Abstract
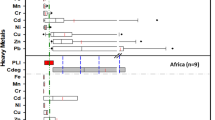
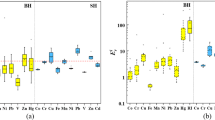
In order to expound on the present situation and potential risk of road dust heavy metals in major cities, a total of 114 literatures mainly over the past two decades, involving more than 5000 sampling sites in 61 cities of 21 countries, were screened through the collection and analysis of research papers. The concentration, sources, distribution, health risk, sample collection, and analytical methods of heavy metal research on road dust in cities around the world are summarized. The results show that Cd, Zn, and Cu in many urban road dusts in the world are higher than the grade II of the Chinese maximum allowable concentration of potentially toxic elements in the soil. Geo-accumulation index values show that Pb > Cd > Zn > Cu had the highest contamination levels. Hazard index assessment indicates Pb and Cr had the highest potential health risk, especially for children in which ingestion was found as the main exposure pathway. Moreover, through comparative analysis, it is found that some pollutants are higher in developed and industrialized cities and transport (53%) followed by industrial emissions (35%) provide the major contributions to the sources of heavy metals.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Andrzej, K., Małgorzata, R., & Maria, W. (2011). Application of Enrichment Factor (Ef) to the interpretation of results from the biomonitoring studies. Ecological Chemistry and Engineering , 18(2), 171–182.
Ahmed, F., & Ishiga, H. (2006). Trace metal concentrations in street dusts of Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Atmospheric Environment., 40, 3835–3844. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSENV.2006.03.004
Akhter M. S., Madany, I. M. (1993). Heave metals in street and house dust in Bahrain. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution., 66, 111–119.
Ali, M. U., Liu, G., Yousaf, B., Abbas, Q., Ullah, H., Munir, M. A. M., & Fu, B. (2017). Pollution characteristics and human health risks of potentially (eco)toxic elements (PTEs) in road dust from metropolitan area of Hefei, China. Chemosphere, 181, 111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.061
Al-Khashman, O. A. (2004). Heavy metal distribution in dust, street dust and soils from the work place in Karak Industrial Estate, Jordan. Atmospheric Environment, 38, 6803–6812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.09.011
Al-Khashman, O. A. (2007). Determination of metal accumulation in deposited street dusts in Amman, Jordan. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 29, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-006-9067-8
Anil B., Robert D. E. (2002). Chromium-based regulations and greening in metal finishing industries in the USA. Environmental Science & Policy, 5, (2), 121–133, ISSN 1462-9011, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1462-9011(02)00028-X.
Anselin, L. (1995). Local indicators of spatial association—LISA. Geographical Analysis, 27, 93–115.
Apeagyei, E., Bank, M. S., & Spengler, J. D. (2011). Distribution of heavy metals in road dust along an urban-rural gradient in Massachusetts. Atmospheric Environment, 45(13), 2310–2323.
Arslan, H. (2001). Heavy metals in street dust in Bursa, Turkey. Journal of Trace and Microprobe Techniques, 19, 439–445. https://doi.org/10.1081/TMA-100105058
Barbara, Z., Vladimir N. U., Stefano C. (2016). Nickel impact on human health: An intrinsic disorder perspective. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Proteins and Proteomics, 1864 (12), 1714–1731, ISSN 1570-9639, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.09.008.
Benhaddya, M. L., Boukhelkhal, A., Halis, Y., & Hadjel, M. (2016). Human health risks associated with metals from urban soil and road dust in an oilfield area of Southeastern Algeria. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 70, 556–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-015-0244-6
Biljana D. Škrbić, Maja Buljovčić, Grigorije Jovanović, Igor Antić. (2018). Seasonal, spatial variations and risk assessment of heavy elements in street dust from Novi Sad, Serbia. Chemosphere, 2018(205), 452–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.124
Birch, G. F., & Olmos, M. A. (2008). Sediment-bound heavy metals as indicators of human influence and biological risk in coastal water bodies. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 65, 1407–1413.
Cao, S., Duan, X., Zhao, X., Ma, J., Dong, T., Huang, N., Sun, C., He, B., & Wei, F. (2014). Health risks from the exposure of children to As, Se, Pb and other heavy metals near the largest coking plant in China. Science of the Total Environment, 472, 1001–1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.124
CEPA (Chinese Environmental Protection Administration, Environmental Quality Standard for Soils) (GB15618–1995), Beijing, 1995.
Charlesworth, S., Everett, M., McCarthy, R., Ordóñez, A., & de Miguel, E. (2003). A comparative study of heavy metal concentration and distribution in deposited street dusts in a large and a small urban area: Birmingham and Coventry, West Midlands, UK. Environment International, 29, 563–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00015-1
Chen, J., Tan, M., Li, Y., Zheng, J., Zhang, Y., Shan, Z., Zhang, G., & Li, Y. (2008). Characteristics of trace elements and lead isotope ratios in PM2.5 from four sites in Shanghai. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 156, 36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2007.11.122
Chen, X., Mao, J., He, S., et al. (2012). Heavy metal pollution of dust in Fuzhou urban parks. Urban Environment & Urban Ecology, 25, 31–34. (in Chinese).
Chen, H., Teng, Y., Lu, S., Wang, Y., & Wang, J. (2015). Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Science of the Total Environment, 512–513, 143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2015.01.025
Chon HT, Kim KW, Kim JY. (1995). Metal contamination of soils and dusts in Seoul metropolitan city, Korea. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 17(3):139–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00126082. PMID: 24194184.
Christoforidis, A., & Stamatis, N. (2009). Heavy metal contamination in street dust and roadside soil along the major national road in Kavala’s region, Greece. Geoderma, 151, 257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEODERMA.2009.04.016
CNEMC (China National Environmental Monitoring Centre). (1990). The Background Values of Chinese Soils. Environmental Science Press of China.
De Miguel, E., Llamas, J. F., Chacón, E., & Mazadiego, L. F. (1999). Sources and pathways of trace elements in urban environments: A multi-elemental qualitative approach. Science of the Total Environment, 235, 355–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00234-X
Dehghani, S., Moore, F., Keshavarzi, B., & Hale, B. A. (2017). Health risk implications of potentially toxic metals in street dust and surface soil of Tehran, Iran. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 136, 92–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.10.037
Divrikli, U., Soylak, M., Elci, L., & Dogan, M. (2008). Trace heavy metal levels in street dust samples from Yozgat City Center, Turkey. Journal of trace and microprobe techniques, 21(2), 351–361. https://doi.org/10.1081/TMA-120020270
Du, Y., Gao, B., Zhou, H., Ju, X., Hao, H., & Yin, S. (2013). Health risk assessment of heavy metals in road dusts in Urban Parks of Beijing, China. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 18, 299–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2013.04.039
Duzgoren-Aydin, N. S., Wong, C. S. C., Aydin, A., Song, Z., You, M., & Li, X. D. (2006). Heavy metal contamination and distribution in the urban environment of Guangzhou, SE China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health 28, 375–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-005-9036-7
El-Desoky, G. E., Aboul-Soud, M. A. M., Al-Othman, Z. A., Habila, M., & Giesy, J. P. (2014). Seasonal concentrations of lead in outdoor and indoor dust and blood of children in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36, 583–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9582-3
Fergusson, J. E., & Ryan, D. E. (1984). The elemental composition of street dust from large and small urban areas related to city type, source and particle size. Science of the Total Environment, 34, 101–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(84)90044-5
Ferreira-Baptista, L., & De Miguel, E. (2005). Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: A tropical urban environment. Atmospheric Environment., 39, 4501–4512. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSENV.2005.03.026
Gope, M., Masto, R. E., George, J., Hoque, R. R., & Balachandran, S. (2017). Bioavailability and health risk of some potentially toxic elements (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in street dust of Asansol, India. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 138, 231–241.
Gracia, R. C., & Snodgrass, W. R. (2007). Lead toxicity and chelation therapy. The American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy, 64, 45–53. https://doi.org/10.2146/ajhp060175
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975e1001.
Han, Y. M., Du, P. X., Cao, J. J., & Posmentier, E. S. (2006). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Science of the Total Environment., 355, 176–186.
Han, Y., Cao, J., Posmentier, E. S., Fung, K., Tian, H., & An, Z. (2008). Particulate-associated potentially harmful elements in urban road dusts in Xi’an, China. Applied Geochemistry, 23, 835–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APGEOCHEM.2007.09.008
Hu, X., Zhang, Y., Luo, J., Wang, T., Lian, H., & Ding, Z. (2011). Bioaccessibility and health risk of arsenic, mercury and other metals in urban street dusts from a mega-city, Nanjing, China. Environmental Pollution, 159, 1215–1221. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2011.01.037
Huang, R. (1987). Environmental peodology. Higher Education Press.
Ibha, S., Sinha S., Vaibhav S., Rajeev P.S. (2021). Impact of cadmium pollution on food safety and human health. Current Opinion in Toxicology, 27, pp 1–7, ISSN 2468-2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cotox.2021.04.004.
Jelena R. Ž., Yaqin J., Biljana D. Š., & Maja B. B. (2019). Occurrence of heavy elements in street dust from sub/urban zone of Tianjin: pollution characteristics and health risk assessment. Journal of Environmental Science and Health - Part A, 54(10), 999–1010. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2019.1631092
Jerome Nriagu (2019) Zinc Deficiency in Human Health. In Jerome Nriagu (Editor) Encyclopedia of Environmental Health (2nd Edition). Elsevier, pp 489–499, ISBN 9780444639523, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-409548-9.11433-2.
Karim, Z., & Qureshi, B. A. (2014). Health risk assessment of heavy metals in Urban Soil of Karachi, Pakistan. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 20, 658–667. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2013.791535
Keshavarzi, B., Tazarvi, Z., Rajabzadeh, M. A., & Najmeddin, A. (2015). Chemical speciation, human health risk assessment and pollution level of selected heavy metals in urban street dust of Shiraz, Iran. Atmospheric Environment, 119, 1–10.
Khanal, R., Furumai, H., Nakajima, F., & Yoshimura, C. (2018). Carcinogenic profile, toxicity and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons accumulated from urban road dust in Tokyo, Japan. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 165, 440–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2018.08.095
Lanphear, B. P., Hornung, R., Khoury, J., Yolton, K., Baghurst, P., Bellinger, D. C., Canfield, R. L., Dietrich, K. N., Bornschein, R., Greene, T., Rothenberg, S. J., Needleman, H. L., Schnaas, L., Wasserman, G., Graziano, J., & Roberts, R. (2005). Low-level environmental lead exposure and children’s intellectual function: An international pooled analysis. Environmental Health Perspective, 113, 894–899. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.7688
Li, S., & Jia, Z. (2018). Heavy metals in soils from a representative rapidly developing megacity (SW China): Levels, source identification and apportionment. CATENA, 163, 414–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.12.035
Li, X., Poon, C., & Liu, P. S. (2001). Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and street dusts in Hong Kong. Applied Geochemistryistry, 16, 1361–1368. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00045-2
Li, X., Lee, S. I., Wong, S. C., Shi, W., & Thornton, I. (2004). The study of metal contamination in urban soils of Hong Kong using a GIS-based approach. Environmental Pollution, 129, 113–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2003.09.030
Li, H., Chen, Z., Wang, J., Xu, S., Shi, G., Zhang, J., & Wang, L. (2007). Research of spatial variability of heavy metal pollution of dust in Shanghai urban area based on the GIS. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 27, 803–809.
Li, H., Qian, X., Hu, W., Wang, Y., & Gao, H. (2013a). Chemical speciation and human health risk of trace metals in urban street dusts from a metropolitan city, Nanjing, SE China. Science of the Total Environment., 456–457, 212–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.03.094
Li, Z., Feng, X., Li, G., Bi, X., Zhu, J., Qin, H., Dai, Z., Liu, J., Li, Q., & Sun, G. (2013b). Distributions, sources and pollution status of 17 trace metal/metalloids in the street dust of a heavily industrialized city of central China. Environmental Pollution, 182, 408–416.
Li, K., Liang, T., Wang, L., & Yang, Z. (2015). Contamination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in road dust in Bayan Obo Mining Region in Inner Mongolia, North China. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 25(12), 1439–1451.
Li, H. H., Chen, L. J., Yu, L., Guo, Z. B., Shan, C. Q., Lin, J. Q., Gu, Y. G., Yang, Z. B., Yang, Y. X., Shao, J. R., Zhu, X. M., & Cheng, Z. (2017). Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of human exposure to oral bioaccessibility of heavy metals via urban street dusts from different functional areas in Chengdu, China. Science of the Total Environment, 586, 1076–1084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.092
Liu, C. H., & Cen, K. (2007). Chemical composition and possible sources of elements in street dusts in Beijing. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 27, 1181–1188. (in Chinese).
Liu, D., Fayuan, W., Wenli, Z., & Yujian. (2012). Heavy metal pollution in street dusts from different functional zones of Luoyang City and its potential ecological risk. Environmental Science, 33, 253–259.
Liu, E., Yan, T., Birch, G., & Zhu, Y. (2014). Pollution and health risk of potentially toxic metals in urban road dust in Nanjing, a mega-city of China. Science of the Total Environment, 476–477, 522–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2014.01.055
Liu, A., Hong, N., Zhu, P., & Guan, Y. (2019). Characterizing petroleum hydrocarbons deposited on road surfaces in urban environments. Science of the Total Environment, 653, 589–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.428
Lu, X., Wang, L., Lei, K., Huang, J., & Zhai, Y. (2009). Contamination assessment of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel in street dust of Baoji, NW China. The Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161, 1058–1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2008.04.052
Luo, X. S., Ding, J., Xu, B., Wang, Y. J., Li, H. B., & Yu, S. (2012). Incorporating bioaccessibility into human health risk assessments of heavy metals in urban park soils. Science of the Total Environment, 424, 88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.053
Marek, J. (2013). An investigation into the mechanisms of wear of zinc from the surface of zinc-coated car-body sheets during friction. Wear, 303, (1–2), 519–523, ISSN 0043-1648, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2013.04.005.
Men, C., Liu, R., Xu, F., Wang, Q., Guo, L., & Shen, Z. (2018). Pollution characteristics, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. Science of the Total Environment, 612, 138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.123
Müller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geo-Journal 2, 108e118.
Mun’im Mohd Han, N., Latif, M. T., Othman, M., Dominick, D., Mohamad, N., Juahir, H., & Tahir, N. M. (2014). Composition of selected heavy metals in road dust from Kuala Lumpur city center. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72(3), 849–859.
Muriel Bost, Sabine Houdart, Marion Oberli, Esther Kalonji, Jean-François Huneau, Irène Margaritis. (2016). Dietary copper and human health: Current evidence and unresolved issues. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 35, pp 107–115, ISSN 0946-672X, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2016.02.006.
Naseem, F., Rashid, A., Izhar, T., Khawar, M. I., Bano, S., Ashraf, A., & Adnan, M. N. (2017). An integrated approach to air pollution modeling from climate change perspective using ARIMA forecasting. The Journal of Applied Agriculture and Biotechnology, 2(2), 38–45.
Nazzal, Y., Rosen, M. A., & Al-Rawabdeh, A. M. (2013). Assessment of metal pollution in urban road dusts from selected highways of the Greater Toronto Area in Canada. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(2), 1847–1858.
Pan, H., Lu, X., & Lei, K. (2017). A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of Xi’an, China: Contamination, source apportionment and spatial distribution. Science of the Total Environment, 609, 1361–1369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.004
Qiang, L., Yang, W., Jingshuang, L., Quanying, W., & Mingying, Z. (2015). Grain-size distribution and heavy metal contamination of road dusts in urban parks and squares in Changchun, China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 37(1), 71–82.
Rasmussen, P., Subramanian, K., & Jessiman, B. (2001). A multi-element profile of house dust in relation to exterior dust and soils in the city of Ottawa, Canada. Science of the Total Environment, 267, 125–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00775-0
Rastegari Mehr, M., Keshavarzi, B., Moore, F., Sharifi, R., Lahijanzadeh, A., & Kermani, M. (2017). Distribution, source identification and health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in urban areas of Isfahan province, Iran. The Journal of African Earth Sciences, 132, 16–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.04.026
Reimann, C., Fabian, K., Manfred Birke, M., Filzmoser, P., Demetriades, A., Négrel, P., Oorts, K., Matschullat, J., & Caritat, P. (2018). GEMAS: Establishing geochemical background and threshold for 53 chemical elements in European agricultural soil. Applied Geochemistry, 2018(88), 302–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.01.021
Richa Shrivastava, Upreti, R.K., Seth, P.K., Chaturvedi, U.C. (2020). Effects of chromium on the immune system. FEMS Immunology & Medical Microbiology, 34 (1), 1–7, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-695X.2002.tb00596.x
Saeedi, M., Hosseinzadeh, M., Jamshidi, A., & Pajooheshfar, S. P. (2009). Assessment of heavy metals contamination and leaching characteristics in highway side soils, Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 151, 231–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0264-z
Saeedi, M., Li, L. Y., & Salmanzadeh, M. (2012). Heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Pollution and ecological risk assessment in street dust of Tehran. The Journal of Hazardous Materials, 227–228, 9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2012.04.047
Sumia, S., Audil, R., Rimao, H., Faiza, N., & Aniqa B. (2021). Chemical exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and hematological evaluation among petrol pump workers in Islamabad, Pakistan. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2021.1980059
Sanleandro, P. M., Navarro, A. S., Díaz-Pereira, E., Zuñiga, F. B., Muñoz, M. R., & Iniesta, M. J. D. (2018). Assessment of heavy metals and color as indicators of contamination in street dust of a city in SE Spain: Influence of traffic intensity and sampling location. Sustainability, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114105
Sezgin, N., Ozcan, H. K., Demir, G., Nemlioglu, S., & Bayat, C. (2004). Determination of heavy metal concentrations in street dusts in Istanbul E-5 highway. Environment International, 29(7), 979–985.
Shabbaj, I. I., Alghamdi, M. A., Shamy, M., Hassan, S. K., Alsharif, M. M., & Khoder, M. I. (2018). Risk assessment and implication of human exposure to road dust heavy metals in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(1), 36.
Shahab, A., Zhang, H., Ullah, H., Rashid, A., Rad, S., Li, J., & Xiao, H. (2020). Pollution characteristics and toxicity of potentially toxic elements in road dust of a tourist city, Guilin, China: Ecological and health risk assessment. Environmental Pollution, 266, 115419.
Shi, G., Chen, Z., Xu, S., Zhang, J., Wang, L., Bi, C., & Teng, J. (2008). Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai, China. Environmental Pollution, 156, 251–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2008.02.027
Shi, Z., Zhang, W., Liu, Y., Wu, F., Dong, M., Su, H., & Ming, Q. (2011). Heavy metal pollution and the ecological risk assessment of urban street dust in Kunming, China. In 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (pp. 2169–2172). IEEE.
Soltani, N., Keshavarzi, B., Moore, F., Tavakol, T., Lahijanzadeh, A. R., Jaafarzadeh, N., & Kermani, M. (2015). Ecological and human health hazards of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in road dust of Isfahan metropolis, Iran. Science of the Total Environment., 505, 712–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2014.09.097
Song, B., Guo, G., Lei, M., & Wang, Y. (2018). Assessments of contamination and human health risks of heavy metals in the road dust from a mining county in Guangxi, China. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 24, 1606–1622.
Sutherland, R. A., & Tolosa, C. A. (2000). Multi-element analysis of road-deposited sediment in an urban drainage basin, Honolulu, Hawaii Hawaii. Environmental Pollution, 110(3), 483–495.
Swaroop, A.., Bagchi, M., Preuss, H.G., Zafra-Stone, S., Ahmad, T., & Bagchi, D. (2019). In John B. Vincent Editor(s) The Nutritional Biochemistry of Chromium (III) (Second Edition), Chapter 8—Benefits of chromium (III) complexes in animal and human health. Elsevier,pp 251–278, ISBN 9780444641212, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-64121-2.00008-8.
Tang, J., Han, W., Li, Na., et al. (2011). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal element concentrations in atmospheric deposition in Harbin city, Northeast China. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 31, 3087–3091.
Tang, R., Ma, K., Zhang, Y., & Mao, Q. (2013). The spatial characteristics and pollution levels of metals in urban street dust of Beijing, China. Applied Geochemistry, 35, 88–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APGEOCHEM.2013.03.016
Tang, Z., Huang, Q., Yang, Y., Nie, Z., Cheng, J., Yang, J., Wang, Y., & Chai, M. (2016). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and heavy metals in road dusts from a plastic waste recycling area in north China: Implications for human health. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(1), 625–637.
Tang, Z., Chai, M., Cheng, J., Jin, J., Yang, Y., Nie, Z., Huang, Q., & Li, Y. (2017). Contamination and health risks of heavy metals in street dust from a coal-mining city in eastern China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 138, 83–91.
Tanner, P. A., Ma, H.-L., & Yu, P. K. N. (2008). Fingerprinting metals in urban street dust of Beijing, Shanghai, and Hong Kong. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 7111–7117.
Tanushree, B., Chakraborty, S., Bhumika, F., & Piyal, B. (2011). Heavy metal concentrations in street and leaf deposited dust in Anand city, India. Research Journal of Chemical Sciences ISSN, 2231, 606X.
Tijhuis, L., Brattli, B., & Sæther, O. M. (2002). A geochemical survey of topsoil in the City of Oslo, Norway. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 24, 67–94. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013979700212
Tomlinson, D., et al. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen, 33, 566.
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). (2002). Child-specific Exposure Factors Handbook (EPA-600-P-00e002B). National Center for Environmental Assessment.
Varrica, D., Dongarrà, G., Sabatino, G., & Monna, F. (2003). Inorganic geochemistry of roadway dust from the metropolitan area of Palermo, Italy. Environmental Geology, 44(2), 222–230.
Wang, J., Ren, H., & Zhang, X. (2006). Distribution patterns of lead in urban soil and dust in Shenyang city, Northeast China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 28, 53–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-005-9011-3
Wang, L., Lu, X., Ren, C., Li, X., & Chen, C. (2014). Contamination assessment and health risk of heavy metals in dust from Changqing industrial park of Baoji, NW China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(5), 2095–2104.
Wei, B., Jiang, F., Li, X., & Mu, S. (2009). Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in urban road dusts from Urumqi, NW China. Microchemical Journal, 93, 147–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROC.2009.06.001
Wei, B., Jiang, F., Li, X., & Mu, S. (2010). Contamination levels assessment of potential toxic metals in road dust deposited in different types of urban environment. Environmental Earth Sciences, 61(6), 1187–1196.
Wei, X., Gao, B., Wang, P., Zhou, H., & Lu, J. (2015). Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in street dusts from different functional areas in Beijing, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 112, 186–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.11.005
Yang, Z., Lu, W., Liu, X., & Xin, X. (2010). Heavy metal identification for near-surface urban dust in Changchun City. Journal of Arid Land Resource Environment, 24(12), 155–160.
Yang, T., Zeng, Q., Liu, Z., & Liu, Q. (2011). Magnetic properties of the road dusts from two parks in Wuhan city, China: Implications for mapping urban environment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 177(1–4), 637–648.
Yang, J., Teng, Y., Song, L., & Zuo, R. (2016). Tracing sources and contamination assessments of heavy metals in road and foliar dusts in a typical mining city, China. PLoS One, 11(12), e0168528.
Yousaf, B., Amina, L.G., Wang, R., Imtiaz, M., Rizwan, M.S., Zia-ur-Rehman, M., Qadir, A., Si, Y. (2016). The importance of evaluating metal exposure and predicting human health risks in urban–periurban environments influenced by emerging industry. Chemosphere, 150, 79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2016.02.007
Yu, R., He, L., Cai, R., Li, B., Li, Z., & Yang, K. (2017). Heavy metal pollution and health risk in China. Global Health Journal, 1(1), 47–55.
Yu, B., Wang, Y., & Zhou, Q. (2014). Human health risk assessment based on toxicity characteristic leaching procedure and simple bioaccessibility extraction test of toxic metals in urban street dust of Tianjin, China. PLoS One, 9(3), e92459.
Zhang, M., & Wang, H. (2009). Concentrations and chemical forms of potentially toxic metals in road-deposited sediments from different zones of Hangzhou, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 21, 625–631.
Zhang, J., Deng, H., Chen, Z., & Xu, S. (2007). Heavy metal pollution in the urban street dust of Shanghai city, Chinese. Journal of Soil Science, 38, 727–731.
Zhang, C., Qiao, Q., Appel, E., & Huang, B. (2012). Discriminating sources of anthropogenic heavy metals in urban street dusts using magnetic and chemical methods. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 119, 60–75.
Zhang, J., Chen, Q., Wang, Q., Ding, Z., Sun, H., & Xu, Y. (2019). The acute health effects of ozone and PM2.5 on daily cardiovascular disease mortality: A multi-center time series study in China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 174, 218–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.085
Zhao, N., Lu, X., Chao, S., & Xu, X. (2015). Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in less than 100 μm particles of street dust from Xining, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(5), 2319–2327.
Zheng, J., Tan, M., Shibata, Y., Tanaka, A., Li, Y., Zhang, G., Zhang, Y., & Shan, Z. (2004). Characteristics of lead isotope ratios and elemental concentrations in PM10 fraction of airborne particulate matter in Shanghai after the phase-out of leaded gasoline. Atmospheric Environment, 38, 1191–1200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2003.11.004
Zheng, N., Liu, J., Wang, Q., & Liang, Z. (2010). Health risk assessment of heavy metal exposure to street dust in the zinc smelting district, Northeast of China. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 726–733.
Zheng, D. M., Jin, D., Lin, X., & Li, H. Y. (2016). The exposure of heavy metals of street dust during heating period and unheating period in Shenyang. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35(4), 1047.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52150410408), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2021M693187), Guangxi Natural Science Foundation Project (Grant No. 2020GXNSFBA159040), and Guangxi Young and Middle-aged Teachers Basic Ability Improvement Project (Grant No. 2020KY06036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS and SR involved in conceptualization; AS and SR involved in data curation; SR involved in formal analysis; SR and HX involved in funding acquisition; JS and ZH involved in investigation; HU contributed to methodology; NZ involved in project administration, ; HX contributed to resources; AS contributed to software; MRT involved in supervision; LH involved in validation; AR involved in visualization; AS involved in roles/writing—original draft; SR and HX involved in writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding this publication.
Animal research
This study does not involve any animal or human based research.
Consent to participate
This study does not involve any individual or personal data gathering.
Consent to publish
All the authors have consent to publish this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahab, A., Hui, Z., Rad, S. et al. A comprehensive review on pollution status and associated health risk assessment of human exposure to selected heavy metals in road dust across different cities of the world. Environ Geochem Health 45, 585–606 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01255-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01255-3