Abstract
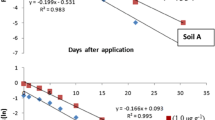
Weed infestation is a major biotic limitations in wheat cultivation; thus, various herbicides are being applied to control these weeds. Therefore, this study was undertaken for two successive years to assess degradation behaviours, persistence and residue risk imposed by carfentrazone, fenoxaprop-p-ethyl and pinoxaden sprayed as post-emergence herbicides in the wheat crop for management of weeds. Soil and crop samples were collected at periodically at after two hour of herbicide application till harvest of wheat crop and analysed by a high-performance liquid chromatograph. Degradation of carfentrazone, pinoxaden and fenoxaprop-p-ethyl, in the soil of wheat field occurred rapid to moderately with the mean half-life 9.92, 11.7 and 11.8 days, respectively. Persistence was found to be dependent on the weather parameters as well as physicochemical properties of the soil and herbicides. Half-life of studied herbicides was found to be negatively correlated with persistence (R2 0.38, p = 0.05, n = 3) and vapour pressure (R2 0.99, p = 0.05, n = 3). Principal component analysis revealed that the first two Principal Components (PCs) had eigenvalues more than 1, and the first and second PCs contributed 77.4 and 22.6% in herbicide residues and different parameters variation, respectively. Terminal residues of carfentrazone, pinoxaden and fenoxaprop-p-ethyl in the wheat straw, grains and soil were found below the maximum residue limits. Owing to the moderate persistence under wheat field conditions, carfentrazone, pinoxaden and fenoxaprop-p-ethyl are supposed to be safe for control of weeds in wheat crop and hence, suspected risk on the human and environment or crop produce under evaluated doses is negligible.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abit, M., Rainbolt, C., Krutz, L., Shaner, D., & Hanson, B. (2012). Effects of long-term use on simazine dissipation in central California vineyards. Weed Science, 60, 531–536.
Bararpour, T., Korres, N. E., Burgos, N. R., Hale, R. R., & Tseng, T. M. P. (2018). Performance of pinoxaden on the control of diclofop-resistant Italian Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L. ssp. multiflorum) in winter wheat. Agriculture, 8, 114.
Barizon, R. R. M., Figueiredo, R. O., de Souza Dutra, D. R. C., Regitano, J. B., & Ferracini, V. L. (2020). Pesticides in the surface waters of the Camanducaia River watershed. Brazilian Journal of Environmental Science Health B, 55, 283–292.
Benoit, P., Perceval, J., Stenrod, M., Moni, C., Eklo, O. M., Barriuso, E., & Sveistrup, T. (2007). Availability and biodegradation of metribuzin in alluvial soils as affected by temperature and soil properties. European Journal of Weed Research, 47, 517–526.
Cederlund, H., Börjesson, E., Önneby, K., & Stenström, J. (2007). Metabolic and co-metabolic degradation of herbicides in the fine material of railway ballast. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 39(2), 473–484.
Chhonkar, R. S., & Malik, R. K. (2002). Isoproturon resistance in Phalaris minor and its response to alternate herbicides. Weed Technology, 16, 116–123.
Curran, W. S. (2013). Persistence of herbicides in soil (pp. 1–4). USA: Agronomy Facts. Penn State College of Agricultural Science.
Dixit, A., Sondhia, S., & Varshney, J. G. (2011). Bioefficacy of pinoxaden in wheat and its residual effect on succeeding crop. Indian Journal of Agricultural Science, 81(7), 659–661.
Dotray, P. A., Baughma, W. J., & Grichar, T. A. (2010). Peanut response to carfentrazone-ethyl and pyraflufen-ethyl applied post-emergence. Peanut SciEnce, 37(1), 52–57.
Duan, J., Sun, M., Shen, Y., Gao, B., Zhang, Z., Gao, T., & Wang, M. (2018). Enantioselective acute toxicity and bioactivity of carfentrazone-ethyl enantiomers. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination, 2018(101), 651–656.
European Commission Safety of the Food Chain Pesticides and Biocides (2015). Guidance document on analytical quality control and method validation procedures for pesticides residues analysis in food and feed. SANTE/11945/2015.
Fahad, S., Hussain, S., Chauhan, B. H., Saud, S., Wu, C., Hasan, S., Tanveer, M., Jan, A., & Huang, J. (2015). Weed growth and crop yield loss in wheat as influenced by row spacing and weed emergence times. Crop Protection, 71, 101–108.
Gaonkar, O. D., Nambi, I. M., & Govindarajan, S. K. (2019). Soil organic amendments: Impacts on sorption of organophosphate pesticides on an alluvial soil. Journal of Soils Sediments, 19, 566–578.
García-Cansino, L., García, M. Á., & Marina, M. L. (2021). Simultaneous enantiomeric separation of carfentrazone-ethyl herbicide and its hydrolysis metabolite carfentrazone by cyclodextrin electrokinetic chromatography analysis of agrochemical products and a degradation study. Molecules, 2021(26), 5350.
Gianessi, L. P. (2013). The increasing importance of herbicides in worldwide crop production. Pest Management Science, 69(10), 1099–1105.
Godfray, H. C., Beddington, J. R., Crute, I. R., Haddad, L., García, D., Muir, J. F., Pretty, J., Robinson, S., Thomas, S. M., & Toulmin, C. (2010). Food security: the challenge for feeding 9 billion people. Science, 327(5967), 812–818.
Guo, B., Yin, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, S., & Wang, H. (2020). The degradation dynamics and safety evaluation of florasulam and carfentrazone-ethyl in wheat and soil. Environmental Chemistry, 2, 441–447.
Guo, Q. Y. (2002). Effect of fenoxaprop-p-ethyl on controlling wild oats at spring wheat fields. Pestic., 41, 37–38.
Han, L., Xu, Y., Dong, M., & Qian, C. (2007). Dissipation and residues of carfentrazone-ethyl in wheat and soil. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 79, 445–447.
Heap, I. (2021). The International Herbicide-Resistant Weed Database. www. weedscience.org. Accessed: October 26, 2021.
Herrero-Hernández, E., Simón-Egea, A. B., Sánchez-Martín, M. J., Rodríguez-Cruz, M. S., & Andrades, M. S. (2020). Monitoring and environmental risk assessment of pesticide residues and some of their degradation products in natural waters of the Spanish vineyard region included in the denomination of origin Jumilla. Environmental Pollution, 264, 114666.
Jing, X., Wang, T., Jiali Yang, J., Wang, Y., & Xu, H. (2018). Effects of biochar on the fate and toxicity of herbicide fenoxaprop-ethyl in soil. Royal Society Open Science. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.171875
Jing, X., Yao, G., Liu, D., Liu, M., Wang, P., & Zhou, Z. (2016). Environmental fate of chiral herbicide fenoxaprop-ethyl in water-sediment microcosms. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 26797.
Klein, M. (2002). The calculation of pesticide leaching close to railway tracks using PELMO. Journal of Plant Disease and Protestation, 18, 405–412.
Koschnick, T. J., Haller, W. T., & Chen, A. W. (2004). Carfentrazone-ethyl pond dissipation and efficacy on floating plants. Journal of Aquatic Plant Management, 42, 103–108.
Li, M., Ma, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, Q., Saleem, M., Yang, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2021). Ecotoxicity of herbicide carfentrazone-ethyl towards earthworm Eisenia fetida in soil Comparative Biochemistry Physiology. Part C Toxicology and Pharmacology, 253(4), 109250.
Liu, J., Song, Y., Tang, M., Lu, Q., & Zong, G. (2020). Enhanced dissipation of xenobiotic agrochemicals harnessing soil microbiome in the tillage-reduced rice-dominated agroecosystem. Journal of Hazardous Material, 398, 122954.
Liu, L., Gao, S. B., & Lin, F. G. (2000). The using technology of Affinity 40DF. Chinese Journal of Pesticide, 39(8), 41–42.
Locke, M. A., Reddy, K. N., & Zablotowicz, R. M. (2002). Weed management in conservation crop production systems. Weed Biology and Management, 2, 123–132.
Lyon, D. L., Kniss, A., & Miller, S. R. (2009). Carfentrazone improves broadleaf weed control in proso and foxtail millets. Weed Technology, 21, 84–87.
Manus, S. M., Payvandi, S., Sweeney, P., Jones, N., Andrew, R., Schofield, D., White, J., Garry Hamer, P., Langride, G., Tirso, L., Oteyza, G., Rincon, V. J., Dorn, R., & Bird, & M, Grrener, M. (2021). Regulatory groundwater monitoring: Realistic residues of pinoxaden and metabolites at vulnerable locations. The Science of Total Environment, 761, 143313.
Maqueda, C., Villaverde, J., Sopena, F., Undabeytia, S., & Morillo, S. (2009). Effects of soil characteristics on metribuzin dissipation using clay-gel-based formulations. Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 57, 3273–3278.
Marín-Benito, J. M., Carpio, M. J., Sánchez-Martín, M. J., & Rodríguez-Cruz, M. S. (2020). Previous degradation study of two herbicides to simulate their fate in a sandy loam soil: effect of the temperature and the organic amendments. Science of Total Environment, 653, 1301–1310.
Memoli, V., De Marco, A., Baldantoni, D., De Nicola, F., & Maisto, G. (2017). Short and long-term effects of a single application of two organic amendments. Ecosphere, 8, e02009.
Nady, M. F., & NBelal, E. B. (2013). Effect of phytotoxicity of pendimethalin residues and its bioremediation on growth and anatomical characteristics of Cucumis sativus and Echinochloa crus-galli plants. Asian Journal of Crop Science, 5(3), 222–237.
Oerke, E. C. (2006). Crop losses to pests. Journal of Agricultural SciEnce, 144, 31–43.
Porter, D. J., Kopec, M., & Hofer, U. (2005). Pinoxaden-a new selective post-emergence graminicide for wheat and barley. Weed Science Society of America, 45, 95.
Punia, S. S., Singh, S. K., & Poonia, T. M. (2018). Bio-efficacy of carfentrazone-ethyl 40% DF against weeds in wheat and its carryover effect on succeeding sorghum. Indian Journal of Weed Science, 50(4), 399–401.
Senseman, S.A. (2007). Herbicide handbook. 9th Ed. Weed Sci. Soc. America, Champaign, p 458.
Singh, S. B., Das, T. K., & Kulsherestha, G. (2012). Persistence of herbicide fenoxaprop ethyl and its acid metabolite in soil and wheat crop under Indian tropical conditions. Journal of Environmental Science Health, Part B Pesticide and Food Contamination and Agricultural Wastes, 748(5), 324–330.
Soares, P. R. S., Birolli, W. G., & Ferreira, I. M. (2021). Biodegradation pathway of the organophosphate pesticides chlorpyrifos, methyl parathion and profenofos by the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii CBMAI 935 and its potential for methylation reactions of phenolic compounds. Mar Pollution Bulletin, 166, 112185–112196.
Sondhia, S. (2006). Herbicides residues in soil, water and food chain, Annual Report 2005–06. pp. 17–24. Published by National Research Centre for Weed Science, Jabalpur.
Sondhia, S. (2014). Herbicides residues in soil, water, plants and non-targeted organisms and human health implications: an Indian perspective. Indian Journal of Weed Science, 46(1), 66–85.
Sondhia, S. (2018). Herbicide residues analysis. Satish Serial Publishing House.
Sondhia, S. (2019). Leaching of pyrazosulfuron-ethyl in a sandy loam soil under natural rains in field lysimeters. International Journal of Chemical Studies, 7(1), 313–318.
Sondhia, S., Rajput, S., Verma, R. K., & Kumar, A. (2016). Biodegradation of the herbicide penoxsulam (Triazolopyrimidine Sulphonamide) by fungal strains of Aspergillus in Soil. Applied Soil Ecology, 105, 196–206.
Sondhia, S., Waseem, U., & Varma, R. K. (2013). Fungal degradation of an acetolactate synthase (ALS) inhibitor pyrazosulfuron-ethyl in soil. Chemosphere, 93(9), 2140–2147.
Storkey, J., Mead, A., Addy, J., & MacDonald, A. J. (2021). Agricultural intensification and climate change have increased the threat from weeds. Global Change BiolOgy. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15585
Sun, D., Pang, J., Qiu, J., Li, L., Liu, C., & Jiao, B. (2013). Enantioselective degradation and enantiomerization of indoxacarb in soil. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 61, 11273–11277.
Tandon, S. (2019). Degradation of fenoxaprop-p-ethyl and its metabolite in soil and wheat crops. Journal of Food Protection, 82(11), 1959–1964.
Thompson, W. M., & Nissen, S. J. (2000). Absorption and fate of carfentrazone-ethyl in Zea mays, Glycine max, and Abutilon theophrasti. Weed Science, 48, 15–19.
Timsina, J., & Connor, D. J. (2001). Productivity and management of rice-wheat cropping systems: issues and challenges. Field Crop Research, 69, 93–132.
Tomkiel, M., Baćmaga, M., Borowik, A., Wyszkowska, J., & Kucharski, J. (2018). The sensitivity of soil enzymes, microorganisms and spring wheat to soil contamination with carfentrazone-ethyl. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, B, 53, 97–107.
Torstensson, L., Cederlund, H., Börjesson, E., & Stenström, J. (2002). Environmental problems with the use of diuron on Swedish railways. Pesticide Outlook, 13, 108–111.
Vaghasia, M., & Nadiyadhara,. (2013). Effect of post-emergence herbicides in groundnut and its residual effect on succeeding crops. International Journal for Crop Improvement, 4(2), 54–58.
Walder, F., Schmid, M. W., Riedo, J., Valzano-Held, A. Y., Banerjee, S., Büchi, L., Bucheli, T. D., & van der Heijden, M. G. A. (2022). Soil microbiome signatures are associated with pesticide residues in arable landscapes. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 174, 108830.
Walia, U.S., Gill, B.S., & Sindhu, V.K. (2007). Pinoxaden-a new alternate herbicide for controlling Phalaris minor in wheat. ISWS biennial conference on new and emerging issues in weed science 2–3 November 2007 held at Hisar, Haryana pp 93.
Walsh, M. J., & Powles, S. B. (2014). Management of herbicide resistance in wheat cropping systems: learning from the Australian experience. Pest Management Science, 70, 1324–1328.
Wu, J. X., Zhang, Y., Wang, K., & Zhang, H. Y. (2015). Residue analysis and dissipation of fenoxaprop-P-ethyl and its metabolite fenoxaprop-P in rice ecosystem. Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 70(7), 897–902.
Xiaoxu, C., Yu, S., Han, L., Sun, S., Zhi, Y., & Li, W. (2011). Residues and dissipation of the herbicide fenoxaprop-P-ethyl and its metabolite in wheat and soil. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 87(1), 50–53.
Zhang, Q., Saleem, M., & Wang, C. (2019). Effects of biochar on the earthworm (Eisenia foetida) in soil contaminated with and/or without pesticide mesotrione. Science of Total Environment, 671, 52–58.
Zhao, S. M., Xu, W., Zhang, W. L., & ZWuGuangMu, H. C. W. (2021). In depth biochemical identification of a novel methyl parathion hydrolase from Azohydromonas australica and its high effectiveness in the degradation of various organophosphorus pesticides. Bioresource Technology, 323, 124641–124650.
Zhu, F. G. N., Liu, H. J., & Zhu, J. W. (2000). Residue and degradation of fenoxaprop-ethyl and its metabolites in wheat and soil. PesticIde, 5, 19–20.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Dr Shobha Sondhia, Dr Sreekanthpak Dasari and Dr Deepak V. Pawar. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Dr Shobha Sondhia and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sondhia, S., Pawar, D.V. & Dasari, S. Degradation dynamics, correlations, and residues of carfentrazone-ethyl, fenoxaprop-p-ethyl, and pinoxaden under the continuous application in the wheat field. Environ Geochem Health 45, 8851–8865 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01487-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01487-x