Abstract
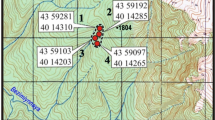
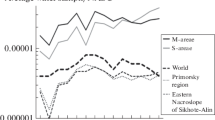
To test the “rare earth” hypothesis of geophagy, geological and hydrogeochemical studies unparalleled anywhere in the world were carried out at kudurs (salt licks) in two districts in the Primorsky Krai, Russia. The mineral and chemical compositions of geophagic earth consumed by animals, the chemical composition of surface waters and vegetation, and the chemical composition of biological tissues of red deer (Cervus elaphus) were studied in this research. It was found that ultra-fresh surface and fontinal waters in the studied areas contain anomalously high concentrations of rare earth elements (REE), the sums of which exceeded the average values in the Primorsky Krai and worldwide by tenfold, and more. The presence of landscape REE anomalies is confirmed by elevated concentrations of these elements in vegetation. Using electron microscopy, it was determined that the sources of REE in landscape components are rocks containing secondary, readily soluble, REE minerals (hydrophosphates and fluorocarbonates). The study of the chemical composition of animal tissues showed the presence of significant concentrations of heavy REE (HREE) in the blood and brain, which indirectly indicates a high probability of animals developing stress reactions against the background REE-elementosis. Eaten earthy substances in both areas are represented by mixtures of smectite clays and zeolites with high ion-exchange properties. In the digestive tract of animals, such sorbents actively interact with the biological electrolyte, saturating it with sodium ions and absorbing HREE. The main meaning of geophagy is regulation of the concentration and proportion of REE in the body. Sometimes it manifests itself in intake of significant amounts of Na.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anawar, H. M., Freitasdo, M. C., Canha, N., Dionísio, I., Dung, M. H., Galinha, C., & Pacheco, A. M. G. (2012). Assessment of bioaccumulation of REEs by plant species in a mining area by INAA. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 294(3), 377–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-1669-2
Anderson, C. R., & Pedersen, K. (2003). In situ growth of Gallionella biofilms and partitioning of lanthanides and actinides between biological material and ferric oxyhydroxides. Geobiology, 1(2), 169–178. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1472-4669.2003.00013.x
Anell, B., & Lagercrantz, S. (1958). Geophagical customs. In Studia ethnographica Upsaliensia 17
Barmettler, F., Castelberg, C., Fabbri, C., & Brandl, H. (2016). Microbial mobilization of rare earth elements (REE) from mineral solids—A mini review. AIMS Microbiology, 2(2), 190–204. https://doi.org/10.3934/microbiol.2016.2.190
Blair-West, J. R., Bott, E., Coghlan, J., Denton, D. A., Goding, J. R., & Wintour, M. (1964). The regulation of electrolyte metabolism of ruminant animals in arid zones. In Environmental Physiology and Psychology in Arid Conditions. In Proceedings of the Lucknow Symposium (pp. 289–299).
Blair-West, J. R., Coghlan, J. P., Denton, D. A., Nelson, J. F., Orchard, E., Scoggins, B. A., et al. (1968). Physiological, morphological and behavioural adaptation to a sodium deficient environment by wild native Australian and introduced species of animals. Nature, 217(5132), 922–928. https://doi.org/10.1038/217922a0
Blair-West, J., Denton, D., Gellatly, D., McKinley, M., Nelson, J., & Weisinger, R. (1987). Changes in sodium appetite in cattle induced by changes in CSF sodium concentration and osmolality. Physiology and Behavior, 39(4), 465–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9384(87)90374-X
Bromley, G. F., & Kucherenko, S. P. (1983). Noble deer or ibex (Cervus elaphus L., 1758) // in book: Ungulates of the South of the Far East. - Moscow: Nauka, 1983 (pp. 158–193).
Bukhman, G., Ziegler, J., & Parry, E. (2008). Endomyocardial fibrosis: Still a mystery after 60 Years. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2(2), e97. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0000097
Burchfield, S. R., Elich, M. S., & Woods, S. C. (1977). Geophagia in response to stress and arthritis. Physiology and Behavior, 19(2), 265–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9384(77)90337-7
Cao, X., Chen, Y., Gu, Z., & Wang, X. (2000). Determination of trace rare earth elements in plant and soil samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 76(4), 295–309. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067310008034137
Chekryzhov, I. Y., Popov, V. K., Panichev, A. N., Seredin, V. V., & Smirnova, E. V. (2010). New data on the stratigraphy, volcanism, and zeolite mineralization of the Cenozoic Vanchinskaya depression in primorye. Russian Journal of Pacific Geology, 4(4), 314–330. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819714010040044
Cragin, F. W. (1836). Art. VIII. Observations on cachexia africana or dirt-eating. The American Journal of the Medical Sciences, 17(34), 356–364. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000441-183617340-00008
de Araújo, A. L. L., De Nadai Fernandes, E. A., Bacchi, M. A., & De França, E. J. (2012). Bioaccumulation pattern of lanthanides in pteridophytes and magnoliophytes species from Atlantic forest. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 291(1), 187–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-011-1283-8
Denton, D. A. (1965). Evolutionary aspects of the emergence of aldosterone secretion and salt appetite. Physiological Reviews, 45(2), 245–295. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1965.45.2.245
Denton, D. A., Coding, J. R., Sabine, J. R., & Wright, R. D. (1961). Adaptation of ruminant animals to variation of salt intake. In Salinity Problems in the Arid Zones. In Proceedings of Teheran Symposium (pp. 3–8). Paris: UNESCO.
Dudeney, A. W. L., & Sbai, M. L. (1993). Bioleaching of rare-earth-bearing phosphogypsum. In International biohydrometallurgy symposium (pp. 39–43).
Eapen, J. T. (1998). Elevated levels of cerium in tubers from regions endemic for endomyocardial fibrosis (EMF). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 60(1), 168–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001289900606
Feng, L., Xiao, H., He, X., Li, Z., Li, F., Liu, N., et al. (2006). Neurotoxicological consequence of long-term exposure to lanthanum. Toxicology Letters, 165(2), 112–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2006.02.003
Fu, F. F., Akagi, T., Yabuki, S., & Iwaki, M. (2001). The variation of REE (rare earth elements) patterns in soil-grown plants: A new proxy for the source of rare earth elements and silicon in plants. Plant and Soil, 235(1), 53–64. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011837326556
Gaillardet, J., Viers, J., & Dupré, B. (2003). Trace elements in river waters in treatise on geochemistry. Elsevier.
Gromet, L. P., Haskin, L. A., Korotev, R. L., & Dymek, R. F. (1984). The “North American shale composite”: Its compilation, major and trace element characteristics. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 48(12), 2469–2482. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(84)90298-9
Kutty, V. R., Abraham, S., & Kartha, C. C. (1996). Geographical distribution of endomyocardial fibrosis in South Kerala. International Journal of Epidemiology, 25(6), 1202–1207. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/25.6.1202
Lebedeva, E., Panichev, A., Kharitonova, N., Kholodov, A., & Golokhvast, K. (2020). Diversity, abundance, and some characteristics of bacteria isolated from earth material consumed by wild animals at kudurs in the Sikhote-Alin Mountains, Russia. International Journal of Microbiology, 2020, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8811047
Li, F., Shan, X., Zhang, T., & Zhang, S. (1998). Evaluation of plant availability of rare earth elements in soils by chemical fractionation and multiple regression analysis. Environmental Pollution, 102(2–3), 269–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(98)00063-3
Li, X., Chen, Z., Chen, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2013). A human health risk assessment of rare earth elements in soil and vegetables from a mining area in Fujian Province. Southeast China. Chemosphere, 93(6), 1240–1246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.06.085
Liu, J., Shen, Z., Yang, W., Che, J., Xie, L., & Lei, H. (2002). Effect of long-term intake of rare earth in drinking water on trace elements in brains of mice. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 562–564. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/84120x/200205/11260071.html.
Marzec-Wróblewska, U., Kamiński, P., Łakota, P., Ludwikowski, G., Szymański, M., Wasilow, K., et al. (2015). Determination of rare earth elements in human sperm and association with semen quality. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 69(2), 191–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-015-0143-x
Mason, D. (1833). On Atrophia a Ventriculo (Mal d’Estomac,) or dirt-eating. Edinburgh Medical and Surgical Journal, 39(115), 289–296.
McNeill, K. (1987). A history of medicine and surgery in Jamaica. Journal of the Medical Association of Jamaica, 1, 7–12.
Meryem, B., Hongbing, J. L., Yang, G., Ding, H., & Li, C. (2016). Distribution of rare earth elements in agricultural soil and human body (scalp hair and urine) near smelting and mining areas of Hezhang China. Journal of Rare Earths, 34(11), 1156–1167. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(16)60148-5
Meybeck, M. (2003). Global occurrence of major elements in rivers in treatise on geochemistry. Elsevier.
Ozaki, T., Ambe, S., Enomoto, S., Minai, Y., Yoshida, S., & Makide, Y. (2002). Multitracer study on the uptake mechanism of yttrium and rare earth elements by autumn fern. Radiochimica Acta. https://doi.org/10.1524/ract.2002.90.5_2002.303
Panichev, A. M. (2011). Lithophagy: Geological, ecological and biomedical aspects (p. 148). Publish. House "Nauka", Moscow. ISBN 978-5-02-037491-1
Panichev, A. M. (2015). Rare earth elements: review of medical and biological properties and their abundance in the rock materials and mineralized spring waters in the context of animal and human geophagia reasons evaluation. Achievements in the Life Sciences, 9(2), 95–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.als.2015.12.001
Panichev, A. M. (2016). Lithophagy: Reasons of the phenomenon [Litofagija: Prichiny fenomena]. Priroda, 4, 25–35.
Panichev, A. M., Golokhvast, K. S., Gulkov, A. N., & Chekryzhov, I. Y. (2013). Geophagy in animals and geology of kudurs (mineral licks): A review of Russian publications. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 35(1), 133–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-012-9464-0
Panichev, A. M., Popov, V. K., Chekryzhov, I. Y., Seryodkin, I. V., Sergievich, A. A., & Golokhvast, K. S. (2017). Geological nature of mineral licks and the reasons for geophagy among animals. Biogeosciences, 14(11), 2767–2779. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-14-2767-2017
Panichev, A. M., Popov, V. K., Chekryzhov, I. Y., Seryodkin, I. V., Stolyarova, T. A., Zakusin, S. V., et al. (2016). Rare earth elements upon assessment of reasons of the geophagy in Sikhote-Alin region (Russian Federation), Africa and other world regions. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 38(6), 1255–1270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9788-7
Panichev, A. M., Seryodkin, I. V., Kalinkin, Y. N., Makarevich, R. A., Stolyarova, T. A., Sergievich, A. A., & Khoroshikh, P. P. (2018). Development of the “rare-earth” hypothesis to explain the reasons of geophagy in Teletskoye Lake are kudurs (Gorny Altai, Russia). Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 40(4), 1299–1316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0056-x
Panichev, A. M., Trepet, S. A., Chekryzhov, I. Y., Loktionova, O. A., & Krupskaya, V. V. (2014). Causes of geophagy by ungulate animals in the Caucasus mountains. Achievements in the Life Sciences, 8(1), 35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.als.2014.11.002
Protano, G., & Riccobono, F. (2002). High contents of rare earth elements (REEs) in stream waters of a Cu–Pb–Zn mining area. Environmental Pollution, 117(3), 499–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00173-7
Redling, K. (2006). Rare earth elements in agriculture with emphasis on animal husbandry (p. 360). Dissertation Thesis, Veterinary Faculty, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München. https://doi.org/10.5282/edoc.5936
Seredin, V. V., & Chekryzhov, I. Y. (2011). Ore potentiality of the Vanchin Graben, Primorye Russia. Geology of Ore Deposits, 53(3), 202–220. https://doi.org/10.1134/S107570151103007X
Smith, B., Chenery, S. R., Cook, J., Styles, M., Tiberindwa, J., Hampton, C., et al. (1998). Geochemical and environmental factors controlling exposure to cerium and magnesium in Uganda. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 65(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6742(98)00066-1
Stankevich, S. S., Barabash, N. A., & Baranovskaya, N. V. (2013). Micronutrient composition of women’s breast milk, who live in industrial cities. International youth school “geochemistry of living substance” (pp. 94–99). Tomsk Polytechnic University.
Stockstad, D. S., Morris, M. S., & Lory, E. C. (1953). Chemical characteristics of natural licks used by big game animals in western Montana. In Transactions of the North American Wildlife and Natural Resources Conference (Vol. 18, pp. 247–257). Washington, D.C.: Wildlife Management Institute.
Sun, S., & McDonough, W. F. (1989). Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1), 313–345. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Tyler, G., & Olsson, T. (2005). Rare earth elements in forest-floor herbs as related to soil conditions and mineral nutrition. Biological Trace Element Research, 106(2), 177–192. https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:106:2:177
Vakh, E. A. (2014). Geochemistry of rare earth elements in natural and technogenic waters in the south of the Russian Far East. Russia: Far Eastern Federal University.
Vetrennikov, V. V. (1976). Geological framework of the Sikhote-Alin State Nature Reserve and the Central Sikhote-Alin. Far Eastern Book Publishers.
Vodyanitskii, Y. N., & Rogova, O. B. (2016). The biogeochemistry of lantanides in soils. Dokuchaev Soil Bulletin, 84, 101–118. https://doi.org/10.19047/0136-1694-2016-84-101-118
Wei, B., Li, Y., Li, H., Yu, J., Ye, B., & Liang, T. (2013). Rare earth elements in human hair from a mining area of China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 96, 118–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.05.031
Zhenggui, W., Ming, Y., Xun, Z., Fashui, H., Bing, L., Ye, T., et al. (2001). Rare earth elements in naturally grown fern Dicranopteris linearis in relation to their variation in soils in South-Jiangxi region (Southern China). Environmental Pollution, 114(3), 345–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00240-2
Zhenghua, W., Jun, L., Hongyan, G., Xiaorong, W., & Chunsheng, Y. (2001). Adsorption isotherms of lanthanum to soil constituents and effects of pH, EDTA and fulvic acid on adsorption of lanthanum onto goethite and humic acid. Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability, 13(3), 75–81. https://doi.org/10.3184/09542290178277544
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the administration and staff of the Sikhote-Alin Nature Reserve and the Joint Directorate of the Lazovsky Reserve and the Call of the Tiger National Park for their assistance in the research. Special thanks to N.V. Zarubina, G.A. Gorbach, E.A. Tkalina, N.V. Khurkalo, Yu.M. Ivanova, E.V. Elovsky, N.V. Gruda, who took part in the preparation and analysis of the factual material.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Russian Science Foundation (Projects No. 20–67-47005 and 20–67-47021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no any conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panichev, A.M., Baranovskaya, N.V., Seryodkin, I.V. et al. Landscape REE anomalies and the cause of geophagy in wild animals at kudurs (mineral salt licks) in the Sikhote-Alin (Primorsky Krai, Russia). Environ Geochem Health 44, 1137–1160 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01014-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01014-w