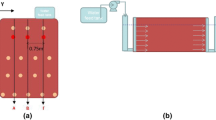
Abstract
In recent years, more focus has been placed on integrated metal removal processes. Electrokinetic (EK) treatment is superior to other technologies because it can be applied to a variety of mediums. Green nanoparticles, on the other hand, have the potential to significantly reduce pollutant concentrations in a short period of time. In this study, we investigated the possibility of combining green zero-valent iron (nZVI) with EK on Cd and Zn-contaminated sediment. For green synthesis, extracts of dry leaves of mulberry (ML-nZVI) and oak (OL-nZVI) were used, both abundantly present in the Republic of Serbia. The results show that, despite the fact that their availability was greatly reduced, the metals were concentrated and stabilized to a significant extent in the middle of the EK cell (z/L 0.5) after all treatments. When the results were compared, OL-nZVI proved to be a more effective nanomaterial even with smaller doses of OL-nZVI, which is important in terms of achieving better economic benefits. This study identified green nano zero-valent iron as a powerful tool for metal removal when combined with electrokinetic (EK) treatment, which improves green nZVI longevity and migration. This study of the combined green nZVI—EK remediation treatment, in particular, will have an impact on future research in this field, given the achieved efficiency.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelfatah, A. M., Fawzy, M., Eltaweil, A. S., & El-Khouly, M. E. (2021). Green synthesis of nano-zero-valent iron using ricinus communis seeds extract: Characterization and application in the treatment of methylene blue-polluted water. ACS Omega, 6, 25397–25411. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c03355
Alazaiza, M. Y. D., Albahnasawi, A., Ali, G. A. M., Bashir, M. J. K., Copty, N. K., Amr, S. S. A., Abushammala, M. F. M., & Al Maskari, T. (2021). Recent advances of nanoremediation technologies for soil and groundwater remediation: A review. Water. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162186
Azhar, U., Ahmad, H., Shafqat, H., Babar, M., Shahzad Munir, H. M., Sagir, M., Arif, M., Hassan, A., Rachmadona, N., Rajendran, S., Mubashir, M., & Khoo, K. S. (2022). Remediation techniques for elimination of heavy metal pollutants from soil: A review. Environmental Research, 214, 113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113918
Bae, S., & Hanna, K. (2015). Reactivity of nanoscale zero-valent iron in unbuffered systems: Effect of pH and Fe(II) dissolution. Environmental Science & Technology, 49, 10536–10543. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01298
Boparai, H. K., Joseph, M., & Carroll, D. M. O. (2013). Cadmium (Cd2+) removal by nano zerovalent iron: Surface analysis, effects of solution chemistry and surface complexation modeling. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1651-8
Černík, M., Hrabal, J., & Nosek, J. (2020). Combination of Electrokinetics and nZVI Remediation. In Part of the Applied Environmental Science and Engineering for a Sustainable Future book series (AESE) (pp. 65–85). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29840-1_2
Černíková, M., Nosek, J., & Černík, M. (2020). Combination of nZVI and DC for the in-situ remediation of chlorinated ethenes: An environmental and economic case study. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125576
Czinnerová, M., Vološčuková, O., Marková, K., Ševců, A., Černík, M., & Nosek, J. (2020). Combining nanoscale zero-valent iron with electrokinetic treatment for remediation of chlorinated ethenes and promoting biodegradation: A long-term field study. Water Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115692
De Gisi, S., Minetto, D., Lofrano, G., Libralato, G., Conte, B., Todaro, F., & Notarnicola, M. (2017). Nano-scale Zero Valent Iron (nZVI) treatment of marine sediments slightly polluted by heavy metals. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 60, 139–144. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1760024
Debnath, A., Singh, P. K., & Chandra Sharma, Y. (2021). Metallic contamination of global river sediments and latest developments for their remediation. Journal of Environmental Management, 298, 113378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113378
Desalegn, B., Megharaj, M., Chen, Z., & Naidu, R. (2019). Green synthesis of zero valent iron nanoparticle using mango peel extract and surface characterization using XPS and GC-MS. Heliyon, 5, 7e01750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01750
Dubovina, M., Krčmar, D., Grba, N., Watson, M. A., Rađenović, D., Tomašević-Pilipović, D., & Dalmacija, B. (2018). Distribution and ecological risk assessment of organic and inorganic pollutants in the sediments of the transnational Begej canal (Serbia–Romania). Environmental Pollution, 236, 773–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.014
SRPS EN 12879:2007. (2007). Characterization of sludges—Determination of the loss on Ignition of dry mass.
SRPS EN 12880:2007. (2007). Characterization of sludges—Determination of dry residue and water content.
Essa, M. H., Mu’Azu, N. D., Lukman, S., & Bukhari, A. (2013). Integrated electrokinetics-adsorption remediation of saline-sodic soils: Effects of voltage gradient and contaminant concentration on soil electrical conductivity. Science World Journal. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/618495
Garcia-Blas, N., Jimenez-Relinque, E., & Castellote, M. (2022). Surfactants in electrokinetic remediation of sediments to enhance the removal of metals. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 22(11), 2853–2864. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03299-5
Gardner, K. (2005). Electrochemical Remediation and stabilization of contaminated sediments. Civil Engineering Department University of New Hampshire Durham, NH 03824, pp. 1–34.
Official Gazette. (2012). Regulation on Limit Values for Pollutants in Surface and Groundwaters and Sediments, and the Deadlines for Their Achievement. Belgrade, Serbia. Gazette No. 50/2012.
Gidudu, B., & Chirwa, E. M. N. (2022). Electrokinetic remediation of contaminated soil. Molecules, 27, 7381. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217381Academic
Gil-Díaz, M., Pinilla, P., Alonso, J., & Lobo, M. C. (2017). Viability of a nanoremediation process in single or multi-metal(loid) contaminated soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 321, 812–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.09.071
Gomes, H. I., Rodrıguez-Maroto, M. J., Ribeiro, B. A., Pamukcu, S., & Dias-Ferreira, C. (2016). Electrokinetics across disciplines and continents: New strategies for sustainable development. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20179-5
Gomes, H. I., & Bustos, E. B. (2021). Combined use of remediation technologies with electrokinetics. Electrokinetic Remediation for Environmental Security and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119670186.ch3
Gomes, H. I., Dias-Ferreira, C., Ottosen, L. M., & Ribeiro, A. B. (2015). Electroremediation of PCB contaminated soil combined with iron nanoparticles: Effect of the soil type. Chemosphere, 131, 157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.007
Gomes, H. I., Fan, G., Mateus, E. P., Dias-ferreira, C., & Ribeiro, A. B. (2014). Assessment of combined electro—Nanoremediation of molinate contaminated soil. Science of Total Environment, 493, 178–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.05.112
Guo, Y., Li, X., Liang, L., Lin, Z., Su, X., & Zhang, W. (2021). Immobilization of cadmium in contaminated soils using sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron: Effectiveness and remediation mechanism. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 420, 126605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126605
Han, D., Wu, X., Li, R., Tang, X., Xiao, S., & Scholz, M. (2021). Critical review of electro-kinetic remediation of contaminated soils and sediments: Mechanisms, performances and technologies. Water, Air and Soil Pollution. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05182-4
Huang, C. W., Chai, Z. Y., Yen, P. L., How, C. M., Yu, C. W., Chang, C. H., & Liao, V. H. C. (2020). The bioavailability and potential ecological risk of copper and zinc in river sediment are affected by seasonal variation and spatial distribution. Aquatic Toxicology, 227, 105604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2020.105604
ISO 5667-12:1995 (1995). Water quality e sampling—Part 12: Guidance on Sampling of Bottom Sediments ISO 11074 2:1998. https://www.iso.org/standard/11776.html.
ISO 11464:2006 (2006). Soil quality e pretreatment of samples for physico-chemical analyses. https://www.iso.org/standard/37718.html.
ISO 11348-1:2008 (2008). Water quality determination of the inhibitory effect of water samples on the light emission of vibrio fischeri (Luminiscent Bacteria Test). London: British Standards Institution.
ISO 11277:2009 (2009). Soil quality e determination of particle size distribution in mineral soil material e method by sieving and sedimentation. https://www.iso.org/standard/54151.html.
Jain, C. K. (2004). Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of River Yamuna, India. Water Research, 38, 569–578.
Jakovljev, N. (2022). Next is the silting of Plovni Begej, the biggest problem is heavy metals in the silt. https://www.danas.rs/vesti/drustvo/na-redu-izmuljivanje-plovnog-begeja-najveci-problem-teski-metali-u-mulju/
Jiang, D., Zeng, G., Huang, D., Chen, M., Zhang, C., Huang, C., & Wan, J. (2018). Remediation of contaminated soils by enhanced nanoscale zero valent iron. Environmental Research, 163, 217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.01.030
Kecić, V., Kerkez, Đ, Prica, M., Lužanin, O., Bečelić-Tomin, M., Pilipović, D. T., & Dalmacija, B. (2018). Optimization of azo printing dye removal with oak leaves-nZVI/H2O2 system using statistically designed experiment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 202, 65–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.117
Kerkez, D., Radjenović, D., Pilipović, D. T., Bečelić-Tomin, M., Slijepčević, N., Rončević, S., & Dalmacija, B. (2019). Leachability and microstructural analysis of clay and lime stabilized/solidified polluted sediment—Long-term performance. Periodica Polytechnica Chemical Engineering. https://doi.org/10.3311/PPch.13403
Krcmar, D., Varga, N., Prica, M., Cveticanin, L., Zukovic, M., Dalmacija, B., & Corba, Z. (2018). Application of hexagonal two dimensional electrokinetic system on the nickel contaminated sediment and modelling the transport behavior of nickel during electrokinetic treatment. Separation and Purification Technology, 192, 253–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.10.008
Landner, L., & Reuther, R. (2005). Speciation, mobility and bioavailability of metals in the environment. In: Metals in society and in the environment. Environmental pollution (Vol. 8). Dordrecht: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-2742-7_6
Liang, W., Dai, C., Zhou, X., & Zhang, Y. (2014). Application of zero-valent iron nanoparticles for the removal of aqueous zinc ions under various experimental conditions. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085686
Liu, M., Wang, J., Xu, M., Tang, S., Zhou, J., Pan, W., Ma, Q., & Wu, L. (2022). Nano zero-valent iron-induced changes in soil iron species and soil bacterial communities contribute to the fate of Cd. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 424, 127343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127343
Machado, S., Pacheco, J. G., Nouws, H. P. A., Albergaria, J. T., & Delerue-Matos, C. (2015). Characterization of green zero-valent iron nanoparticles produced with tree leaf extracts. Science of Total Environment, 533, 76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.091
Machado, S., Pinto, S. L., Grosso, J. P., Nouws, H. P. A., Albergaria, J. T., & Delerue-Matos, C. (2013). Green production of zero-valent iron nanoparticles using tree leaf extracts. Science of Total Environment, 445–446, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.033
Marathe, R. B. (2012). XRD and SEM analysis of Tapti river sediment: A case study. Archives of Applied Science Research, 4(1), 78–84.
Mathur, S., Singh, D., & Ranjan, R. (2022). Remediation of heavy metal(loid) contaminated soil through green nanotechnology. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2022.932424
Mystrioti, C., Xanthopoulou, T. D., Tsakiridis, P. E., Papassiopi, N., & Xenidis, A. (2016). Comparative evaluation of five plant extracts and juices for nanoiron synthesis and application for hexavalent chromium reduction. Science of the Total Environment, 539, 105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.091
Namieśnik, J., & Rabajczyk, A. (2010). The speciation and physico-chemical forms of metals in surface waters and sediments. Chemical and Speciation Bioavailability, 22, 1–24. https://doi.org/10.3184/095422910X12632119406391
O’Carroll, D., Sleep, B., Krol, M., Boparai, H., & Kocur, C. (2013). Nanoscale zero valent iron and bimetallic particles for contaminated site remediation. Advances in Water Resources, 51, 104–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.02.005
Ottosen, L. M., Larsen, T. H., Jensen, P. E., Kirkelund, G. M., Kerrn-jespersen, H., Tuxen, N., & Hyldegaard, B. H. (2019). Electrokinetics applied in remediation of subsurface soil contaminated with chlorinated ethenes e A review. Chemosphere, 235, 113–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.075
Peng, S., Wang, X., & Zhang, X. (2020). Research progress of in-situ remediation of polluted soil and groundwater by electrokinetic and permeable reaction barrier. E3S Web Conference, 143, 10–13. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202014302043
Peng, W., Li, X., Xiao, S., & Fan, W. (2018). Review of remediation technologies for sediments contaminated by heavy metals. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 18, 1701–1719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-1921-7
Poguberović, S. S., Krčmar, D. M., Maletić, S. P., Kónya, Z., Pilipović, D. D. T., Kerkez, D. V., & Rončević, S. D. (2016). Removal of As(III) and Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using “green” zero-valent iron nanoparticles produced by oak, mulberry and cherry leaf extracts. Ecological Engineering, 90, 42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.01.083
Popov, N., Rončević, S., Duduković, N., Krčmar, D., Mihaljev, Ž, Živkov Baloš, M., & Đorđievski, S. (2021). Ex situ remediation of sediment from Serbia using a combination of electrokinetic and stabilization/solidification with accelerated carbonation treatments. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(12), 14969–14982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11621-2
Rauret, G., Lopez-Sanchez, J. F., Sahuquillo, A., Rubio, R., Davidson, C., Ure, A., & Quevauviller, P. (1999). Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1, 57–61. https://doi.org/10.1039/a807854h
Rounds, S. A. (2006). Alkalinity and acid neutralizing capacity. National Field Manual for the Collection of Water-Quality Data (TWRI Book 9). http://water.usgs.gov/owq/FieldManual/Chapter6/section6.6/pdf/6.6.pdf.
Ryan, P. C., Wall, A. J., Hillier, S., & Clark, L. (2002). Insights into sequential chemical extraction procedures from quantitative XRD: A study of trace metal partitioning in sediments related to frog malformites. Chemical Geology, 184(3–4), 337–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00390-4
Saleem, M. (2021). Efficient removal of copper and cadmium from contaminated soil utilizing electrokinetic process. Yanbu Journal of Engineering and Science, 18(1), 37–45. https://doi.org/10.53370/001c.28950
Saleem, M., Chakrabarti, M. H., Irfan, M. F., Hajimolana, S. A., Hussain, M. A., Diya’uddeen, B. H., & Daud, W. M. A. W. (2011). Electrokinetic remediation of nickel from low permeability soil. International Journal Electrochemical Science, 6, 4264–4275.
Selvi, A., Rajasekar, A., Theerthagiri, J., Ananthaselvam, A., Sathishkumar, K., Madhavan, J., & Rahman, P. K. S. M. (2019). Integrated remediation processes toward heavy metal removal/recovery from various environments—A review. Frontiers in Environmental Science. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2019.00066
Shrestha, R., Fischer, R., & Rahner, D. (2003). Behavior of cadmium, lead and zinc at the sediment-water interface by electrochemically initiated processes. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 222, 261–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(03)00231-0
Slijepčević, N., Pilipović, D. T., Kerkez, Đ, Krčmar, D., Bečelić-Tomin, M., Beljin, J., & Dalmacija, B. (2021). A cost effective method for immobilization of Cu and Ni polluted river sediment with nZVI synthesized from leaf extract. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127816
Soares, A., Ramos, S., Albergaria, T., & Delerue-Matos, C. (2018). Green zero valent iron nanoparticles dispersion through a sandy column using different injection sequences. Science of Total Environment, 637–638, 935–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.096
Sojka, M., & Jaskuła, J. (2022). Heavy metals in river sediments: contamination, toxicity, and source identification—A case study from Poland. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710502
Song, B., Zeng, G., Gong, J., Liang, J., Xu, P., Liu, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., Cheng, M., Liu, Y., Ye, S., Yi, H., & Ren, X. (2017). Evaluation methods for assessing effectiveness of in situ remediation of soil and sediment contaminated with organic pollutants and heavy metals. Environmental International, 105, 43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.05.001
Song, Y., Tang, H., Yan, Y., Guo, Y., Wang, H., & Bian, Z. (2022). Combining electrokinetic treatment with modified zero-valent iron nanoparticles for rapid and thorough dechlorination of trichloroethene. Chemosphere, 292, 133443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133443
SRPS ISO 10390:2007. (2007). Soil Quality—Determination of pH.
SRPS ISO 11265:2007. (2007). Soil quality—Determination of the specific electrical conductivity.
Stefaniuk, M., Oleszczuk, P., & Ok, Y. S. (2016). Review on nano zerovalent iron (nZVI): From synthesis to environmental applications. Chemical Engineering Journal, 287, 618–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.11.046
Tang, H., Wang, J., Zhang, S., Pang, H., Wang, X., Chen, Z., Li, M., Song, G., Qiu, M., & Yu, S. (2021). Recent advances in nanoscale zero-valent iron-based materials: Characteristics, environmental remediation and challenges. Journal of Cleaner Production, 319, 128641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128641
USEPA Method 3051a. (2007). Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Sediments. sludges, soils and, Revision vol. 1.
USEPA Method 7000B. (2007). Flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry. ReVision 2.
USEPA Method 7010. (2007). Graphite furnace absorption spectrophotometry. Revision, 0.
USEPA Method 9080. (1986). Cation-exchange capacity of soils (ammonium acetate), SW-846: test methods for evaluating solid waste - physical/chemical methods. Washington D.C., United States. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-12/documents/9080.pdf.
Varga, N., Dalmacija, B., Prica, M., Kerkez, D., Becelic-Tomin, M., Spasojevic, J., & Krcmar, D. (2017). The application of solar cells in the electrokinetic remediation of metal contaminated sediments. Water Environmental Research, 89, 663–671. https://doi.org/10.2175/WERD1600172.1
Vítková, M., Rákosová, S., Michálková, Z., & Komárek, M. (2017). Metal(loid)s behaviour in soils amended with nano zero-valent iron as a function of pH and time. Journal of Environmental Management, 186, 268–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.06.003
Wang, P., Shen, F., Li, R., Guo, D., Liang, W., Liu, T., & Zhang, Z. (2022). Remediation of Cd and Zn contaminated soil by zero valent iron (Fe0): A field trial. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 28, 102603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2022.102603
Wang, X., & Li, Y. (2011). Measurement of Cu and Zn adsorption onto surficial sediment components: New evidence for less importance of clay minerals. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 189(3), 719–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.03.045
Wang, Y., Li, A., & Cui, C. (2021). Remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils by electrokinetic technology: Mechanisms and applicability. Chemosphere, 265, 129071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129071
Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Su, G., Yang, K., & Lin, D. (2021). Transformation and implication of nanoparticulate zero valent iron in soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 412, 125207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125207
Wojtkowska, M. (2013). Migration and forms of metals in bottom sediments of Czerniakowskie Lake. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 90, 165–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0881-7
Zhao, X., Liu, W., Cai, Z., Han, B., Qian, T., & Zhao, D. (2016). An overview of preparation and applications of stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles for soil and groundwater remediation. Water Research, 100, 245–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.019
Acknowledgements
The research was financed by the Science Fund of the Republic of Serbia, #7753609, BEuSED. We are also grateful to Srđan Rakić from Department of Physics, Faculty of Sciences, University of Novi Sad, Serbia for X-ray diffraction analysis.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the writing of this manuscript. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duduković, N., Slijepčević, N., Tomašević Pilipović, D. et al. Integrated application of green zero-valent iron and electrokinetic remediation of metal-polluted sediment. Environ Geochem Health 45, 5943–5960 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01609-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01609-5