Abstract
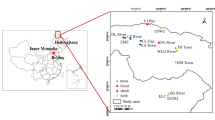
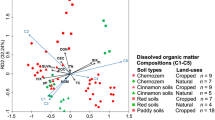
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) plays an important role in promoting or suppressing methylmercury (MeHg) production in wetlands. However, the effects of DOM spectral characteristics on MeHg levels remain poorly understood in boreal peatlands in Northeast China, where is undergoing remarkable climate warming. In the present work, soil samples were collected from 22 peatlands in the Greater Khingan Mountains (GKM) to test the hypothesis that DOM spectral properties control MeHg levels. DOM was characterized by UV–Vis absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy; the three-dimensional fluorescence excitation-emission matrix (EEM) was used to unveil the origin of DOM. The average total mercury (THg) and MeHg contents were 112.76 µg/kg and 12.43 µg/kg across all peatlands, respectively. There was a significantly positive correlation between MeHg and the longitude spanning the range from 120 to 123°E (p < 0.05). Proportions of MeHg to THg (%MeHg), 12.3% on average, were positively correlated with DOM humification degree at p < 0.05 level. Protein-like components of DOM (P-like) were negatively related to %MeHg. DOM had positive effects on THg, and P-like components, HIX and BIX can negatively affect THg as well as MeHg. Our findings demonstrate that the spectral characteristics of DOM in soil are crucial to the content of methyl mercury in the GKM soil.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Bachand, P. A., Bachand, S. M., Fleck, J. A., Alpers, C. N., Stephenson, M., & Windham-Myers, L. (2014). Methylmercury production in and export from agricultural wetlands in California, USA: The need to account for physical transport processes into and out of the root zone. Science of the Total Environment, 472, 957–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.086
Barkay, T., Kroer, N., & Poulain, A. J. (2011). Some like it cold: Microbial transformations of mercury in polar regions. Polar Research, 30(1), 15469. https://doi.org/10.3402/polar.v30i0.15469
Birdwell, J. E., & Engel, A. S. (2010). Characterization of dissolved organic matter in cave and spring waters using UV–Vis absorbance and fluorescence spectroscopy. Organic Geochemistry, 41(3), 270–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.11.002
Bracho, R., Natali, S., Pegoraro, E., Crummer, K. G., Schädel, C., Celis, G., Hale, L., Wu, L., Yin, H., & Tiedje, J. M. (2016). Temperature sensitivity of organic matter decomposition of permafrost-region soils during laboratory incubations. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 97, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.02.008
Bravo, A. G., Bouchet, S., Tolu, J., Björn, E., Mateos-Rivera, A., & Bertilsson, S. (2017). Molecular composition of organic matter controls methylmercury formation in boreal lakes. Nature Communications, 8(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14255
Celo, V., Lean, D. R., & Scott, S. L. (2006). Abiotic methylation of mercury in the aquatic environment. Science of the Total Environment, 368(1), 126–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.09.043
Chen, W., Westerhoff, P., Leenheer, J. A., & Booksh, K. (2003). Fluorescence excitation−emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environmental Science and Technology, 37(24), 5701–5710. https://doi.org/10.1021/es034354c
Corrales, J., Naja, G. M., Dziuba, C., Rivero, R. G., & Orem, W. (2011). Sulfate threshold target to control methylmercury levels in wetland ecosystems. Science of the Total Environment, 409(11), 2156–2162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.02.030
Cory, R. M., McKnight, D. M., Chin, Y. P., Miller, P., & Jaros, C. L. (2007). Chemical characteristics of fulvic acids from Arctic surface waters: Microbial contributions and photochemical transformations. Journal of Geophysical Research Biogeosciences. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JG000343
Feng, X., Qiu, G., Fu, X., He, T., Li, P., & Wang, S. (2009). Mercury pollution in the environment. Chemical Progress, 21(Z1), 436–457.
Gao, Y., & zhao, H., Gao, F., Zhu, H., Qu, H. and Zhao, F. (2016). Climate change trend in future and its influence on wetlands in the greater Khingan Mountains. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 38(01), 47–56.
Gong, P., Wang, X.-P., Xue, Y.-G., Xu, B.-Q., & Yao, T.-D. (2014). Mercury distribution in the foliage and soil profiles of the Tibetan forest: Processes and implications for regional cycling. Environmental Pollution, 188, 94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.01.020
Graham, A. M., Aiken, G. R., & Gilmour, C. C. (2012). Dissolved organic matter enhances microbial mercury methylation under sulfidic conditions. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(5), 2715–2723. https://doi.org/10.1021/es203658f
Halbach, K., Mikkelsen, Ø., Berg, T., & Steinnes, E. (2017). The presence of mercury and other trace metals in surface soils in the Norwegian Arctic. Chemosphere, 188, 567–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.012
He, R., Xu, R., & Wei, C. (2015). Spectral characterization of dissolved organic matter in bio-treated effluent of coking wastewater. Environmental Chemistry, 34(1), 129–136.
He, W., & Hur, J. (2015). Conservative behavior of fluorescence EEM-PARAFAC components in resin fractionation processes and its applicability for characterizing dissolved organic matter. Water Research, 83, 217–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.06.044
He, X., Xi, B., Wei, Z., Li, M., Geng, C., Yu, H., & Liu, H. (2010). Three-dimensional excitation emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopic characterization of complexation between mercury(II) and dissolved organic matter extracted from landfill leachate. Analytical Chemistry, 38(10), 1417–1422.
Herrero Ortega, S., Catalán, N., Björn, E., Gröntoft, H., Hilmarsson, T. G., Bertilsson, S., Wu, P., Bishop, K., Levanoni, O., & Bravo, A. G. (2018). High methylmercury formation in ponds fueled by fresh humic and algal derived organic matter. Limnology and Oceanography, 63(S1), S44–S53. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10722
Heyes, A., Moore, T., Rudd, J. W., & Dugoua, J. (2000). Methyl mercury in pristine and impounded boreal peatlands, experimental Lakes Area, Ontario. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 57(11), 2211–2222. https://doi.org/10.1139/f00-197
Hill, J. R., O’Driscoll, N. J., & Lean, D. R. (2009). Size distribution of methylmercury associated with particulate and dissolved organic matter in freshwaters. Science of the Total Environment, 408(2), 408–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.09.030
Hudelson, K. E., Drevnick, P. E., Wang, F., Armstrong, D., & Fisk, A. T. (2020). Mercury methylation and demethylation potentials in Arctic lake sediments. Chemosphere, 248, 126001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126001
Huguet, A., Vacher, L., Relexans, S., Saubusse, S., Froidefond, J.-M., & Parlanti, E. (2009). Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Organic Geochemistry, 40(6), 706–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.03.002
Jiang, T., Bravo, A. G., Skyllberg, U., Björn, E., Wang, D., Yan, H., & Green, N. W. (2018). Influence of dissolved organic matter (DOM) characteristics on dissolved mercury (Hg) species composition in sediment porewater of lakes from southwest China. Water Research, 146, 146–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.08.054
Klapstein, S. J., Ziegler, S. E., Risk, D. A., & O’Driscoll, N. J. (2018). Assessing the utility of dissolved organic matter photoreactivity as a predictor of in situ methylmercury concentration. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 68, 160–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.02.025
Lehnherr, I., & St. Louis, V.L., Emmerton, C.A., Barker, J.D. and Kirk, J.L. (2012). Methylmercury cycling in high Arctic wetland ponds: Sources and sinks. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(19), 10514–10522. https://doi.org/10.1021/es300576
Lescord, G. L., Emilson, E. J., Johnston, T. A., Branfireun, B. A., & Gunn, J. M. (2018). Optical properties of dissolved organic matter and their relation to mercury concentrations in water and biota across a remote freshwater drainage basin. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(6), 3344–3353. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b05348
Liess, S., Snyder, P. K., & Harding, K. J. (2012). The effects of boreal forest expansion on the summer Arctic frontal zone. Climate Dynamics, 38(9), 1805–1827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-011-1064-7
Liu, R., Wang, Q., Lu, X., Zhuangwei, M., & Fang, F. (2002). Mercury in the peat bog ecosystem in the Xiaoxing ’an Mountain in China. Environmental Science, 23(4), 102–106.
Liu, J., & Ding, Z. (2007). Progress in research on mercury methylation in environment. Earth and Environment, 03, 215–222.
Liu, Y., Chai, X., Hao, Y., Gao, X., Lu, Z., Zhao, Y., Zhang, J., & Cai, M. (2015). Total mercury and methylmercury distributions in surface sediments from Kongsfjorden, Svalbard, Norwegian Arctic. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(11), 8603–8610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3942-0
MacMillan, G. A., Girard, C., Chételat, J., Laurion, I., & Amyot, M. (2015). High methylmercury in Arctic and subarctic ponds is related to nutrient levels in the warming eastern Canadian Arctic. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(13), 7743–7753. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00763
Mitchell, C. P., & Gilmour, C. C. (2008). Methylmercury production in a chesapeake bay salt marsh. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeo Sciences, 113(2), 1.
Mu, C., Zhang, F., Chen, X., Ge, S., Mu, M., Jia, L., Wu, Q., & Zhang, T. (2019). Carbon and mercury export from the Arctic rivers and response to permafrost degradation. Water Research, 161, 54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.082
Ohno, T. (2002). Fluorescence inner-filtering correction for determining the humification index of dissolved organic matter. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(4), 742–746. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0155276
Olson, C., Jiskra, M., Biester, H., Chow, J., & Obrist, D. (2018). Mercury in active-layer tundra soils of alaska: concentrations, pools, origins and spatial distribution. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 32(7), 1058–1073. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017GB005840
Ouellet, J.-F., Lucotte, M., Teisserenc, R., Paquet, S., & Canuel, R. (2009). Lignin biomarkers as tracers of mercury sources in lakes water column. Biogeochemistry, 94(2), 123–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-009-9314-z
Paranjape, A. R., & Hall, B. D. (2017). Recent advances in the study of mercury methylation in aquatic systems. Facets, 2(1), 85–119. https://doi.org/10.1139/facets-2016-0027
Pedersen, T., & Calvert, S. (1990). Anoxia vs productivity: What controls the formation of organic-carbon-rich sediments and sedimentary rocks? AAPG Bulletin, 74(4), 454–466. https://doi.org/10.1306/0C9B232B-1710-11D7-8645000102C1865D
Ravichandran, M. (2004). Interactions between mercury and dissolved organic matter––a review. Chemosphere, 55(3), 319–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.11.011
Rocha, J. C., Junior, É. S., Zara, L. F., Rosa, A. H., dos Santos, A., & Burba, P. (2000). Reduction of mercury (II) by tropical river humic substances (Rio Negro)—a possible process of the mercury cycle in Brazil. Talanta, 53(3), 551–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(00)00532-4
Schaefer, J. K., & Morel, F. M. (2009). High methylation rates of mercury bound to cysteine by Geobacter sulfurreducens. Nature Geoscience, 2(2), 123–126. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo412
Schaefer, J. K., Rocks, S. S., Zheng, W., Liang, L., Gu, B., & Morel, F. M. (2011). Active transport, substrate specificity, and methylation of Hg (II) in anaerobic bacteria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(21), 8714–8719. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1105781108
Schartup, A. T., Mason, R. P., Balcom, P. H., Hollweg, T. A., & Chen, C. Y. (2013). Methylmercury production in estuarine sediments: Role of organic matter. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(2), 695–700. https://doi.org/10.1021/es302566w
Schuster, P. F., Schaefer, K. M., Aiken, G. R., Antweiler, R. C., Dewild, J. F., Gryziec, J. D., Gusmeroli, A., Hugelius, G., Jafarov, E., Krabbenhoft, D. P., Liu, L., Herman-Mercer, N., Mu, C., Roth, D. A., Schaefer, T., Striegl, R. G., Wickland, K. P., & Zhang, T. (2018). Permafrost stores a globally significant amount of mercury. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(3), 1463–1471. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL075571
Semeraro, T., Giannuzzi, C., Beccarisi, L., Aretano, R., De Marco, A., Pasimeni, M. R., Zurlini, G., & Petrosillo, I. (2015). A constructed treatment wetland as an opportunity to enhance biodiversity and ecosystem services. Ecological Engineering, 82, 517–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.05.042
St. Pierre, K., Chétélat, J., Yumvihoze, E. and Poulain, A. (2014). Temperature and the sulfur cycle control monomethylmercury cycling in high Arctic coastal marine sediments from Allen Bay, Nunavut Canada. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(5), 2680–2687. https://doi.org/10.1021/es405253g
Van Breemen, N. (1995). How sphagnum bogs down other plants. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 10(7), 270–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-5347(95)90007-1
Vasilevich, R. S., Beznosikov, V. A., Lodygin, E. D., & Kondratenok, B. M. (2014). Complexation of mercury(II) ions with humic acids in tundra soils. Eurasian Soil Science, 47(3), 162–172. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229314030089
Wallschläger, D., Desai, M. V., & Wilken, R.-D. (1996). The role of humic substances in the aqueous mobilization of mercury from contaminated floodplain soils. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 90(3), 507–520. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00282665
Wang, S., Qin, J., Xie, B., Liu, C., Chen, Y., Tang, Y., & Sun, H. (2020). Spectroscopic characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in Zoige alpine peatland soils along a soil moisture gradient. Ecological Environmental Science, 29(04), 676–685. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2020.04.005
Wang, Q., Shen, W., & Ma, Z. (2000). Estimation of mercury emission from coal combustion in China. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 2711–2713. https://doi.org/10.1021/es990774j
Wang, X., Bao, Z., Lin, C.-J., Yuan, W., & Feng, X. (2016). Assessment of global mercury deposition through litterfall. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(16), 8548–8557. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b06351
Waples, J. S., Nagy, K. L., Aiken, G. R., & Ryan, J. N. (2005). Dissolution of cinnabar (HgS) in the presence of natural organic matter. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(6), 1575–1588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2004.09.029
Weber, J. H. (1993). Review of possible paths for abiotic methylation of mercury (II) in the aquatic environment. Chemosphere, 26(11), 2063–2077. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(93)90032-Z
Yang, Y., & Wang, D. (2006). Research progress in temporal and spatial distribution of atmospheric mercury. Sichuan Environment, 25(6), 91–95. https://doi.org/10.14034/j.cnki.schj.2006.06.024
Yang, Z., Fang, W., Lu, X., Sheng, G.-P., Graham, D. E., Liang, L., Wullschleger, S. D., & Gu, B. (2016). Warming increases methylmercury production in an Arctic soil. Environmental Pollution, 214, 504–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.069
Yao, A., Qin, C., & Mou, S. (2004). Effect of humus on environmental mobility of mineral bound mercury. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 02, 274–277.
Zhang, M., Dai, J., & Wang, R. (2011). Research progress of the effect of dissolved organic matter(DOM) on adsorption migration and bioavailability of Hg in soil. Environmental Pollution and Control, 33(05), 95–110. https://doi.org/10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2011.05.022
Zhang, J., Lv, P., Wang, L., & Yu, Z. (2015). Spatial variation of heavy metal contents and contamination assessment in forest soils in Daxing ’an Mountains. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34(03), 810–819. https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.2015.0110
Zhang, S., Wang, Q., Cui, J., Sun, X., & Zheng, D. (2009). CV-AFS determination of methyl mercury in sediment and soil samples with ultrasonic extraction. Physical and Chemical Examination (chemistry Section), 45(11), 1273–1275.
Zhang, Z., Li, M., Li, Z., Xue, Z., & Jiang, M. (2020). Unexpected high methylmercury contents related to soil organic carbon and its molecular composition in wetland soils of the Yarlung Tsangbo River. Tibet. Geoderma, 377, 114607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114607
Zhao, H., Gong, L., Qu, H., Zhu, H., Li, X., & Zhao, F. (2016). The climate change variations in the northern greater Khingan Mountains during the past centuries. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 26(5), 585–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-016-1287-y
Zheng, D., Zhang, S., Ma, H., & Li, H. (2020). Simulation of methylmercury content and SRB methylation in phragmites australis soil under different salinity conditions. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 231(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4382-8
Zheng, W., & Hintelmann, H. (2010). Nuclear field shift effect in isotope fractionation of mercury during abiotic reduction in the absence of light. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 114(12), 4238–4245. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp910353y
Zsolnay, A., Baigar, E., Jimenez, M., Steinweg, B., & Saccomandi, F. (1999). Differentiating with fluorescence spectroscopy the sources of dissolved organic matter in soils subjected to drying. Chemosphere, 38(1), 45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00166-0
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41771103, U20A2083, and U19A2042) and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (No. 2018265).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YX contributed to study design, sample measurement, data curation and analysis, and writing—original draft preparation. XZ contributed to assisting sample collection and sample measurement. DZ contributed to methodology and investigation. ZZ contributed to study design, methodology, and manuscript revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This work was performed in compliance with ethical standards.
Humans and animals research
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors were informed about and agreed to the protocol.
Consent to publish
All authors were allowed to read and approve the final manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, Y., Zhang, X., Zheng, D. et al. Impacts of spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter on methylmercury contents in peatlands, Northeast China. Environ Geochem Health 45, 913–923 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01257-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01257-1