Abstract
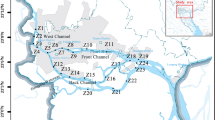
Recently, antibiotics have been frequently detected in the hyporheic zone (HZ) as a novel contaminant. Bioavailability assessment has gradually attracted more attention in order to provide a more realistic assessment of human health risks. In this study, two typical antibiotics, oxytetracycline (OTC) and sulfamethoxazole (SMZ), were used as target pollutants in the HZ of the Zaohe–Weihe River, and the polar organics integrated sampler was used to analyze the variation of antibiotics bioavailability. According to the characteristics of the HZ, the total concentration of pollutants, pH, and dissolved oxygen (DO) were selected as major predictive factors to analyze their correlation with the antibiotics bioavailability. Then the predictive antibiotic bioavailability models were constructed by stepwise multiple linear regression method. The results showed that there was a highly significant negative correlation between OTC bioavailability and DO (P < 0.001), while SMZ bioavailability showed a highly significant negative correlation with total concentration of pollutants (P < 0.001) and a significant negative correlation with DO (P < 0.01). The results of correlation analysis were further verified by Principal Component Analysis. Based on the experimental data, we constructed eight prediction models for the bioavailability of two antibiotics and verified them. The data points of the six prediction models were distributed in the 95% prediction band, indicating that the models were more reliable and accurate. The prediction models in this study provide reference for the accurate ecological risk assessment of the bioavailability of pollutants in the HZ, and also provide a new idea for predicting the bioavailability of pollutants in practical applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albero, B., Luis Tadeo, J., Escario, M., Miguel, E., & Ana Perez, R. (2018). Persistence and availability of veterinary antibiotics in soil and soil-manure systems. Science of the Total Environment, 643, 1562–1570.
Ambade, B. (2014). Characterization and source of fog water contaminants in central India. Natural Hazards, 70(2), 1535–1552.
Ambade, B., Sethi, S. S., Kumar, A., & Sankar, T. K. (2022). Solvent extraction coupled with gas chromatography for the analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in riverine sediment and surface water of Subarnarekha River and its tributary, India. Miniaturized analytical devices (pp. 71–89). Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527827213.ch4
Ambade, B., Sethi, S. S., Kurwadkar, S., Kumar, A., & Sankar, T. K. (2021). Toxicity and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water, sediments and groundwater vulnerability in Damodar River Basin. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 13, 100553.
Balram, A. (2012). Physico-chemical assessment of rain, fog and runoff water.
Blaine, A. C., Rich, C. D., Sedlacko, E. M., Hundal, L. S., Kumar, K., Lau, C., Mills, M. A., Harris, K. M., & Higgins, C. P. (2014). Perfluoroalkyl acid distribution in various plant compartments of edible crops grown in biosolids-amended soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(14), 7858–7865.
Bradham, K. D., Scheckel, K. G., Nelson, C. M., Seales, P. E., Lee, G. E., Hughes, M. F., Miller, B. W., Yeow, A., Gilmore, T., Serda, S. M., Harper, S., & Thomas, D. J. (2011). Relative bioavailability and bioaccessibility and speciation of arsenic in contaminated soils. Environmental Health Perspectives, 119(11), 1629–1634.
Brix, K. V., DeForest, D. K., Tear, L., Grosell, M., & Adams, W. J. (2017). Use of multiple linear regression models for setting water quality criteria for copper: A complementary approach to the biotic ligand model. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(9), 5182–5192.
Brix, K. V., DeForest, D. K., Tear, L., Peijnenburg, W., Peters, A., Middleton, E. T., & Erickson, R. (2020). Development of empirical bioavailability models for metals. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 39(1), 85–100.
Carvalho, I. T., & Santos, L. (2016). Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: A review of the European scenario. Environment International, 94, 736–757.
Castle, G. D., Mills, G. A., Bakir, A., Gravell, A., Schumacher, M., Townsend, I., Jones, L., Greenwood, R., Knott, S., & Fones, G. R. (2018). Calibration and field evaluation of the Chemcatcher (R) passive sampler for monitoring metaldehyde in surface water. Talanta, 179, 57–63.
Chang, W.-T., Lee, C.-L., Brimblecombe, P., Fang, M.-D., Chang, K.-T., & Liu, J. T. (2015). The effects of flow rate and temperature on SPMD measurements of bioavailable PAHs in seawater. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 97(1), 217–223.
Chung, H. S., Lee, Y.-J., Rahman, M. M., Abd El-Aty, A. M., Lee, H. S., Kabir, M. H., Kim, S., Park, B.-J., Kim, J.-E., Hacimuftuoglu, F., Nahar, N., Shin, H.-C., & Shim, J.-H. (2017). Uptake of the veterinary antibiotics chlortetracycline, enrofloxacin, and sulphathiazole from soil by radish. Science of the Total Environment, 605, 322–331.
Creusot, N., Tapie, N., Piccini, B., Balaguer, P., Porcher, J. M., Budzinski, H., & Ait-Aissa, S. (2013). Distribution of steroid- and dioxin-like activities between sediments, POCIS and SPMD in a French river subject to mixed pressures. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(5), 2784–2794.
Deleebeeck, N. M., De Schamphelaere, K. A., & Janssen, C. R. (2008). A novel method for predicting chronic nickel bioavailability and toxicity to Daphnia magna in artificial and natural waters. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27(10), 2097–2107.
Feng, R. Y., Duan, L., Shen, S. Q., Cheng, Y., Wang, Y. H., Wang, W. K., & Yang, S. K. (2023). Temporal dynamic of antibiotic resistance genes in the Zaohe-Weihe hyporheic zone: Driven by oxygen and bacterial community. Ecotoxicology, 32(1), 57–72.
Figueroa, R. A., Leonard, A., & Mackay, A. A. (2004). Modeling tetracycline antibiotic sorption to clays. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 483.
Gao, Z., Yu, L., Clark, S., Trehy, M., Moore, T., Westenberger, B., Buhse, L., Kauffman, J., Bishop, B., Velazquez, L., & Furness, S. (2015). Dissolution testing for bioavailability of over-the-counter (OTC) drugs-a technical note. An Official Journal of the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists, 16(5), 1227–1233.
Godlewska, K., Stepnowski, P., & Paszkiewicz, M. (2020). Application of the polar organic chemical integrative sampler for isolation of environmental micropollutants: A review. Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry, 50(1), 1–28.
Gu, C., & Karthikeyan, K. G. (2005). Interaction of tetracycline with aluminum and iron hydrous oxides. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(8), 2660–2667.
Guo, M., Gong, Z., Li, X., Allinson, G., Rookes, J., & Cahill, D. (2017). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons bioavailability in industrial and agricultural soils: Linking SPME and Tenax extraction with bioassays. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 140, 191–197.
Hu, S., Zhang, Y., Shen, G., Zhang, H., Yuan, Z., & Zhang, W. (2019). Adsorption/desorption behavior and mechanisms of sulfadiazine and sulfamethoxazole in agricultural soil systems. Soil & Tillage Research, 186, 233–241.
Kaufman, M. H., Cardenas, M. B., Buttles, J., Kessler, A. J., & Cook, P. L. M. (2017). Hyporheic hot moments: Dissolved oxygen dynamics in the hyporheic zone in response to surface flow perturbations. Water Resources Research, 53(8), 6642–6662.
Klein, E. Y., Van Boeckel, T. P., Martinez, E. M., Pant, S., Gandra, S., Levin, S. A., Goossens, H., & Laxminarayan, R. (2018). Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115(15), E3463–E3470.
Könemann, H. (1981). Quantitative structure-activity relationships in fish toxicity studies. Part 1: Relationship for 50 industrial pollutants. Toxicology, 19(3), 209–221.
Kong, W., Li, C., Dolhi, J. M., Li, S., He, J., & Qiao, M. (2012). Characteristics of oxytetracycline sorption and potential bioavailability in soils with various physical-chemical properties. Chemosphere, 87(5), 542–548.
Kovalakova, P., Cizmas, L., McDonald, T. J., Marsalek, B., Feng, M., & Sharma, V. K. (2020). Occurrence and toxicity of antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A review. Chemosphere, 251, 126351.
Kurwadkar, S., Sethi, S. S., Mishra, P., & Ambade, B. (2022). Unregulated discharge of wastewater in the Mahanadi River Basin: Risk evaluation due to occurrence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in surface water and sediments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 179, 113686.
Li, H. B., Li, J., Ma, L. Q., & Juhasz, A. L. (2018, Jul 01–06). Arsenic relative bioavailability in contaminated soils: comparison of animal models, dosing schemes, and biological endpoints.Arsenic in the Environment [Environmental arsenic in a changing world (as2018)]. In 7th International Congress and Exhibition on Arsenic in the Environment (As) - Environmental Arsenic in a Changing World, Chinese Acad Sci, Inst Urban Environm, Beijing, PEOPLES R CHINA.
Liu, Y., Liu, C., Nelson, W. C., Shi, L., Xu, F., Liu, Y., Yan, A., Zhong, L., Thompson, C., Fredrickson, J. K., & Zachara, J. M. (2017). Effect of water chemistry and hydrodynamics on nitrogen transformation activity and microbial community functional potential in hyporheic zone sediment columns. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(9), 4877–4886.
Lourenco, R. A., de Oliveira, F. F., Nudi, A. H., Wagener, A. D. R., Meniconi, M. D. G., & Francioni, E. (2015). PAH assessment in the main Brazilian offshore oil and gas production area using semi-permeable membrane devices (SPMD) and transplanted bivalves. Continental Shelf Research, 101, 109–116.
Louzon, M., Pauget, B., Pelfrene, A., Gimbert, F., Vaufleury, A., & d. (2021). Combining human and snail indicators for an integrative risk assessment of metal(loid)-contaminated soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 409, 124182.
Lungu-Mitea, S., Vogs, C., Carlsson, G., Montag, M., Frieberg, K., Oskarsson, A., & Lundqvist, J. (2021). Modeling bioavailable concentrations in zebrafish cell lines and embryos increases the correlation of toxicity potencies across test systems. Environmental Science & Technology, 55(1), 447–457.
Ma, R. X., Wang, B., Lu, S. Y., Zhang, Y. Z., Yin, L., Huang, J., Deng, S. B., Wang, Y. J., & Yu, G. (2016). Characterization of pharmaceutically active compounds in Dongting Lake, China: Occurrence, chiral profiling and environmental risk. Science of the Total Environment, 557, 268–275.
Miller, E. L., Nason, S. L., Karthikeyan, K. G., & Pedersen, J. A. (2016). Root uptake of pharmaceuticals and personal care product ingredients. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(2), 525–541.
Muller, A. K., Leser, K., Kampfer, D., Riegraf, C., Crawford, S. E., Smith, K., Vermeirssen, E. L. M., Buchinger, S., & Hollert, H. (2019). Bioavailability of estrogenic compounds from sediment in the context of flood events evaluated by passive sampling. Water Research, 161, 540–548.
Pan, M., & Chu, L. M. (2016). Adsorption and degradation of five selected antibiotics in agricultural soil. Science of the Total Environment, 545, 48–56.
Peralta-Maraver, I., Reiss, J., & Robertson, A. L. (2018). Interplay of hydrology, community ecology and pollutant attenuation in the hyporheic zone. Science of the Total Environment, 610, 267–275.
Qiao, M., Ying, G. G., Singer, A. C., & Zhu, Y. G. (2018). Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment. Environment International, 110, 160–172.
Schaper, J. L., Seher, W., Nuetzmann, G., Putschew, A., Jekel, M., & Lewandowski, J. (2018). The fate of polar trace organic compounds in the hyporheic zone. Water Research, 140, 158–166.
Shen, S. Q., Yang, S. K., Zhang, D., Jia, Y., Zhang, F. F., Wang, Y. H., & Wang, W. K. (2022). Spatial distribution of antibiotic resistance genes of the Zaohe-Weihe Rivers, China: Exerting a bottleneck in the hyporheic zone. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(25), 38410–38424.
Terzopoulou, E., & Voutsa, D. (2016). Active and passive sampling for the assessment of hydrophilic organic contaminants in a river basin-ecotoxicological risk assessment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(6), 5577–5591.
Uddin, M., Chen, J., Qiao, X., Tian, R., & Zhu, M. (2020). Insight into dynamics and bioavailability of antibiotics in paddy soils by in situ soil moisture sampler. Science of the Total Environment, 703, 135562.
Veltman, K., Hendriks, A. J., Huijbregts, M. A. J., Wannaz, C., & Jolliet, O. (2014). Toxicokinetic Toxicodynamic (TKTD) modeling of Ag toxicity in freshwater organisms: Whole-body sodium loss predicts acute mortality across aquatic species. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(24), 14481–14489.
Weatherill, J. J., Atashgahi, S., Schneidewind, U., Krause, S., Ullah, S., Cassidy, N., & Rivett, M. O. (2018). Natural attenuation of chlorinated ethenes in hyporheic zones: A review of key biogeochemical processes and in-situ transformation potential. Water Research, 128, 362–382.
Yan, K., Dong, Z., Naidu, R., Liu, Y., Li, Y., Wijayawardena, A., Sanderson, P., Li, H., & Ma, L. Q. (2020). Comparison of in vitro models in a mice model and investigation of the changes in Pb speciation during Pb bioavailability assessments. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 388, 121744.
Zhang, J., Luo, M., Zhang, D., Feng, R., Jia, Y., Meng, J., & Yang, S. (2022). Hydrolysis of norfloxacin in the hyporheic zone: Kinetics and pathways. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(54), 82481–82491.
Zhang, Q.-Q., Ying, G.-G., Pan, C.-G., Liu, Y.-S., & Zhao, J.-L. (2015). Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(11), 6772–6782.
Acknowledgements
The authors are also thankful to all experts involved for their valuable outputs and help. T.Z. contributed to formal analysis and writing—original draft. H.L. contributed to investigation, funding acquisition, and validation. M.Z. contributed to methodology and software. R.F. contributed to investigation. R.H. contributed to data curation. J.Z. contributed to writing—review & editing. Y.C. contributed to writing—review & editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Funding
Henan Province Transportation Science and Technology Project (No. 2020G-2-10); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41977163); the key research and development program of Shaanxi (No. 2022ZDLSF06-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors are also thankful to all experts involved for their valuable outputs and help. T.Z.: Formal analysis, Writing-original draft. H.L.: Investigation, Funding acquisition, Validation. M.Z.: Methodology, Software. R.F.: Investigation. R.H.: Data curation. J.Z.: Writing-review & editing. Y.C.: Writing-review & editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, T., Li, H., Zhou, M. et al. Prediction models and major controlling factors of antibiotics bioavailability in hyporheic zone. Environ Geochem Health 45, 5785–5797 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01624-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01624-6