Abstract
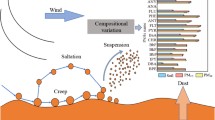
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are emitted to the atmosphere by various anthropogenic activities as well as natural sources, they undergo long-range transport, are degraded (e.g., by photolysis) and finally they are deposited onto the surface and potentially accumulate in topsoil. The dry deposition of particle-bound PAHs dominates the accumulation of PAHs in soil and their further fate in soil is governed by sorption/desorption from these airborne particles. This paper offers an overview on concentrations of particle-bound PAHs, the dry deposition fluxes and finally concentrations of PAHs in soil. In addition, spatial and temporal variations of PAHs are considered. The results show that concentrations of particle-bound PAHs typically range from 1 mg g−1 up to 10 mg g−1 in cities with coal-based heating in winter and in countries with coal-based industry incl. electrical power production. These values are very high and exceed the legal limits set in soils by orders of magnitude. Atmospheric deposition rates typically reach several mg m−2 a−1, but in winter, especially in countries with heating, deposition rates are up to 10 times higher. PAHs concentrations in soils show a very wide variation from less than 1 µg g−1 in rural areas up to 10 µg g−1 in urban space, which is about 1000 times lower than the concentration of PAHs on particles in the atmosphere. This demonstrates the relevance of high concentrations of PAHs on airborne particles deposited on soils, which also highlights the importance of considering incremental lifetime cancer risk models for both air and soil and assessing the total health risk of PAHs to humans.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
Abdel-Shafy, H. I., & Mansour, M. S. (2016a). A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egyptian Journal of Petroleum, 25(1), 107–123.
Agency, U.E.P. (2009) risk assessment guidance for superfund, volume I: Human health evaluation manual (Part F, supplemental guidance for inhalation risk assessment)(EPA-540-R-070-002), office of superfund remediation and technology innovation Washington, DC.
Aichner, B., Bussian, B. M., Lehnik-Habrink, P., & Hein, S. (2015). Regionalized concentrations and fingerprints of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in German forest soils. Environmental Pollution, 203, 31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.03.026
Arellano, L., Fernández, P., López, J., Rose, N. L., Nickus, U., Thies, H., Stuchlik, E., Camarero, L., Catalan, J., & Grimalt, J. O. (2014). Atmospheric deposition of polybromodiphenyl ethers in remote mountain regions of Europe. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 14(9), 4441–4457. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-4441-2014
Bae, S. Y., Yi, S. M., & Kim, Y. P. (2002). Temporal and spatial variations of the particle size distribution of PAHs and their dry deposition fluxes in Korea. Atmospheric Environment, 36(35), 5491–5500. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00666-0
Balmer, J. E., Hung, H., Yu, Y., Letcher, R. J., & Muir, D. C. (2019). Sources and environmental fate of pyrogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Arctic. Emerging Contaminants, 5, 128–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2019.04.002
Billet, S., Abbas, I., Le Goff, J., Verdin, A., André, V., Lafargue, P.-E., Hachimi, A., Cazier, F., Sichel, F., & Shirali, P. (2008). Genotoxic potential of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons-coated onto airborne particulate matter (PM2.5) in human lung epithelial A549 cells. Cancer Letters, 270(1), 144–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.04.044
Birgül, A., Tasdemir, Y., & Cindoruk, S. S. (2011). Atmospheric wet and dry deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) determined using a modified sampler. Atmospheric Research, 101(1–2), 341–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2011.03.012
Błaszczyk, E., Rogula-Kozłowska, W., Klejnowski, K., Fulara, I., & Mielżyńska-Švach, D. (2017). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons bound to outdoor and indoor airborne particles (PM2.5) and their mutagenicity and carcinogenicity in Silesian kindergartens, Poland. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, 10(3), 389–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-016-0457-5
Bozlaker, A., Muezzinoglu, A., & Odabasi, M. (2008). Atmospheric concentrations, dry deposition and air–soil exchange of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in an industrial region in Turkey. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 153(3), 1093–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.064
Budzinski, H., Jones, I., Bellocq, J., Pierard, C., & Garrigues, P. (1997). Evaluation of sediment contamination by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Gironde estuary. Marine Chemistry, 58(1–2), 85–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4203(97)00028-5
Butler, J., Butterworth, V., Kellow, S. C., & Robinson, H. G. (1984). Some observations on the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) content of surface soils in Urban areas. Science of the Total Environment, 33(1–4), 75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(84)90382-6
Byambaa, B., Yang, L., Matsuki, A., Nagato, E. G., Gankhuyag, K., Chuluunpurev, B., Banzragch, L., Chonokhuu, S., Tang, N., & Hayakawa, K. (2019). Sources and characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ambient total suspended particles in Ulaanbaatar City, Mongolia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(3), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030442
CCME. (2010). Canadian soil quality guidelines for potentially carcinogenic and other PAHs: Scientific criteria document. CCME Winnipeg.
Cébron, A., Norini, M.-P., Beguiristain, T., & Leyval, C. (2008). Real-time PCR quantification of PAH-ring hydroxylating dioxygenase (PAH-RHDα) genes from Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria in soil and sediment samples. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 73(2), 148–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2008.01.009
Chantara, S., & Sangchan, W. (2009). Sensitive analytical method for particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A case study in Chiang Mai, Thailand. ScienceAsia, 35(1), 42–48. https://doi.org/10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2009.35.042
Chen, F., Hu, W., & Zhong, Q. (2013). Emissions of particle-phase polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Fu Gui-shan tunnel of Nanjing, China. Atmospheric Research, 124, 53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.12.008
Cheng, C., Bi, C., Wang, D., Yu, Z., & Chen, Z. (2018). Atmospheric deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Shanghai: The spatio-temporal variation and source identification. Frontiers of Earth Science, 12(1), 63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.022
Choi, S.-D., Shunthirasingham, C., Daly, G. L., Xiao, H., Lei, Y. D., & Wania, F. (2009). Levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Canadian mountain air and soil are controlled by proximity to roads. Environmental Pollution, 157(12), 3199–3206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.05.032
Chuesaard, T., Chetiyanukornkul, T., Kameda, T., Hayakawa, K., & Toriba, A. (2013). Influence of biomass burning on the levels of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their nitro derivatives in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 14(4), 1247–1257. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2013.05.0161
da Rocha, G. O., Lopes, W. A., de Paula Pereira, P. A., de Castro Vasconcellos, P., Oliveira, F. S., Carvalho, L. S., dos Conceição Santos, L., & de Andrade, J. B. (2009). Quantification and source identification of atmospheric particulate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their dry deposition fluxes at three sites in Salvador Basin, Brazil, impacted by mobile and stationary sources. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 20(4), 680–692. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0103-50532009000400012
da Rocha, G. O., Lopes, W. A., Pereira, P. A., de Castro Vasconcellos, P., Oliveira, F. S., Carvalho, L. S., dos Santos Conceição, L., & de Andrade, J. B. (2009). Quantification and source identification of atmospheric particulate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their dry deposition fluxes at three sites in Salvador Basin, Brazil, impacted by mobile and stationary sources. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 20(4), 680–692. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0103-50532009000400012
Dachs, J., & Eisenreich, S. J. (2000). Adsorption onto aerosol soot carbon dominates gas-particle partitioning of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(17), 3690–3697. https://doi.org/10.1021/es991201+
Deary, M. E., Ekumankama, C. C., & Cummings, S. P. (2016). Development of a novel kinetic model for the analysis of PAH biodegradation in the presence of lead and cadmium co-contaminants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 307, 240–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.12.015
Demircioglu, E., Sofuoglu, A., & Odabasi, M. (2011). Particle-phase dry deposition and air–soil gas exchange of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Izmir, Turkey. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186(1), 328–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.005
Devi, N. L., Yadav, I. C., Shihua, Q., Dan, Y., Zhang, G., & Raha, P. (2016). Environmental carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil from Himalayas, India: Implications for spatial distribution, sources apportionment and risk assessment. Chemosphere, 144, 493–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.08.062
Dong, T. T., Stock, W. D., Callan, A. C., Strandberg, B., & Hinwood, A. L. (2020). Emission factors and composition of PM2. 5 from laboratory combustion of five Western Australian vegetation types. Science of the Total Environment, 703, 134796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134796
Dong, Z., Jiang, N., Zhang, R., Xu, Q., Ying, Q., Li, Q., & Li, S. (2020). Molecular characteristics, source contributions, and exposure risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the core city of Central Plains Economic Region, China: Insights from the variation of haze levels. Science of the Total Environment, 757, 143885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143885
Du, W., Yun, X., Luo, Z., Chen, Y., Liu, W., Sun, Z., Zhong, Q., Qiu, Y., Li, X., & Zhu, Y. (2019). Submicrometer PM1. 0 exposure from household burning of solid fuels. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 7(1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.9b00633
Edwards, N. T. (1983). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH’s) in the terrestrial environment—a review. Journal of Environmental Quality, 12(4), 427–441. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1983.00472425001200040001x
Fazeli, G., Karbassi, A., Khoramnejadian, S., & Nasrabadi, T. (2019). Evaluation of Urban soil pollution: A combined approach of toxic metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). International Journal of Environmental Research, 13(5), 801–811.
Feng, D., Liu, Y., Gao, Y., Zhou, J., Zheng, L., Qiao, G., Ma, L., Lin, Z., & Grathwohl, P. (2017). Atmospheric bulk deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Shanghai: Temporal and spatial variation, and global comparison. Environmental Pollution, 230, 639–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.022
Fernández, P., Carrera, G., Grimalt, J. O., Ventura, M., Camarero, L., Catalan, J., Nickus, U., Thies, H., & Psenner, R. (2003). Factors governing the atmospheric deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to remote areas. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(15), 3261–3267. https://doi.org/10.1021/es020137k
Fuzzi, S., Baltensperger, U., Carslaw, K., Decesari, S., Denier van der Gon, H., Facchini, M. C., Fowler, D., Koren, I., Langford, B., & Lohmann, U. (2015). Particulate matter, air quality and climate: Lessons learned and future needs. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15(14), 8217–8299. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-8217-2015
Gaga, E. O., & Ari, A. (2011). Gas–particle partitioning of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in an urban traffic site in Eskisehir, Turkey. Atmospheric Research, 99(2), 207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2010.10.013
Gaga, E. O., & Arı, A. (2019). Gas-particle partitioning and health risk estimation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) at urban, suburban and tunnel atmospheres: Use of measured EC and OC in model calculations. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 10(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2018.05.004
Garban, B., Blanchoud, H., Motelay-Massei, A., Chevreuil, M., & Ollivon, D. (2002). Atmospheric bulk deposition of PAHs onto France: Trends from urban to remote sites. Atmospheric Environment, 36(34), 5395–5403. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00414-4
Garrido, A., Jiménez-Guerrero, P., & Ratola, N. (2014). Levels, trends and health concerns of atmospheric PAHs in Europe. Atmospheric Environment, 99, 474–484.
Gocht, T. (2005). The four greek elements: Mass balance of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in small catchments of rural areas. Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen.
Gocht, T., Klemm, O., & Grathwohl, P. (2007). Long-term atmospheric bulk deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in rural areas of Southern Germany. Atmospheric Environment, 41(6), 1315–1327.
Gune, M., Ma, W.-L., Sampath, S., Li, W., Li, Y.-F., Udayashankar, H., Balakrishna, K., & Zhang, Z. (2017). Occurrence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in air and soil surrounding a coal-fired thermal power plant in the south west coast of India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05380-y
Han, Y., Bandowe, B. A. M., Schneider, T., Pongpiachan, S., Ho, S. S. H., Wei, C., Wang, Q., Xing, L., & Wilcke, W. (2021). A 150-year record of black carbon (soot and char) and polycyclic aromatic compounds deposition in Lake Phayao, north Thailand. Environmental Pollution, 269, 116148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116148PMID-33310199
He, Q., Zhang, L., Cui, Y., Cheng, M., Guo, L., Liu, M., & Chen, L. (2017). Particle dry deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and its risk assessment in a typical coal-polluted and basin city, northern China. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 8(6), 1081–1089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2017.04.008
Hien, T. T., Kameda, T., Takenaka, N., & Bandow, H. (2007). Distribution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with particle size in urban aerosols at the roadside in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Atmospheric Environment, 41(8), 1575–1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.10.045
Hong, W.-J., Li, Y.-F., Li, W.-L., Jia, H., Minh, N. H., Sinha, R. K., Moon, H.-B., Nakata, H., Chi, K. H., & Kannan, K. (2020). Soil concentrations and soil-air exchange of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in five Asian countries. Science of the Total Environment, 711, 135223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135223
Johnsen, A. R., Wick, L. Y., & Harms, H. (2005). Principles of microbial PAH-degradation in soil. Environmental Pollution, 133(1), 71–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.04.015
Karaca, G. (2016). Spatial distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) concentrations in soils from Bursa, Turkey. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 70(2), 406–417.
Kim, K.-H., Jahan, S. A., Kabir, E., & Brown, R. J. (2013). A review of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their human health effects. Environment International, 60, 71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2013.07.019
Kim, S.-K., Lee, D. S., Shim, W. J., Yim, U. H., & Shin, Y.-S. (2009). Interrelationship of pyrogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) contamination in different environmental media. Sensors, 9(12), 9582–9602. https://doi.org/10.3390/s91209582
Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A., Smreczak, B., & Ukalska-Jaruga, A. (2017). The impact of selected soil organic matter fractions on the PAH accumulation in the agricultural soils from areas of different anthropopressure. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(12), 10955–10965. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6610-8
Kong, S., Li, X., Li, L., Yin, Y., Chen, K., Yuan, L., Zhang, Y., Shan, Y., & Ji, Y. (2015). Variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric PM2. 5 during winter haze period around 2014 Chinese Spring Festival at Nanjing: Insights of source changes, air mass direction and firework particle injection. Science of the Total Environment, 520, 59–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.001
Kozielska, B. (2018). Health hazards from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons bound to submicrometer particles in Gliwice (Poland). MATEC Web of Conferences, EDP Sciences, 247, 00034.
Kozielska, B., Rogula-Kozłowska, W., & Klejnowski, K. (2015). Selected organic compounds in fine particulate matter at the regional background, urban background and urban traffic points in Silesia (Poland). International Journal of Environmental Research, 9(2), 575–584.
Krauß, M., Wilcke, W., & Zech, W. (2000). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls in forest soils: Depth distribution as indicator of different fate. Environmental Pollution, 110(1), 79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00280-8
Kumar, A., Sankar, T. K., Sethi, S. S., & Ambade, B. (2020). Characteristics, toxicity, source identification and seasonal variation of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons over East India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(1), 678–690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06882-5
Lin, Y., Qiu, X., Ma, Y., Ma, J., Zheng, M., & Shao, M. (2015). Concentrations and spatial distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and nitrated PAHs (NPAHs) in the atmosphere of North China, and the transformation from PAHs to NPAHs. Environmental Pollution, 196, 164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.10.005
Liu, G., Yu, L., Li, J., Liu, X., & Zhang, G. (2011). PAHs in soils and estimated air–soil exchange in the Pearl River Delta, south China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 173(1–4), 861–870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1429-0
Liu, X., Zhao, D., Peng, L., Bai, H., Zhang, D., & Mu, L. (2019). Gas–particle partition and spatial characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ambient air of a prototype coking plant. Atmospheric Environment, 204, 32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.02.012
Liu, Y., Gao, Y., Yu, N., Zhang, C., Wang, S., Ma, L., Zhao, J., & Lohmann, R. (2015). Particulate matter, gaseous and particulate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in an urban traffic tunnel of China: Emission from on-road vehicles and gas-particle partitioning. Chemosphere, 134, 52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.065
Lors, C., Damidot, D., Ponge, J.-F., & Périé, F. (2012). Comparison of a bioremediation process of PAHs in a PAH-contaminated soil at field and laboratory scales. Environmental Pollution, 165, 11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.02.004
Luo, L., Lin, S., Huang, H., & Zhang, S. (2012). Relationships between aging of PAHs and soil properties. Environmental Pollution, 170, 177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.07.003
Ma, W.-L., Zhu, F.-J., Hu, P.-T., Qiao, L.-N., & Li, Y.-F. (2020). Gas/particle partitioning of PAHs based on equilibrium-state model and steady-state model. Science of the Total Environment, 706, 136029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136029
Ma, Y.-G., Lei, Y. D., Xiao, H., Wania, F., & Wang, W.-H. (2010). Critical review and recommended values for the physical-chemical property data of 15 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at 25 C. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 55(2), 819–825. https://doi.org/10.1021/je900477x
Maliszewska-Kordybach, B., Smreczak, B., & Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A. (2009). Concentrations, sources, and spatial distribution of individual polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in agricultural soils in the Eastern part of the EU: Poland as a case study. Science of the Total Environment, 407(12), 3746–3753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.01.010
Martellini, T., Giannoni, M., Lepri, L., Katsoyiannis, A., & Cincinelli, A. (2012). One year intensive PM2. 5 bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons monitoring in the area of Tuscany, Italy. Concentrations, source understanding and implications. Environmental Pollution, 164, 252–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.12.040
Martin, H. (2000). Development of passive samplers for time-integrated deposition and groundwater monitoring: Adsorption cartridges and ceramic dosimeters. Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen.
Mastral, A. M., & Callen, M. S. (2000). A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) emissions from energy generation. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(15), 3051–3057. https://doi.org/10.1021/es001028d
Means, B. (1989). Risk-assessment guidance for superfund. Volume 1. Human health evaluation manual. Part A. Interim report (Final), Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC (USA). Office of Solid Waste.
Meierdierks, J. (2019) Soil-atmosphere exchange of PAHs: The determination of concentration gradients with passive samplers, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen.
Müller, J. (1984). Atmospheric residence time of carbonaceous particles and particulate PAH-compounds. Science of the Total Environment, 36, 339–346.
Nadal, M., Schuhmacher, M., & Domingo, J. (2004). Levels of PAHs in soil and vegetation samples from Tarragona County, Spain. Environmental Pollution, 132(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.04.003
Nam, J. J., Sweetman, A. J., & Jones, K. C. (2009). Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in global background soils. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 11(1), 45–48. https://doi.org/10.1039/B813841A
Nam, J. J., Thomas, G. O., Jaward, F. M., Steinnes, E., Gustafsson, O., & Jones, K. C. (2008). PAHs in background soils from Western Europe: Influence of atmospheric deposition and soil organic matter. Chemosphere, 70(9), 1596–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.08.010
Nasrabadi, T., Ruegner, H., Schwientek, M., Ghadiri, A., Hashemi, S. H., & Grathwohl, P. (2021). Dilution of PAHs loadings of particulate matter in air, dust and rivers in urban areas: A comparative study (Tehran megacity, Iran and city of Tübingen, SW-Germany). Science of the Total Environment, 806, 151268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151268.
Oliveira, M., Slezakova, K., Delerue-Matos, C., do Carmo Pereira, M., & Morais, S. (2016). Assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in indoor and outdoor air of preschool environments (3–5 years old children). Environmental Pollution, 208, 382–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.10.004
Omar, N. Y. M., Abas, M. R. B., Ketuly, K. A., & Tahir, N. M. (2002). Concentrations of PAHs in atmospheric particles (PM-10) and roadside soil particles collected in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Atmospheric Environment, 36(2), 247–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00425-3
Peng, C., Chen, W., Liao, X., Wang, M., Ouyang, Z., Jiao, W., & Bai, Y. (2011). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soils of Beijing: Status, sources, distribution and potential risk. Environmental Pollution, 159(3), 802–808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.11.003
Peng, C., Ouyang, Z., Wang, M., Chen, W., Li, X., & Crittenden, J. C. (2013). Assessing the combined risks of PAHs and metals in urban soils by urbanization indicators. Environmental Pollution, 178, 426–432.
Pham, C. T., Tang, N., Toriba, A., & Hayakawa, K. (2015). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and nitropolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric particles and soil at a traffic site in Hanoi, Vietnam. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, 35(5), 355–371.
Qu, C., Albanese, S., Lima, A., Hope, D., Pond, P., Fortelli, A., Romano, N., Cerino, P., Pizzolante, A., & De Vivo, B. (2019). The occurrence of OCPs, PCBs, and PAHs in the soil, air, and bulk deposition of the Naples metropolitan area, southern Italy: Implications for sources and environmental processes. Environment International, 124, 89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.12.031
Quezada-Maldonado, E. M., Sánchez-Pérez, Y., Chirino, Y. I., & García-Cuellar, C. M. (2021). Airborne Particulate Matter induces oxidative damage, DNA adduct formation and alterations in DNA repair pathways. Environmental Pollution. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117313
Ravindra, K., Sokhi, R., & Van Grieken, R. (2008). Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source attribution, emission factors and regulation. Atmospheric Environment, 42(13), 2895–2921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.12.010
Rogula-Kozłowska, W., Kozielska, B., Błaszczak, B. & Klejnowski, K. (2012). The mass distribution of particle-bound PAH among aerosol fractions: A case-study of an urban area in Poland. In Organic pollutants ten years after the Stockholm convention—Environmental and analytical update (pp. 163–190). InTech: Rijeka, Croatia.
Rogula-Kozłowska, W., Kozielska, B., & Klejnowski, K. (2013). Concentration, origin and health hazard from fine particle-bound PAH at three characteristic sites in Southern Poland. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 91(3), 349–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1060-1
Rogula-Kozłowska, W., Kozielska, B., Majewski, G., Rogula-Kopiec, P., Mucha, W., & Kociszewska, K. (2018). Submicron particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Polish teaching rooms: Concentrations, origin and health hazard. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 64, 235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.06.022
Schwarz, K. (2010) Atmogenic pollutants as reactive tracers for identification and quantification of important transport processes in a karst area at the catchment scale, Universität Tübingen.
Schwarz, K., Gocht, T., & Grathwohl, P. (2011). Transport of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in highly vulnerable karst systems. Environmental Pollution, 159(1), 133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.09.026
Shannigrahi, A., Fukushima, T., & Ozaki, N. (2005). Comparison of different methods for measuring dry deposition fluxes of particulate matter and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the ambient air. Atmospheric Environment, 39(4), 653–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.10.025
Shen, M., Xing, J., Ji, Q., Li, Z., Wang, Y., Zhao, H., Wang, Q., Wang, T., Yu, L., & Zhang, X. (2018). Declining pulmonary function in populations with long-term exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons-enriched PM2. 5. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(11), 6610–6616.
Sheu, H.-L., Lee, W.-J., Lin, S. J., Fang, G.-C., Chang, H.-C., & You, W.-C. (1997). Particle-bound PAH content in ambient air. Environmental Pollution, 96(3), 369–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(97)00044-4
Sicre, M., Marty, J., Saliot, A., Aparicio, X., Grimalt, J., & Albaiges, J. (1987). Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons in different sized aerosols over the Mediterranean Sea: Occurrence and origin. Atmospheric Environment 1967, 21(10), 2247–2259. https://doi.org/10.1016/0004-6981(87)90356-8
Slezakova, K., Castro, D., Delerue-Matos, C., da Conceição Alvim-Ferraz, M., & do MoraisCarmo Pereira, S. M. (2013). Impact of vehicular traffic emissions on particulate-bound PAHs: Levels and associated health risks. Atmospheric Research, 127, 141–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.06.009
Srogi, K. (2007). Monitoring of environmental exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 5(4), 169–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-007-0095-0
Tang, L., Tang, X., Zhu, Y., Zheng, M., & Miao, Q. (2005). Contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban soils in Beijing, China. Environment International, 31(6), 822–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2005.05.031
Tasdemir, Y., & Esen, F. (2007). Dry deposition fluxes and deposition velocities of PAHs at an urban site in Turkey. Atmospheric Environment, 41(6), 1288–1301.
Tiwari, M., Sahu, S., Rathod, T., Bhangare, R., Ajmal, P., & Kumar, A. V. (2020). Measurement of size-fractionated atmospheric particulate matter and associated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Mumbai, India, and their dry deposition fluxes. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, 13(8), 939–949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-020-00849-z
Tobiszewski, M. (2014). Application of diagnostic ratios of PAHs to characterize the pollution emission sources. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology. IPCBEE, 69, 41–44.
USEPA (1991). Risk assessment guidance for superfund, volume 1, human health evaluation manual (part B, development of risk‐based preliminary remediation goals). EPA/540/R-92/003.
Valdivia, A. E. L., Larico, J. A. R., Peña, J. S., & Wannaz, E. D. (2020). Health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) adsorbed in PM 2.5 and PM 10 in a region of Arequipa, Peru. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(3), 3065–3075.
Vane, C. H., Kim, A. W., Beriro, D. J., Cave, M. R., Knights, K., Moss-Hayes, V., & Nathanail, P. C. (2014). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) in urban soils of Greater London, UK. Applied Geochemistry, 51, 303–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.09.013
Wang, C., Wang, X., Gong, P., & Yao, T. (2014). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface soil across the Tibetan Plateau: Spatial distribution, source and air–soil exchange. Environmental Pollution, 184, 138–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.08.029
Wang, G., Kawamura, K., Xie, M., Hu, S., Gao, S., Cao, J., An, Z., & Wang, Z. (2009). Size-distributions of n-alkanes, PAHs and hopanes and their sources in the urban, mountain and marine atmospheres over East Asia. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 9(22), 8869–8882. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-9-8869-2009
Wang, Q., Dong, Z., Guo, Y., Yu, F., Zhang, Z., & Zhang, R. (2020). Characterization of PM 2.5-Bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at two central China cities: Seasonal variation, sources, and health risk assessment. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 78(1), 20–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-019-00671-4
Wang, Q., Liu, M., Li, Y., Liu, Y., Li, S., & Ge, R. (2016). Dry and wet deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and comparison with typical media in urban system of Shanghai, China. Atmospheric Environment, 144, 175–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.08.079
Wang, R., Liu, G., Chou, C.-L., Liu, J., & Zhang, J. (2010). Environmental assessment of PAHs in soils around the Anhui Coal District, China. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 59(1), 62–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9440-6
Wang, S., Ji, Y., Zhao, J., Lin, Y., & Lin, Z. (2020). Source apportionment and toxicity assessment of PM2. 5-bound PAHs in a typical iron-steel industry city in northeast China by PMF-ILCR. Science of the Total Environment, 713, 136428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136428
Wang, W., Simonich, S. L. M., Wang, W., Giri, B., Zhao, J., Xue, M., Cao, J., Lu, X., & Tao, S. (2011). Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon concentrations and gas/particle partitioning at background, rural village and urban sites in the North China Plain. Atmospheric Research, 99(2), 197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2010.10.002
Wang, Y., Bao, M., Zhang, Y., Tan, F., Zhao, H., Zhang, Q., & Li, Q. (2020). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the atmosphere and soils of Dalian, China: Source, urban-rural gradient, and air-soil exchange. Chemosphere, 244, 125518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125518
Wick, A.F., Haus, N.W., Sukkariyah, B.F., Haering, K.C. & Daniels, W.L. (2011). Remediation of PAH-contaminated soils and sediments: a literature review. CSES Department, internal research document, 102.
Wilcke, W. (2000). Synopsis polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soil—a review. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 163(3), 229–248. https://doi.org/10.1002/1522-2624(200006)163:3%3c229::AID-JPLN229%3e3.0.CO;2-6
Wilcke, W. (2007). Global patterns of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soil. Geoderma, 141(3–4), 157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.07.007
Wilcke, W., Krauss, M., Safronov, G., Fokin, A. D., & Kaupenjohann, M. (2005). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soils of the Moscow Region—concentrations, temporal trends, and small-scale distribution. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34(5), 1581–1590. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2005.0005
Wu, J., Sha, C., Li, D., Shen, C., Tang, H., & Huang, S. (2021). Spatial and seasonal variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (Pahs) deposition flux and sources in shanghai. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-902028/v1.
Wu, S., Tao, S., Xu, F., Dawson, R., Lan, T., Li, B., & Cao, J. (2005). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in dustfall in Tianjin, China. Science of the Total Environment, 345(1–3), 115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.11.003
Yamasaki, H., Kuwata, K., & Miyamoto, H. (1982). Effects of ambient temperature on aspects of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environmental Science & Technology, 16(4), 189–194.
Yang, X., Ren, D., Sun, W., Li, X., Huang, B., Chen, R., Lin, C., & Pan, X. (2015). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with total suspended particles and surface soils in Kunming, China: Distribution, possible sources, and cancer risks. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(9), 6696–6712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3858-8
Yunker, M. B., Macdonald, R. W., Vingarzan, R., Mitchell, R. H., Goyette, D., & Sylvestre, S. (2002). PAHs in the Fraser River basin: A critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Organic Geochemistry, 33(4), 489–515.
Zhang, H., Luo, Y., Wong, M. H., Zhao, Q., & Zhang, G. L. (2006). Distributions and concentrations of PAHs in Hong Kong soils. Environmental Pollution, 141(1), 107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.08.031
Zhang, X.-X., Cheng, S.-P., Cheng-Jun, Z., & Shi-Lei, S. (2006). Microbial PAH-degradation in soil: Degradation pathways and contributing factors. Pedosphere, 16(5), 555–565.
Zhang, Y., Deng, S., Liu, Y., Shen, G., Li, X., Cao, J., Wang, X., Reid, B., & Tao, S. (2011). A passive air sampler for characterizing the vertical concentration profile of gaseous phase polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in near soil surface air. Environmental Pollution, 159(3), 694–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.12.002
Zhong, Y., & Zhu, L. (2013). Distribution, input pathway and soil–air exchange of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Banshan Industry Park, China. Science of the Total Environment, 444, 177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.091
Funding
Thanks for the support of China Scholarship Council- Eberhard Karls University Of Tübingen PhD Program to Jialin Liu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL performed the preliminary data collection and analysis, and was a major contributor in wring the manuscript. JJ and PG reviewed and revised the article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Jia, J. & Grathwohl, P. Dilution of concentrations of PAHs from atmospheric particles, bulk deposition to soil: a review. Environ Geochem Health 44, 4219–4234 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01216-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01216-w