Abstract
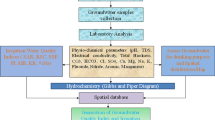
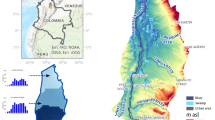
This article aimed to estimate the local underground water associations, which will, in turn, be applied to discuss the location of each underground water cluster in the flow system. Additionally, this investigation intended to evaluate underground water's aptness from aquifers of the study area for domestic agricultural activities and the prime sources of alteration in the water chemistry. Geographically, the region does not have the privilege of the river (except the Yamuna in the eastern part) running through it and thus, has to rely heavily on groundwater. Therefore, it is necessary to study the groundwater characteristics in this region. This investigation manifested two sub-surface water associations (groups) showing two prime underground water types in the study area: the calcium-magnesium-bicarbonate water-types, groups (clusters) 1 member; and the sodium-bicarbonate-chloride water-types consisting of Group 2 members during post-monsoon and pre-monsoon periods. Group 1 is typical of underground water in recharge regions of the underground water flow system. It is the cleanest underground water type in part except for a few groundwater samples. The highest mean salinity was vested in group 2, the signature of underground waters in discharge regions of the underground water flow system. This investigation observes that three principal elements controlled the hydro-chemistry of underground water in the study area: chemical fertilizers from farms, carbonate mineral weathering, calcite, fluorite, silicate minerals, and exchange of cations in the region. All the underground water groups had high sodium (Na) concentrations and will cause the Na-hazard when applied for agricultural activities. Most samples of groups 1 and 2 were within the class II and I area of Doneen's plot during both periods and were therefore acceptable for agricultural activities in the investigation region.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data, models, or codes generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
Aly, A. A., Al-Omran, A. M., & Alharby, M. M. (2015). The water quality index and hydrochemical characterization of groundwater resources in Hafar Albatin, Saudi Arabia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8, 4177–4190.
Anon. (2011). 71-City water-excreta survey, 2005–06. Centre for Science and Environment.
Apambire, W. B., Boyle, D. R., & Michel, F. A. (1997). Geochemistry, genesis, and health implications of fluoriferous groundwaters in the upper regions of Ghana. Environmental Geology, 331, 13–24.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2005). Geochemistry, groundwater, and pollution (2nd ed.). Balkema.
Astel, A., Tsakovski, S., Barbieri, P., & Simeonov, V. (2007). Comparison of self-organizing maps classification approach with cluster and principal components analysis for large environmental data sets. Journal of Water Research, 41(2007), 4566–4578.
Arora, P. (1991). Hydrochemical and hydro-geological studies of Faridkot and adjoining areas in Punjab State, India. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Science, Punjab Univ., Chandigarh.
Banoeng-Yakubo, B., Yidana, S. M., & Nti, E. (2009). Hydrochemical modeling of groundwater using multivariate statistical methods—the Volta Region, Ghana. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 131, 55–63.
Barbiéro, L., & Van Vliet-Lanoe, B. (1998). The alkali soils of the middle Niger valley: Origins, formation, and present evolution. Geoderma, 84, 323–343.
Barbiéro, L., Valles, V., & Régeard, A. (1995). Pre´cipitation de la fluorine et controle ge´ochimique du calcium dans des sols alcalins du NigerComptes Rendue, 321 Se´rie IIa (pp. 1147–1154). Academie des Sciences.
Bhattacharya, P., & Jacks, G. (1995a). Accumulation of fluoride in soil and groundwater in the semi-arid region of Nagaur District, Central Rajasthan, India. Abstract Volume, Miljo¨ - geologisk Konferans-95. University of Bergen.
Bhattacharya, P., Jacks, G. (1995b). Possible occurrences of sepiolite in soil environment and its role in accumulation and mobility of fluorine in a semiarid region of Nagaur District, Rajasthan, Western India. Nordic Society of Clay Research, report no. 10, 5–6.
BIS. (2003). Indian standard specification for drinking water. Is: 10500. Bureau of Indian Standards.
Boyle, D. R. (1976). The geochemistry of fluorine and its application in mineral exploration. Ph.D. thesis, Imperial College Science and Technology, Univ. of London, London.
Brindha, K., Rajesh, R., Murugan, R., & Elango, L. (2011). Fluoride contamination in groundwater in parts of Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 172, 481–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1348-0
Brindha, K., Pavelic, P., Sotoukee, T., Douangsavanh, S., & Elango, L. (2017). Geochemical characteristics and groundwater quality in the Vientiane plain, Laos. Exposure and Health, 9, 89–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0224-8
Bundschuh, J., Farías, B., Martin, R., Storniolo, A., Bhattacharya, P., Cortes, J., Bonorino, G., & Albouy, R. (2004). Groundwater arsenic in the Chaco-Pampean Plain, Argentina: A Case study from Robles county, Santiago del Estero Province. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 231–243.
Castro, E., Schulz, C., Marino, E. (1997). El agua potable en la Provincia de La Pampa. In Consecuencia por la Presencia de fluor y arsenic, Actas II Reunion Geologia Ambiental, San Salvador de Jujuy, Argentina in Spanish.
CGWB. (2012). Groundwater year book India. Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water Resources Government of India.
CGWB. (2014). Dynamics of groundwater resources of India. Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation, Government of India.
CGWB. (2016). Groundwater year book India. Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water Resources Government of India.
CGWB. (2017). Groundwater year book India. Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water Resources Government of India.
Chandrawanshi, C. K., & Patel, K. S. (1999). Fluoride deposition in Central India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 55, 251–265.
Chatterjee, M. K., & Mohabey, N. K. (1998). Potential fluorosis problems around Chandidongri, Madhya Pradesh, India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 20, 1–4.
Chen, J., Li, J., Zhang, Z., & Ni, S. (2014). Long-term groundwater variations in Northwest India from satellite gravity measurements. Global and Planetary Change, 116, 130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2014.02.007
Cloutier, V., Lefebvre, R., Therrien, R., & Savard, M. M. (2008). Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system. Journal of Hydrology, 353, 294–313.
Dapaah-Siakwan, S., & Gyau-Boakye, P. (2000). Hydrogeologic framework and borehole yields in Ghana. Hydrogeology Journal, 8, 405–416.
Das, D. K., Burman, G. K., & Kidwai, A. L. (1981). Chemical composition of monsoon rainwater over Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh during 1977 and 1978. Mausam, 32, 221–228.
Datta, P. S., Tyagi, S. K., Mookerjee, P., Bhattacharya, S. K., Gupta, N., & Bhatnagar, P. D. (1999). Groundwater NO3 and F contamination processes in Pushkar Valley, Rajasthan, as reflected from 18-O isotopic signature and 3H recharge studies. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 56, 209–219.
Davis, S. N., & Dewiest, R. J. M. (1966). Hydrogeology (p. 463). Wiley.
Dinesh, D., Bhat, M. A., Grewal, K. S., & Sheoran, H. S. (2017). (2017) Mineralogy of soils of major geomorphic units of northeastern Haryana, India. Journal of Applied and Natural Science, 9(2), 924–934.
Domenico, P. A., & Schwartz, F. W. (1990). Physical and chemical hydrogeology (p. 1990). Wiley.
Ghesquière, O., Walter, J., Chesnaux, R., & Rouleau, A. (2015). Scenarios of groundwater chemical evolution in a region of the Canadian shield based on multivariate statistical analysis. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies, 4, 246–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2015.06.004
GSI. (2012). Geological Survey of India (updated up to March, 2012) (p. 2012). Northern Region Briefing Book.
Güler, C., & Thyne, G. D. (2004). Hydrologic and geologic factors controlling surface and groundwater chemistry in the Indian Wells-Owens Valley area, southeastern California, USA. Journal of Hydrology, 285, 177–198.
Güler, C., Thyne, G., McCray, J., & Turner, K. (2002). Evaluation and graphical and multivariate statistical methods for classification of water chemistry data. Hydrogeology Journal, 10, 455–474.
Guo, H., & Wang, Y. (2004). Hydrogeochemical processes in shallow quaternary aquifers from the northern part of the Datong Basin, China. Applied Geochemistry, 19(1), 19–27.
Handa, B. K. (1975). Geochemistry and genesis of fluoride-containing groundwaters in India. Ground Water, 13, 275–281.
HARSAC. (2014). Geology map of Haryana. Haryana Satellite Applications Center. www.hrsdi.in/link/thematic/GeologyMap.pdf.
Hem, J. D. (1991). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water (3rd ed.). Scientific Publishers.
Hounslow, A. W. (1995). Water quality data: Analysis and interpretation (p. 396). CRC Lewis Publisher.
Jacks, G., & Sharma, V. P. (1995). Geochemistry of calcic horizons in relation to hillslope processes, southern India. Geoderma, 67, 203–214.
Jacks, G., Rajagopalan, K., Alveteg, T., & Jönsson, M. (1993). Genesis of high-F groundwaters Southern India. Applied Geochemistry, 8(Suppl. 2), 241–244.
Jacks, G., Bhattacharya, P., Chaudhary, V., & Singh, K. P. (2005). Controls on the genesis of some high-fluoride groundwaters in India. Applied Geochemistry, 20, 221–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.07.002
Jain, M., Kulshrestha, U. C., Sarkar, A. K., & Parashar, D. C. (2000). Influence of crustal aerosols on wet deposition at urban and rural sites in India. Atmospheric Environment, 34, 5129–5137.
Jha, S. K., Nayak, A. K., Sharma, Y. K., Mishra, V. K., & Sharma, D. K. (2008). Fluoride accumulation in soil and vegetation in the vicinity of brickfields. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 80, 369–373.
Kaiser, H. F. (1960). The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 20, 141–151.
Kalpana, L., Brindha, K., & Elango, L. (2019). FIMAR: A new fluoride index to mitigate geogenic contamination by managed aquifer recharge. Chemosphere, 220, 381–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.084
Khademi, H., & Mermut, A. R. (1999). Submicroscopy and stable isotope geochemistry of carbonates and associated palygorskite in Iranian Aridisols. European Journal of Soil Science, 50, 207–216.
Kortatsi, B. K. (2007). Hydrochemical framework of groundwater in the Ankobra Basin, Ghana. Aquatic Geochemistry, 13, 41–74.
Kumar, R. (2018). Groundwater conditions and water conservation. Ground Water Cell Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
Long, D., Chen, X., Scanlon, B. R., Wada, Y., Hong, Y., Singh, V. P., Chen, Y., Wang, C., Han, Z., & Yang, W. (2016). Have GRACE satellites overestimated groundwater depletion in the Northwest India Aquifer? Scientific Reports, 6, 24398. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24398
Madhavan, N., & Subramanian, V. (2002). Fluoride in fractioned soil samples of Ajmer district, Rajasthan. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 4, 821–822.
Manikandan, S., Chidambaram, S., Ramanathan, A. L., Prasanna, M. V., Karmegam, U., Singaraja, C., Paramaguru, P., & Jainab, L. (2012). A study on the high fluoride concentration in the magnesium-rich water of hard rock aquifer in Krishnagiri district, Tamilnadu, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0752-x
Morton, M. C. (2019). Widespread contamination found in northwest India’s groundwater. Eos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019EO130161
Mustapha, A., & Aris, A. Z. (2012). Multivariate statistical analysis and environmental modelling of heavy metals pollution by industries. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 21, 1359–1367.
Narmatha, T., Jeyaseelan, A., Mohan, S. P., & Ram Mohan, V. (2011). Integrating multivariate statistical analysis with GIS for groundwater in Pambar Sub Basin, Tamil Nadu, India. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences, 2(2), 392.
Paquet, H., & Millot, G. (1973). Geochemical evolution of clay minerals in the weathered products in soils of the Mediterranean climate. In J. M. Serratosa (Ed.), Proc. Internat. Kaolin Symp. 1972 (Madrid) (pp. 199–206).
Parkhurst, D. L., Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). Phreeqc2 user’s manual and program. USGS, Reston, Va.
Patra, R. C., Dwivedi, S. K., Bhardwa, J. B., & Swarup, D. (2000). Industrial fluorosis in cattle and buffalo around Udaipur, India. Science of the Total Environment, 253, 145–150.
Paul, R., Brindha, K., Gowrisankar, G., Tan, M. L., & Singh, M. K. (2019). Identification of hydrogeochemical processes controlling groundwater quality in Tripura, Northeast India using evaluation indices, GIS, and multivariate statistical methods. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78, 470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8479-6
Piper, A. M. (1944). A graphical procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Transactions—American Geophysical Union, 25, 914–923.
Ramamohana-Rao, N. V., Suryaprakasa-Rao, K., & Schuiling, R. D. (1993). Fluorine distribution in waters of Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geology, 21, 84–89.
Rao, N. S. (1997). The occurrence and behavior of the groundwater in the lower Vamsadhara basin, India. Hydrol. Sci. J./J. Sciences Hydrologique, 42, 877–892.
Rao, S. N., & Devadas, J. D. (2003). Fluoride incidence in groundwater in an area of Peninsular India. Environmental Geology, 45, 243–251.
Rao, S. N., Rao, K. G., & Devadas, J. D. (1998). Variation of fluoride in groundwaters of crystalline terrain. Journal of Environmental Hydrology, 6, 1–5.
Ravish, S., Setia, B., & Deswal, S. (2019). Monitoring of pre-and post-monsoon groundwater quality of the northeastern Haryana region using GIS. Environmental Technology. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1619841
Reddy, T. N., & Raj, P. (1997). Hydro-geological conditions and optimum well discharges in granitic terrain in parts of Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 49, 61–74.
Rodell, M., Velicogna, I., & Famiglietti, J. S. (2009). Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in India. Nature Letters, 460, 999–1002. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08238
Rout, C., Bhattacharya, G. S., Setia, B. (2016). Monitoring of groundwater quality of Nalagarh and Baddi industrial areas of Solan district Himachal Pradesh, India. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, Maharishi Markandeshwar Univ., Mullana Ambala, Haryana, (pp. 1–303).
Sahu, N. K., & Karim, M. A. (1989). Fluoride incidence in natural waters, Gujarat. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 6, 450–456.
Saleh, A., Al-Ruwih, F., & Shehata, M. (1999). Hydrogeochemical processes operating within the main aquifers of Kuwait. Journal of Arid Environments, 42, 195–209.
Samantara, M. K., Padhi, R. K., Sowmya, M., Kumaran, P., & Satpathy, K. K. (2017). Heavy metal contamination, major ion chemistry and appraisal of the groundwater status in coastal aquifer, Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu, India. Ground Water for Sustainable Development, 5, 49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2017.04.001.
Santaren, J., Sanz, J., & Ruiz-Hitzky, E. (1990). Structural Fluorine in Sepiolite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 38, 63–68.
Shepard, D. (1968) A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In Proceedings of the 1968 ACM national conference, (pp 517–524).
Satsangi, G. R., Lakhani, A., Khare, P., Singh, S. P., Kumari, S. S., & Srivastava, S. S. (1998). Composition of rainwater at a semi-arid rural site in India. Atmospheric Environment, 32, 3783–3793.
Satsangi, G. R., Lakhani, A., Khare, P., Singh, S. P., Kumari, S. S., & Srivastava, S. S. (2002). Measurements of major ion concentrations in settled coarse particles and aerosols at a semiarid rural site in India. Environment International, 28, 1–7.
Sharma, S. C. (1999). Report from central ground water board of India. Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) of India.
Singer, A., Kirsten, W., & Bühmann, C. (1995). Fibrous clay minerals in the soils of Namaqualand, South Africa: Characteristics and formation. Geoderma, 66, 43–70.
Singh, S. P., Khare, P., Satsangi, G. S., Lakhani, A., Kumari, S. S., & Srivastava, S. S. (2001). Rainwater composition at a regional representative site of a semi-arid region of India. Water, Air and Soil Pollutions, 127, 93–108.
Todd, D. K., & Mays, L. W. (2005). Groundwater hydrology (p. 636). Wiley.
Torres-Ruiz, J., Lopez-Galindo, A., Gonzalez-Lopez, J. M., & Delgado, A. (1994). Geochemistry of Spanish sepiolite palygorskite deposits. Chemical Geology, 112, 221–245.
Tracy, P. W., Robbins, C. W., & Lewis, G. C. (1984). Fluorite precipitation in a calcareous soil irrigated with high fluoride water. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 48, 1013–1016.
USSL. (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. USDA, Handbook 60, USDA, Washington, DCDC, 147.
Viero, A. P., Roisenberg, C., Roisenberg, A., & Vigo, A. (2009). The origin of fluoride in the granitic aquifer of Porto Alegre, Southern Brazil. Environmental Geology, 56, 1707–1719.
WHO. (2011). Guidelines for drinking water (4th ed.). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Yidana, S. M. (2008). Groundwater resources management for productive uses in the Afram Plains area, Ghana. Ph.D. thesis, Montclair State Univ., Montclair, N.J.
Yidana, S. M. (2009). The hydrochemical framework of surface water basins in southern Ghana. Environmental Geology, 57, 789–796.
Yidana, S. M., & Yidana, A. (2010). An assessment of the origin and variation of groundwater salinity in southeastern Ghana. Journal of Environment and Earth Science, 616, 1259–1273.
Yidana, S. M., Ophori, D., & Banoeng-Yakubo, B. (2008a). Hydro-geological and hydrochemical characterization of the Voltaian Basin: The Afram Plains area, Ghana. Environmental Geology, 53, 1213–1223.
Yidana, S. M., Ophori, D., & Banoeng-Yakubo, B. (2008b). Hydrochemical evaluation of the Voltaian system—the Afram Plains area, Ghana. Journal of Environmental Management, 88, 697–707.
Acknowledgements
We thank the funding agency National Institute of Technology (Govt. of India), Kurukshetra, Haryana, India.
Funding
On behalf of all the authors, the corresponding author wishes to manifest his gratitude to the National Institute of Technology, Kurukshetra, Haryana, India, for funding this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The corresponding author SR performed background research and conducted the study. SR wrote the manuscript and prepared the figures and tables. The co-authors BS and SD supervised the concerning research and aided in data analysis. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The corresponding author states no conflict of interest on behalf of all authors.
Consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Consent to publish
Not Applicable.
Ethical approval
Not Applicable.
Research involving human and animal participants
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravish, S., Setia, B. & Deswal, S. Classification of groundwater using multivariate statistical methods: a case study from a part of Haryana, northwestern India. Environ Geochem Health 45, 1757–1791 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01288-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01288-8