Abstract
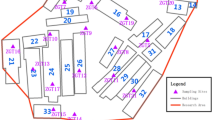
Yunnan Province is the main planting area of the precious Chinese herbal medicines (CHM) Panax notoginseng; however, it locates the geological area with high soil heavy metals in China. The frequent land replacement due to continuous cropping obstacles and excessive application of chemicals makes P. notoginseng prone to be contaminated by heavy metals under the farmland P. notoginseng (FPn) planting. To overcome farmland shortage, understory P. notoginseng (UPn) was developed as a new ecological planting model featured by no chemicals input. However, this newly developed planting system requires urgently the soil–plant heavy metal characteristics and risk assessment. This study aimed to evaluate the pollution status of eight heavy metals in the tillage layer (0–20 cm), subsoil layer (20–40 cm) and the plants of UPn in Lancang County, Yunnan Province. Pollution index (Pi) showed that the contamination degree of heavy metals in the tillage layer and subsoil layer was Cd > Pb > Ni > Cu > Zn > Cr > Hg > As and Pb > Cd > Cu > Ni > Cr > Hg > Zn > As, respectively. Potential ecological risk index (PERI) for the tillage layer and subsoil layer was slight and middle, respectively. The exceeding standard rate of Cd, As, Pb, Hg, Cu in the UPn roots was 5.33%, 5.33%, 13.33%, 26.67% and 1.33%, respectively, while only Cd and Hg in the UPn leaves exceeded the standard 10% and 14%, respectively. The enrichment abilities of Cd and Hg in the roots and leaves of UPn were the strongest, while that of Pb was the weakest. The Hazard index (HI) and target hazard quotient (THQ) of eight heavy metals in the roots and leaves of UPn were less than 1.Therefore, our results prove that Upn has no human health risk and provide a scientific basis for the safety evaluation and extension of UPn.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao, S. D. (2000). Methods of agrochemical analysis of soils. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press.
Brown, G. E., Foster, A. L., & Ostergren, J. D. (1999). Mineral surfaces and bioavailability of heavy metals: A molecular-scale perspective. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 96, 3388–3395.
National Environmental Protect Bureau of China and National Technology Supervise Bureau of China. (2018). In: Chinese Standards: Chinese Standards. Environmental Quality Standard for Soils. GB15618–2018; Environmental Sciences Press of China: Beijing, China.
Cao, Z. H. (2003). Effect of fertilization on soil health quality effect of fertilization on environment quality. Soils, 3, 450–455.
Chen, Y., Zou, J., Sun, H., et al. (2021). Metals in traditional Chinese medicinal materials (TCMM): A systematic review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 207, 111–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111311
Chien, L. C., Hung, T. C., Chang, K. Y., et al. (2002). Daily intake of TBT, Cu, Zn, Cd and As for fishermen in Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 285(1–3), 177–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(01)00916-0
DBS 53/024—2017. Local standards for food safety in Yunnan Province .[S].
Dong, L. L., Xu, J., Feng, G. Q., et al. (2016). Soil bacterial and fungal community dynamics in relation to Panax notoginseng death rate in a continuous cropping system. Science and Reports, 6, 31802.
Du, G. X. (2020). Characteristics and sources of atmospheric mercury in typical Urban area of Yunnan Province. Kunming University of Technology, 06–08.
Fan, J. H., Sun, L. Q., & Wang, P. (2019). Geological characteristic of Yunshan village in the periphery and the formation reason of Pb high value anomaly in soil of Laochang lead-zinc mine in Lancang County, Yunnan Province. Jilin Geology, 38, 49–54.
Fu, Y. W., Dou, X. W., Lu, Q., et al. (2020). Comprehensive assessment for the residual characteristics and degradation kinetics of pesticides in Panax notoginseng and planting soil. Science of the Total Environment, 714, 136718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136718
Gu, J. C., & Zhao, J. (2010). Status of soil contamination by heavy metals and study on remediation techniques in Yunnan. Environmental Science Survey, 29, 68–71.
Hankson, L. (1980). An ecology risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001.
Hu, B. F., Shao, S., Ni, H., et al. (2020). Current status, spatial features, health risks, and potential driving factors of soil heavy metal pollution in China at Province level. Environmental Pollution, 266, 114–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114961
Huang, Y., Teng, Y., Zhang, N., et al. (2018). Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in the Soil-Panax notoginseng system in Yunnan Province, China. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 24(5), 1312–1326. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2017.1411782
JECFA. (2003). Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization Geneva[EB/01]. http://apps.who.int/food-additives-contaminants-jecfa-database/search.aspx, 06–27.
Li, H., Su, W. W., Ye, Y. L., & He, Z. S. (2012). Research on heavy metal pollution in soil within the upper reaches of Lancang River. Guangdong Trace Elements Science, 19, 32–38.
Li, Y. M., Jian-hua, M. A., De-xin, L. I. U., et al. (2015). Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of urban soils in Kaifeng city. China. Environmental Science, 36, 1037–1044.
Li, Z. L., Xie, Q., Zeng, Z., et al. (2021). Enrichment and migration of heavy metals in Mangrove soil-plant system from sea promenade in Zhanjiang. Tropical Geography, 41, 398–409.
Liu, J. J., Wang, Y. T., Qiu, L., et al. (2014). Saponins of Panax notoginseng: chemistry, cellular targets and therapeutic opportunities in cardiovascular diseases. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs, 23, 523–39. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.2014.892582
Liu, Y., Yang, M. Q., Wang, T., et al. (2018). Distribution characteristics of soil heavy metals in Panax notoginseng growing areas in Yunnan Province and their relationship with the contents in Panax notoginseng taproots and leaves. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 46, 298–302.
Ma, L. J., Ma, N., Wang, B. Y., et al. (2021). Ginsenoside distribution in different architectural components of Panax notoginseng inflorescence and infructescence. Journal of Pharmaceutical Biomedical Analysis, 203, 114221.
Ou, X. H., Cui, X. M., Zhu, D. W., et al. (2020). Lowering nitrogen and increasing potassium application level can improve the yield and quality of Panax notoginseng. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11, 595095. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.595095
Ou, X. H., Wang, L., Guo, L. P., et al. (2016). Soil-plant metal relations in Panax notoginseng: An ecosystem health risk assessment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(11), 1089.
Pang, R. L., Wang, S. Y., Wang, R. P., et al. (2019). Study on the enrichment and migration characteristics of heavy metals in soil-grapevine system. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 35, 515–521.
Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (2020 Edition). Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 12–13.
Shi, Y. (2019). Study on the mechanism of K fertilizer decreasing Cd accumulation of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen. Kunming University of Science and Technology, 20.
Stankwitz, C., Kaste, J. M., & Friedland, A. J. (2012). Threshold increases in soil lead and mercury from tropospheric deposition across an elevational gradient. Environmental Science & Technology, 46, 8061–8068. https://doi.org/10.1021/es204208w
Street, R. A., Kulkarni, M. G., Stirk, W. A., et al. (2007). Toxicity of metal elements on germination and seedling growth of widely used medicinal plants belonging to Hyacinthaceae. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 79(4), 371–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-007-9237-0
Tao, L., Bao, L., Liu, Y., et al. (2018). Absorption and accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in Panax notoginseng from different regions of Yunnan. Chinese of Agricultural and Science Bulletin, 34, 74–81.
US EPA (2000) Region 3 Hazardous Site Division. Risk-Based Concentration Table FAQs. PA USA, 12,154–165.
US Epa National Center for Environmental Assessment. (1986). Guidelines for the Health Risk Assessment of Chemical Mixtures. Federal Register, 51, 34014–34025.
Wang, N. (2019). Research analysis based on the sources of heavy metal pollution in agricultural soil. China Metal Bulletin, 01, 289–290.
Wang, Y., Tu, L., Li, Y. B., et al. (2016). Notoginsenoside R1 protects against neonatal cerebral hypoxic-ischemic injury through Estrogen receptor-dependent activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways. Journal of Pharmacology Experimental Therapeutics, 357, 591–605. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.115.230359
Xia, P. G., Guo, H. B., Zhao, H. G., et al. (2016). Optimal fertilizer application for Panax notoginseng and effect of soil water on root rot disease and saponin contents. Journal of Ginseng Research, 40, 38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2015.04.003
Yang, C. M., Chien, M. Y., Chao, P. C., et al. (2021). Investigation of toxic heavy metals content and estimation of potential health risks in Chinese herbal medicine. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 412, 125–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125142
Yang, M. Q., Liu, Y., Huang, W. H., et al. (2018). Accumulation of heavy metal elements in soil and Panax notoginseng in new producing areas. Chinese Agriculture Science Bulletin, 34, 91–97.
Yang, Z. J., Liu, G. Z., Zhang, G. H., Yan, J., Dong, Y., Lu, Y. C., Fan, W., Hao, B., et al. (2021). The chromosome-scale high-quality genome assembly of Panax notoginseng provides insight into dencichine biosynthesis. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 19(5), 869–871. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13558
Zhang, J. (2018). Determination of heavy metals in Panax notoginseng by ICP-MS. Guangzhou Chemistry Industry, 46, 77–79.
Zhang, J. Y., Cun, Z., & Chen, J. W. (2020). Photosynthetic performance and photosynthesis-related gene expression coordinated in a shade-tolerant species Panax notoginseng under nitrogen regimes. BMC Plant Biology, 20, 273. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02434-z
Zhang, X. M., Zhang, X. Y., Zhong, T. Y., et al. (2014). Study on the enrichment and spatial distribution of heavy metals in farmland soils in China. Environmental Sciences, 35(02), 692–703.
Zhang, Y., Zheng, Y., Xia, P., et al. (2019). Impact of continuous Panax notoginseng plantation on soil microbial and biochemical properties. Scientific Reports, 9, 13205. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49625-9
Zhao, L. H., Yang, M. H., Yang, Y. H., et al. (2014). Current situation analysis and countermeasures on contamination of heavy metal in traditional Chinese medicinal materials in China. Chinese Traditional Herbal Drugs, 45, 1199–1206.
Zheng, N., Wang, Q., Zhang, X., et al. (2007). Population health risk due to dietary intake of heavy metals in the industrial area of Huludao city, China[J]. Science of Total Environment, 387, 96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.07.044
Zhou, J., Wang, Z., Sun, T., Zhang, H., & Zhang, X. (2016). Mercury in terrestrial forested systems with highly elevated mercury deposition in southwestern China: The risk to insects and potential release from wildfires. Environmental Pollution, 212, 188–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.01.003
Zhu, M. L., Jiang, Y., Cui, B., et al. (2016). Cadmium accumulation in Panax notoginseng: levels, affecting factors and the non-carcinogenic health risk. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 38, 423–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9728-6
Zhu, M. L., Zeng, X. C., Jiang, Y. X., et al. (2017). Determination of arsenic speciation and the possible source of methylated arsenic in Panax notoginseng. Chemosphere, 168, 1677–1683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.093
Zhu, Y., Teng, Y., Zhang, M. Y., et al. (2015). Pollutant accumulation and microbiological characteristics change in notoginseng-planting soils. Soils, 47, 121–127.
Funding
This research was funded by the Yunnan Provincial Key Programs of Yunnan Eco-friendly Food International Cooperation Research Center project (grant number 2019ZG00901-04), the Major Science and Technique Programs in Yunnan Province (grant numbers 202102AE090042-02 and 202102AA310048) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 31960634).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WF and JY conceived and designed the experiments; ZH, ZS, CL and HS performed the experiments and analyzed the data; SH, GL and WD assisted in design some experiments and data analysis; WF and ZH wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Shen, Z., Liu, C. et al. Characteristics of heavy metal accumulation and risk assessment in understory Panax notoginseng planting system. Environ Geochem Health 45, 9029–9040 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01392-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01392-9