dating. Isotope hydrology (pp. 271–286). IAEA.
Plechacek, A., Scott, S. R., Gotkowitz, M. B., & Ginder-Vogel, M. (2022). Strontium and radium occurrence at the boundary of a confined aquifer system. Applied Geochemistry, 142, 105332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105332
Plummer, L. N. (1977). Defining reactions and mass transfer in part of the Floridan Aquifer. Water Resources Research, 13, 801–812.
Reimer, P. J., Austin, W. E. N., Bard, E., Bayliss, A., Blackwell, P. G., Ramsey, C. B., Butzin, M., Cheng, H., Edwards, R. L., Friedrich, M., Grootes, P. M., Guilderson, T. P., Hajdas, I., Heaton, T. J., Hogg, A. G., Hughen, K. A., Kromer, B., Manning, S. W., Muscheler, R., … Talamo, S. (2020). The IntCal20 Northern Hemisphere radiocarbon age calibration curve (0–55 ka cal BP). Radiocarbon. https://doi.org/10.1017/RDC.2020.41
SanRaR 2.1.4.1074-01. (2001). Drinking water. Hygienic requirements for water quality of centralized drinking water supply systems. Quality control. Sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations approved by the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation on September 26, 2001.
Savinov Yu, A. (1971). Quaternary geology of the north of the Russian Plain (p. 192). Leningrad University Press (In Russian).
Schoeller, H., 1967. Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In Methods and techniques of groundwater investigation and development. Water Res (vol. 33, pp. 44–52). UNESCO.
Schoeller, H. (1977). Geochemistry of groundwater. In Groundwater studies—An international guide for research and practice (vol. 15, pp. 1–18). UNESCO.
Sonnenfeld, P. (1984). Brines and evaporates (p. 613). Academic Press.
Stankovsky, A.F., Verichev, E.M., Dobeiko, I.P., 1985. Vendian of the southeastern White Sea. In B. S. Sokolov, & M. A. Fedonkin (Eds.), Vendian system. Historical-geological and paleontological substantiation. Vol. 2. Stratigraphy and geological processes (pp. 67–76). Nauka.
Stankovsky, A. F., Verichev, E. M., Grib, V. P., & Dobeiko, I. P. (1981). Vendian of the southeastern White Sea. Izv. Academy of sciences of the USSR. Ser. Geol., 2, 78–87.
Staritsky, Yu, G. (ed.) (1981). History of development and minerageny of the cover of the Russian platform (p. 224). Nedra (In Russian).
Stuiver, M., Reimer, P. J., & Reimer, R. W. (2021). CALIB 8.2 [WWW program] at http://calib.org. Accessed 2021–2–16.
Turekian, K. K. (1972). Chemistry of the earth (p. 131). Holt, Rinehart and Winston Inc.
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72, 175–192.
U.S. EPA. (2014). Health effects support document for strontium. EPA 820-P-14-0012014. 2014. www.epa.gov/safewater/ccl/pdf/Strontium.pdf
Valyashko, M. G. (1955). Basic chemical types of natural waters and conditions for their formation. Doklady Akademii Nauk, 102–2, 315–318. (In Russian).
Valyashko, M. G. (1962). On the role of sea water in the formation of the chemical composition of natural waters of sedimentary strata. Geochemistry, 2, 132–141. (In Russian).
Wang, Z. (1999). A historic overview of research and control on Kashin-Beck disease in China. Chinese Journal of Endemiology, 18, 161–163.
Zamana, L. V., Rikhvanov, L. P., Soktoev, B. R., Baranovskaya, N. V., Epova, E. S., Solodukhina, M. A., Mikhailova, L. A., Kopylova, Y. G., & Khvashchevskaya, A. A. (2019). New data on chemical composition of natural waters in the area of distribution of Urov (Kaschin–Beck) disease (Transbaikal region). Bulletin of the Tomsk Polytechnic University, Geo Assets Engineering, 330–1, 121–133. (in Russian).
Zharkov, M. A. (1973). Paleozoic salt-bearing formations of the world (p. 392). Nedra (in Russian).
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation and the Government of the Arkhangelsk region (projects no. № 23-27-10004), https://rscf.ru/project/23-27-10004/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AM wrote the manuscript; DE determined the concentration of strontium, AM and SD collected samples, ES and E.Ch..determined saturation indices
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Malov, A.I., Sidkina, E.S., Ershova, D.D. et al. Time regularities of strontium concentration in drinking groundwater distant from the sea coast. Environ Geochem Health 45, 8097–8118 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01710-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01710-9