Abstract
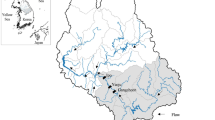
Eutrophication level in lakes and reservoirs depends on both internal and external phosphorus (P) load. Characterization of sediment P fractionation and identifying the P pollution sources are important for assessing the bio-availability of P and the dominant P source, for effectively controlling the water pollution. For determining the availability and sources of sediment P and eutrophication status, spatio-temporal variation in different P fractionation of sediment of hyper-eutrophic Krishnagiri reservoir, Tamil Nadu, India, was investigated. Sediment average total P (TP) content ranged from 4.62 to 5.64 g/kg. Main phosphorus form was the inorganic P (IP), and it makes up to 73.4–87.7% of TP. Among the different P fraction, viz. calcium bound (Ca-P), iron bound (Fe–P), aluminium bound (Al-P), exchangeable (Ex-P) and Organic-P (Org-P), Ca-P was the dominating fraction in both IP and TP. Trend of IP fraction was as follows: Ca-P > Fe–P > Al-P > Ex-P in pre-monsoon season, Fe–P > Ca-P > Al-P > Ex-P in monsoon and Ca-P > Al-P > Fe–P > Ex-P in post-monsoon. Overall the trend was as follows Ca-P > Fe–P > Al-P > Org-P > Ex-P. Bio-available-P (BAP) fractions ranged from 35.2 to 64.0% of TP, indicating its comparative higher value. Pearson’s correlation matrix revealed that there was strong correlation among the different P fractions. Factor analysis indicates that different fractions of P were the dominating factor than the other sediment parameters. The observed variation in sediment P fractionation indicate the differences in source and characterization of P which is very helpful for implementation of effective management practices in controlling pollution that arises due to phosphorus in this hyper-eutrophic reservoir.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated and analysed during the present investigation are not publicly available and upon request data can be available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adhikari, P. L., White, J. R., Maiti, K., & Nguyen, N. (2015). Phosphorus speciation and sedimentary phosphorus release from the Gulf of Mexico sediments: Implication for hypoxia. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 164, 77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2015.07.016
Ambujam, N. K., & Sudha, V. (2016). Environmental impacts of point and non-point source pollution in Krishnagiri reservoir: A case study in South India. International Journal of Environmental and Ecological Engineering, 10(4), 443–449. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1123903
Andrieux-Loyer, F., & Aminot, A. (2001). Phosphorus forms related to sediment grain size and geochemical characteristics in French coastal areas. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 52(5), 617–629. https://doi.org/10.1006/ecss.2001.0766
Anonymous. (2019). District Environmental Plan Krishnagiri District. (As per Hon’ble NGT in O.A.No.710–713/2017 dated 15.07.2019). Retrieved February 26, 2021, from https://cdn.s3waas.gov.in/s37eacb532570ff6858afd2723755ff790/uploads/2019/11/2019112965.pdf.
Anshumali, & Ramanathan, A. L. (2007). Phosphorus fractionation in surficial sediments of Pandoh Lake, Lesser Himalaya, Himachal Pradesh, India. Appllied Geochemistry, 22(9), 1860–1871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2007.03.050
APHA, AWWA, WPCF. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st ed. American Publication of Health Association, Washington, DC
Arunbabu, E., Ravichandran, S., & Sreeja, P. (2014). Sedimentation and internal phosphorus loads in Krishnagiri Reservoir, India. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research & Management, 19(3), 161–173. https://doi.org/10.1111/lre.12069
Barik, S. K., Bramha, S., Bastia, T. K., Behera, D., Kumar, M., Mohanty, P. K., et al. (2019a). Characteristics of geochemical fractions of phosphorus and its bioavailability in sediments of a largest brackish water lake, South Asia. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology, 19(3), 370–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2019.02.002
Barik, S. K., Bramha, S., Bastia, T. K., Behera, D., Mohanty, P. K., & Rath, P. (2019b). Distribution of geochemical fractions of phosphorus and its ecological risk in sediment cores of a largest brackish water lake, South Asia. International Journal of Sediment Research, 34(3), 251–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2018.11.004
Barik, S. K., Bramha, S. N., Mohanty, A. K., Bastia, T. K., Behera, D., & Rath, P. (2016). Sequential extraction of different forms of phosphorus in the surface sediments of Chilika Lake. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9(2), 135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2217-5
Bastami, K. D., Neyestani, M. R., Raeisi, H., Shafeian, E., Baniamam, M., Shirzadi, A., et al. (2018). Bioavailability and geochemical speciation of phosphorus in surface sediments of the Southern Caspian Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletein, 126, 51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.10.095
Biswas, T. D., & Mukherjee, S. K. (1988). Soil science textbook. Total McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited.
Cavalcante, H., Araújo, F., Noyma, N. P., & Becker, V. (2018). Phosphorus fractionation in sediments of tropical semiarid reservoirs. Science of the Total Environment, 619, 1022–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.204
Chandran, R., & Ramamoorthi, K. (1984). Hydrobiological studies in the gradient zone of the Vellar Estuary: 1. Physico-Chemical Parameters. Mahasagar, 17(2), 69–77.
Chen, Y. S., Beveridge, M. C. M., & Telfer, T. C. (1999). Settling rate characteristics and nutrient content of the faeces of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., and the implications for modelling of solid waste dispersion. Aquaculture Research, 30(5), 395–398. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2109.1999.00334.x
Cheng, H., Pu, X., Chen, Y., Hao, F., & Dong, L. (2014). Characterization of phosphorus species and modeling for its organic forms in eutrophic shallow lake sediments, North China. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 8(6), 905–921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-014-0650-4
Compton, J. S., Mallinson, D. J., & Glenn, C. R. (2000). Variations in the global phosphorus cycle. In C. R. Glenn (Ed.), Marine authigenesis: from global to microbial (pp. 21–33). Society for Sedimentary Geology (SEPM).
Dan, S. F., Liu, S. M., & Yang, B. (2020). Geochemical fractionation, potential bioavailability and ecological risk of phosphorus in surface sediments of the Cross River estuary system and adjacent shelf, South East Nigeria (West Africa). Journal of Marine Systems, 201, 103244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2019.103244
Da-Peng, L., & Yong, H. (2010). Sedimentary phosphorus fractions and bioavailability as influenced by repeated sediment resuspension. Ecological Engeneering, 36(7), 958–962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2010.04.014
Das, J., Daroub, S. H., Bhadha, J. H., Lang, T. A., & Josan, M. (2012). Phosphorus release and equilibrium dynamics of canal sediments within the everglades agricultural area, Florida. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 223, 2865–2879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1152-2
Diaz, O. A., Reddy, K. R., & Moor, J. (1994). Solubility of inorganic P in stream water as influenced by pH and calcium concentration. Water Research, 28(8), 1755–1763. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(94)90248-8
Dong, L., Yang, Z., & Liu, X. (2011). Phosphorus fractions, sorption characteristics, and its release in the sediments of Baiyangdian Lake, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 179(1–4), 335–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1740-9
Elangovan, A., & Murali, V. (2020). Mapping the chlorophyll-a concentrations in hypereutrophic Krishnagiri reservoir (India) using landsat 8 operational land imager. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research & Management, 25(4), 377–387. https://doi.org/10.1111/lre.12346
Frossard, E., Stewart, J. W., & St. Arnaud, R. J. . (1989). Distribution and mobility of phosphorus in grassland and forest soils of Saskatchewan. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 69(2), 401–416. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjss89-040
Gao, L., Yang, H., Zhou, J. M., & Lue, J. J. (2004). Lake sediments from Dianchi Lake: A phosphorus sink or source? Pedosphere, 14, 483–490.
Hedley, M. J., Stewart, J. W. B., & Chauhan, B. (1982). Changes in inorganic and organic soil phosphorus fractions induced by cultivation practices and by laboratory incubations 1. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 46(5), 970–976. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1982.03615995004600050017x
Hou, D., He, J., Lü, C., Dong, S., Wang, J., Xie, Z., et al. (2014). Spatial variations and distributions of phosphorus and nitrogen in bottom sediments from a typical north-temperate lake, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(7), 3063–3079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2683-6
Hou, L. J., Liu, M., Yang, Y., Ou, D. N., Lin, X., Chen, H., et al. (2009). Phosphorus speciation and availability in intertidal sediments of the Yangtze Estuary, China. Appllied Geochemistry, 24(1), 120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.11.008
Jackson ML (1967) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi, India.
Jackson, M. L. (1973). Soil Chemical Analysis. Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd.
Jin, X., Wang, S., Pang, Y., & Wu, F. C. (2006). Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake, China. Environmental Pollution, 139(2), 288–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.05.010
Joy, A., Anoop, P., Rajesh, R., Mathew, J., Mathew, A., & Gopinath, A. (2019). Spatial variation of phosphorus fractionation in the coral reef sediments of Lakshadweep Archipelago, Indian Ocean. Chemistry and Ecology, 35(7), 592–612. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2019.1618281
Kaiserli, A., Voutsa, D., & Samara, C. (2002). Phosphorus fractionation in lake sediments–Lakes Volvi and Koronia, N. Greece. Chemosphere, 46(8), 1147–1155. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00242-9
Kumar, B., & Anshumali. (2019). Phosphorus fractionation in surface water and sediments of industrially polluted freshwater reservoir, India. Chemistry and Ecology, 35(3), 219–234. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2018.1554058
Liu, C. W., Lin, K. H., & Kuo, Y. M. (2003). Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 313(1–3), 77–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00683-6
Millero, F., Huang, F., Zhu, X., Liu, X., & Zhang, J. Z. (2001). Adsorption and desorption of phosphate on calcite and aragonite in seawater. Aquatic Geochemistry, 7(1), 33–56. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011344117092
Mohanakrishnan, S. (1988). The Krishnagiri Reservoir Project—A Technical Document. Anna University Publication.
Mudroch, A., & Azcue, J. M. (1995). Manual of aquatic sediment sampling. Lewis Publishers.
Murphy, J. A., & Riley, J. P. (1962). A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta, 27, 31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88444-5
Nelson, D. W., & Sommer, L. E. (1996). Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. Methods of soil analysis: Part 3 Chemical methods, Vol. 5, pp. 961–1010.
Okello, C., Tomasello, B., Greggio, N., Wambiji, N., & Antonellini, M. (2015). Impact of population growth and climate change on the freshwater resources of Lamu Island, Kenya. Water, 7(3), 1264–1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7031264
Parakkandi, J., Saha, A., Sarkar, U. K., Das, B. K., Puthiyottil, M., Muhammadali, S. A., et al. (2021). Spatial and temporal dynamics of phytoplankton in association with habitat parameters in a tropical reservoir, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 14, 827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07194-0
Pearce, A. R., Chambers, L. G., & Hasenmueller, E. A. (2017). Characterizing nutrient distributions and fluxes in a eutrophic reservoir, Midwestern United States. Science of the Total Environment, 581, 589–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.168
Persaud, D., Jaagumagi, R., & Hayton, A. (1993). Guidelines for the protection and management of aquatic sediment quality in Ontario. Water Resources Branch, Ontario Ministry of the Environment, Toronto.
Prabhakar, C., Saleshrani, K., Tharmaraj, K., & Kumar, V. M. (2012). Investigation of plantktonic diversity in Krishnagiri reservoir, Krishnagiri district, Tamil Nadu, India. International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archive, 3(1), 153–156.
Raja, M., Ramkumar, R., Kavitha, M., Balasubramanian, V., Raja, R. K., Anandhi, M., et al. (2015). Ichthyofauna diversity in relation to water quality and habitat characteristics of Krishnagiri Reservoir, Tamil Nadu, India. International Journal of Pure and Applied Biotechnology IJPAB, 2, 1–15.
Ramanibai, R., & Jeyanthi, S. (2010). Benthic diatom diversity of Krishnagirireservoir. Wetlands, Biodiversity and Climate Change, 22, 1–13.
Ramya, V. L., Parakkandi, J., Saha, A., Salim, S. M., Panikkar, P., Sarkar, U. K., et al. (2021). Habitat based fish assemblage and distribution pattern in a large reservoir of peninsular India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 14, 689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07059-6
Randall, M. C., Carling, G. T., Dastrup, D. B., Miller, T., Nelson, S. T., Rey, K. A., et al. (2019). Sediment potentially controls in-lake phosphorus cycling and harmful cyanobacteria in shallow, eutrophic Utah Lake. PLoS ONE, 14(2), e0212238. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212238
Rapin, A., Rabiet, M., Mourier, B., Grybos, M., & Deluchat, V. (2020). Sedimentary phosphorus accumulation and distribution in the continuum of three cascade dams (Creuse River, France). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 6526–6539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07184-6
Renjith, K. R., Chandramohanakumar, N., & Joseph, M. M. (2011). Fractionation and bioavailability of phosphorus in a tropical estuary, Southwest India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 174(1–4), 299–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1458-8
Renuga, K., & Ramanibai, R. (2010). Zooplankton composition present in Krishnagiri reservoir, Tamilnadu, India. Current Biotica, 3, 4519–4525.
Rose, T. J., Hardiputra, B., & Rengel, Z. (2010). Wheat, canola and grain legume access to soil phosphorus fractions differs in soils with contrasting phosphorus dynamics. Plant and Soil, 326(1–2), 159–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-9990-4
Ruban, V., Brigault, S., Demare, D., & Philippe, A. M. (1999). An investigation of the origin and mobility of phosphorus in freshwater sediments from Bort-Les-Orgues Reservoir, France. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1(4), 403–407. https://doi.org/10.1039/A902269D
Saha, A., Parakkandi, J., Ramya, V. L., Salim, S. M., Panikkar, P., Vjaykumar, M. E., et al. (2021a). Evaluation of spatio-temporal variations in physico-chemical limnology, trophic status and cyanobacterial diversity of an impacted tropical reservoir, India for its sustainable management. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1919654
Saha, A., Ramya, V. L., Jesna, P. K., Mol, S. S., Panikkar, P., Vijaykumar, M. E., et al. (2021b). Evaluation of spatio-temporal changes in surface water quality and their suitability for designated uses, Mettur reservoir, India. Natural Resources Research, 30, 1367–1394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09790-5
Saha, A., Salim, S. M., Sudheesan, D., Suresh, V. R., Nag, S. K., Panikkar, P., et al. (2020a). Impacts of a massive flood event on the physico-chemistry and water quality of river Pampa in Western Ghats of India. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1843026
Saha, A., Salim, S. M., Sudheesan, D., Suresh, V. R., Nag, S. K., Panikkar, P., et al. (2020b). Geochemistry, mineralogy and nutrient concentrations of sediment of River Pampa in India during a massive flood event. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13(20), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06053-8
Saluja, R., & Garg, J. K. (2017). Trophic state assessment of Bhindawas Lake, Haryana India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5735-z
Samanta, S., Debnath, D., Maitra, N., Banerjee, M., Chowdhury, A. N., Sharma, A. P., et al. (2015). Sediment phosphorus forms and levels in two tropical floodplain wetlands. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management, 18(4), 467–474. https://doi.org/10.1080/14634988.2015.1114343
Sarkar, U. K., Sandhya, K. M., Mishal, P., Karnatak, G., Lianthuamluaia, L., Kumari, S., et al. (2017). Status, prospects, threats, and the way forward for sustainable management and enhancement of the tropical Indian reservoir fisheries: an overview. Reviews in Fisheries Science & Aquaculture, 26, 155–175. https://doi.org/10.1080/23308249.2017.1373744
Sasitharan, S., & Elangovan, A. (2020). Sediment and nutrient export modeling in a subwatershed of Krishnagiri resevoir project. Pollution Research, 39(2), 385–392.
Shoja, H., Rahimi, G., Fallah, M., & Ebrahimi, E. (2017). Investigation of phosphorus fractions and isotherm equation on the lake sediments in Ekbatan Dam (Iran). Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(6), 235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6548-2
Soliman, N. F., El Zokm, G. M., & Okbah, M. A. (2017). Evaluation of phosphorus bioavailability in El Mex Bay and Lake Mariut sediments. International Journal of Sediment Research, 32(3), 432–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2017.05.006
Sommers, L. E., Harris, R. F., Williams, J. D., Armstrong, D. E., & Syers, J. K. (1972). Fractionation of organic phosphorus in Lake sediments. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 36(1), 51–54.
Søndergaard, M., Jensen, P. J., & Jeppesen, E. (2003). Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia, 506–509, 135–145. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000008611.12704.dd
Song, K., Adams, C. J., & Burgin, A. J. (2017). Relative importance of external and internal phosphorus loadings on affecting lake water quality in agricultural landscapes. Ecological Engineering, 108, 482–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.06.008
Sposito, G. (2008). The Chemistry of Soils. Oxford University Press Inc.
Sudha, V., & Ambujam, N. K. (2012). Longitudinal heterogeneity of sediment characteristics during southwest monsoon season in hyper-eutrophic Krishnagiri reservoir, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(3), 1287–1298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2040-8
Sudha, V., & Ambujam, N. K. (2013). Characterization of bottom sediments and phosphorus fractions in hyper-eutrophic Krishnagiri reservoir located in an agricultural watershed in India. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 15(2), 481–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-012-9388-y
UNEP. Millennium ecosystem assessment synthesis report. Pre-publication final draft approved by MA board on 23rd march, the United Nations environment programme; 2005.
Upadhyay, R., Pandey, A. K., Upadhyay, S. K., Bassin, J. K., & Misra, S. M. (2012). Limnochemistry and nutrient dynamics in Upper Lake, Bhopal, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(11), 7065–7077. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2480-1
Varol, M. (2020). Spatio-temporal changes in surface water quality and sediment phosphorus content of a large reservoir in Turkey. Environmental Pollution, 259, 113860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113860
Viswanath, R. (2004). Mucky transfer Bangalore's sewage contaminates Tamil Nadu's water. Down to earth. April 30, New Delhi. Retrieved December 7, 2020, from https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/mucky-transfer-11152.
Wang, L., & Liang, T. (2015). Distribution characteristics of phosphorus in the sediments and overlying water of Poyang Lake. PLoS ONE, 10(5), e0125859. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125859
Wang, L., Ye, M., Li, Q., Zou, H., & Zhou, Y. (2013). Phosphorus speciation in wetland sediment of Zhujiang (Pearl) River Estuary, China. Chinese Geographical Science, 23(5), 574–583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-013-0627-4
Wang, Q., Jiang, X., Jin, X., & Xu, Y. (2006). Distribution of phosphorus fractions and bio-available phosphorus forms and their relationship in the sediments from different regions of Lake Taihu. Journal of Lake Science, 18, 120–126.
Wen, S., Wang, H., Wu, T., Yang, J., Jiang, X., & Zhong, J. (2020). Vertical profiles of phosphorus fractions in the sediment in a chain of reservoirs in North China: implications for pollution source, bioavailability, and eutrophication. Science of the Total Environment, 704, 135318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135318
Wen, S. L., Wu, T., Yang, J., Li, X., Gong, W., & Zhong, J. (2019). Distribution characteristics and exchange flux of nitrogen and phosphorus at the sediment-water interface of Daheiting Reservoir in winter. Journal Environmental Science (china), 39(3), 1217–1225.
Xiang, S. L., & Zhou, W. B. (2011). Phosphorus forms and distribution in the sediments of Poyang Lake, China. International Journal of Sediment Research, 26(2), 230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6279(11)60089-9
Yan, N. D. (2005). Research needs for the management of water quality issues, particularly phosphorus and oxygen concentrations, related to salmonid cage aquaculture in Canadian freshwaters. Environmental Reviews, 13(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1139/a05-001
Yang, B., Lan, R. Z., Lu, D. L., Dan, S. F., Kang, Z. J., Jiang, Q. C., et al. (2019). Phosphorus biogeochemical cycling in intertidal surface sediments from the Maowei Sea in the northern Beibu Gulf. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 28, 100624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2019.100624
Yang, B., Liu, S. M., Wu, Y., & Zhang, J. (2016). Phosphorus speciation and availability in sediments off the eastern coast of Hainan Island, South China Sea. Continental Shelf Research, 118, 111–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2016.03.003
Zeinalzadeh, K., & Rezaei, E. (2017). Determining spatial and temporal changes of surface water quality using principal component analysis. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies, 13, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2017.07.002
Zhang, R., Yin, A., & Gao, C. (2019). Sediment phosphorus fraction and release potential in the major inflow rivers of Chaohu Lake, Eastern China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(4), 117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8086-6
Zhang, Y., Gao, X., Wang, C., Chen, C. T., Zhou, F., & Yang, Y. (2016). Geochemistry of phosphorus in sediment cores from Sishili Bay, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 113(1–2), 552–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.08.050
Zhang, Z. B., Tan, X. B., Wei, L. L., Yu, S. M., & Wu, D. J. (2012). Comparison between the lower Nansi Lake and its inflow rivers in sedimentary phosphorus fractions and phosphorus adsorption characteristics. Environmental Earth Sciences, 66(5), 1569–1576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1400-6
Zhou, J., Wu, Y., Kang, Q., & Zhang, J. (2007). Spatial variations of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorous and sulfur in the salt marsh sediments of the Yangtze Estuary in China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 71(1–2), 47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2006.08.012
Zhu, M., Zhu, G., Zhao, L., Yao, X., Zhang, Y., Gao, G., et al. (2013). Influence of algal bloom degradation on nutrient release at the sediment–water interface in Lake Taihu, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(3), 1803–1811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1084-9
Zhuan-xi, L., Tang, J. L., & Wang, T. (2009). P retention capacity of agricultural headwater ditch sediments under alkaline condition in purple soils area. China Ecological Engineering, 35, 57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2008.09.02
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Director, ICAR-Central Inland Fisheries Research Institute, Barrackpore, Kolkata, India for providing facilities to undertake the study. Sincere thanks to Director and staff of Department of Fisheries, Govt. of Tamil Nadu, India. Senior author is thankful to M. Pennappa for helping in collection and analysis of sample.
Funding
This work has been funded by ICAR-Central Inland Fisheries Research Institute, Barrackpore, India, from its institutional research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ajoy Saha contributed to the study conception, sample collection and analysis, data analysis, draft manuscript preparation; Jesna P. K. helped in interpretation of data, manuscript review, and editing; V. L. Ramya contributed to research design, sample collection and analysis; Sibina Mol S helped in data interpretation and manuscript reviewing; Preetha Panikkar involved in manuscript review and editing; Vijaykumar M. E. assisted in sample collection and analysis; U.K. Sarkar coordinate the overall work; B. K. Das provided inputs through over all compilation and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, A., Jesna, P.K., Ramya, V.L. et al. Phosphorus fractions in the sediment of a tropical reservoir, India: Implications for pollution source identification and eutrophication. Environ Geochem Health 44, 749–769 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00985-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00985-0