Abstract
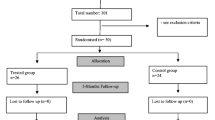
The effects of bath therapy are complex and result from a unique interaction between the aquatic environment and the human body functions. The effect of bath therapy depends on both water temperature and chemical additives (mineral substances and humic substances). Värska Resort Centre, in south-eastern Estonia, uses for the balneotherapy the local curative mud and mineral water. The aim of the study was to evaluate and compare the effects of Värska’s local mud bath and mineral water bath on moderate musculoskeletal pains in working-age people. The study involved 64 working-age subjects: within two weeks, 32 of them received five general mineral water baths, and another 32 received five general curative mud baths. Pain was assessed with the Nordic Musculosceletal Questionnaire, and muscle tension was measured with a myotonometer in m. erector spinae and m. trapezius. Measurements were performed three times: before the start of the study, immediately after the last procedure, and 2–3 weeks after the last procedure. Both the Värska curative mud bath and the Värska mineral water bath showed a positive effect on musculoskeletal pain and muscle tension. Both procedures can be recommended as drug-free interventions for mild to moderate musculoskeletal pain syndrome and muscle tensions, in both prevention and treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, J., Lee, I., & Yi, Y. (2019). The thermal effects of water immersion on health outcomes: An integrative review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16071280
Aranda-Valera, I. C., Alcaraz-Clariana, S., Garcia-Luque, L., Garrido-Castro, J. L., Martinez-Sanchez, I., Gonzalez, C., et al. (2018). Lumbar muscles stiffness in patients with axial spondyloarthritis is altered in comparison with healthy subjects. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-eular.2238
Becker, B. E. (2009). Aquatic therapy: Scientific foundations and clinical rehabilitation applications. PM&R. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2009.05.017
Bourrain, M., Suzuki, M. T., Calvez, A., West, N. J., Lions, J., & Lebaron, P. (2020). In-depth prospection of avène thermal spring water reveals an uncommon and stable microbial community. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.16599
Cheleschi, S., Gallo, I., & Tenti, S. (2020). A comprehensive analysis to understand the mechanism of action of balneotherapy: Why, how, and where they can be used? Evidence from in vitro studies performed on human and animal samples. International Journal of Biometeorology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-020-01890-4
Chuang, L. L., Wu, C. Y., & Lin, K. C. (2012). Reliability, validity, and responsiveness of myotonometric measurement of muscle tone, elasticity, and stiffness in patients with stroke. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2011.09.014
Coccheri, S., Gasbarrini, G., Valenti, M., Nappi, G., & Di Orio, F. (2008). Has time come for a re-assessment of spa therapy? The naiade survey in Italy. International Journal of Biometeorology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-007-0117-4
D’Angelo, D., Coclite, D., Napoletano, A., Fauci, A. J., Latina, R., Gianola, S., Castellini, G., Salomone, K., Gambalunga, F., Sperati, F., Iacorossi, L., & Iannone, P. (2021). The efficacy of balneotherapy, mud therapy and spa therapy in patients with osteoarthritis: An overview of reviews. International Journal of Biometeorology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-021-02102-3
Erceg-Rukavina, T., & Stefanovski, M. (2015). Balneotherapy in treatment of spastic upper limb after stroke. Medical Archives (Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina). https://doi.org/10.5455/medarh.2015.69.31-33
Eröksüz, R., Erol Forestier, F. B., Karaaslan, F., Forestier, R., İşsever, H., Erdoğan, N., Karagülle, M. Z., & Dönmez, A. (2020). Comparison of intermittent and consecutive balneological outpatient treatment (hydrotherapy and peloidotherapy) in fibromyalgia syndrome: A randomized, single-blind, pilot study. International Journal of Biometeorology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-019-01838-3
Espejo Antúnez, L., Caro Puértolas, B., Ibáñez Burgos, B., Porto Payán, J. M., & Torres Piles, S. T. (2013). Effects of mud therapy on perceived pain and quality of life related to health in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Reumatologia Clinica. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reuma.2012.09.005
Fioravanti, A., Cantarini, L., Guidelli, G. M., & Galeazzi, M. (2011). Mechanisms of action of spa therapies in rheumatic diseases: what scientific evidence is there? Rheumatology International. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-010-1628-6
Fioravanti, A., Giannitti, C., Cheleschi, S., Simpatico, A., Pascarelli, N. A., & Galeazzi, M. (2015). Circulating levels of adiponectin, resistin, and visfatin after mud-bath therapy in patients with bilateral knee osteoarthritis. International Journal of Biometeorology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-015-0977-y
Gálvez, I., Torres-Piles, S., & Ortega-Rincón, E. (2018). Balneotherapy, immune system, and stress response: A hormetic strategy? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061687
Goto, Y., Hayasaka, S., Kurihara, S., & Nakamura, Y. (2018). Physical and mental effects of bathing: a randomized intervention study. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9521086
Gregson, W., Black, M. A., Jones, H., Milson, J., Morton, J., Dawson, B., et al. (2011). Influence of cold water immersion on limb and cutaneous blood flow at rest. The American Journal of Sports Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546510395497
Gris, B., Treu, L., Zampieri, R. M., Caldara, F., Romualdi, C., Campanaro, S., & La Rocca, N. (2020). Microbiota of the therapeutic euganean thermal muds with a focus on the main cyanobacteria species. Microorganisms. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101590
Gusi, N., Tomas-Carus, P., Häkkinen, A., Häkkinen, K., & Ortega-Alonso, A. (2006). Exercise in waist-high warm water decreases pain and improves health-related quality of life and strength in the lower extremities in women with fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.21718
Hou, C., Liang, L., Chu, X., Qin, W., Li, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2020). The short-term efficacy of mud therapy for knee osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis. Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000019761
Huber, D., Grafetstätter, C., Proßegger, J., Pichler, C., Wöll, E., Fischer, M., et al. (2019). Green exercise and Mg-Ca-SO4 thermal balneotherapy for the treatment of non-specific chronic low back pain: a randomized controlled clinical trial. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-019-2582-4
Ilahi, S., Masi, A. T., White, A., Devos, A., Henderson, J., & Nair, K. (2020). Quantified biomechanical properties of lower lumbar myofascia in younger adults with chronic idiopathic low back pain and matched healthy controls. Clinical Biomechanics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2019.12.026
Jokić, A., Sremcević, N., Karagülle, Z., Pekmezović, T., & Davidović, V. (2010). Oxidative stress, hemoglobin content, superoxide dismutase and catalase activity influenced by sulphur baths and mud packs in patients with osteoarthritis. Vojnosanitetski Pregled. https://doi.org/10.2298/vsp1007573j
Karagülle, M., & Karagülle, M. Z. (2015). Effectiveness of balneotherapy and spa therapy for the treatment of chronic low back pain: a review on latest evidence. Clinical Rheumatology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2845-2
Kelly, J. P., Koppenhaver, S. L., Michener, L. A., Proulx, L., Bisagni, F., & Cleland, J. A. (2018). Characterization of tissue stiffness of the infraspinatus, erector spinae, and gastrocnemius muscle using ultrasound shear wave elastography and superficial mechanical deformation. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2017.11.001
Kocur, P., Tomczak, M., Wiernicka, M., Goliwąs, M., Lewandowski, J., & Łochyński, D. (2019). Relationship between age, BMI, head posture and superficial neck muscle stiffness and elasticity in adult women. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44837-5
Kulisch, Á., Benkö, Á., Bergmann, A., Gyarmati, N., Horváth, H., Kránicz, Á., et al. (2014). Evaluation of the effect of Lake Hévíz thermal mineral water in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized, controlled, single-blind, follow-up study. European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, 50(4), 373–381
Kuorinka, I., Jonsson, B., Kilbom, A., Vinterberg, H., Biering-Sørensen, F., Andersson, G., & Jørgensen, K. (1987). Standardised Nordic questionnaires for the analysis of musculoskeletal symptoms. Applied Ergonomics. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-6870(87)90010-x
Liu, H., Zeng, C., Gao, S. G., Yang, T., Luo, W., Li, Y. S., Xiong, Y. L., Sun, J. P., & Lei, G. H. (2013). The effect of mud therapy on pain relief in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of International Medical Research. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060513488509
Mano, T., Iwase, S., & Toma, S. (2006). Microneurography as a tool in clinical neurophysiology to investigate peripheral neural traffic in humans. Clinical neurophysiology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2006.06.002
Marandi, A. (2007). Natural chemical composition of groundwater as a basis for groundwater management in the Cambrian-Vendian aquifer system in Estonia [Doctoral dissertation, University of Tartu]. Tartu University Press.
Matsumoto, S. (2018). Evaluation of the role of balneotherapy in rehabilitation medicine. Journal of Nippon Medical School. https://doi.org/10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2018_85-30
Miwa, C., Sugiyama, Y., Mano, T., Iwase, S., & Matsukawa, T. (1997). Sympatho-vagal responses in humans to thermoneutral head-out water immersion. Aviation, Space, and Environmental Medicine, 68(12), 1109–1114
Mooventhan, A., & Nivethitha, L. (2014). Scientific evidence-based effects of hydrotherapy on various systems of the body. North American Journal of Medical Sciences. https://doi.org/10.4103/1947-2714.132935
Morer, C., Roques, C. F., Françon, A., Forestier, R., & Maraver, F. (2017). The role of mineral elements and other chemical compounds used in balneology: data from double-blind randomized clinical trials. International Journal of Biometeorology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-017-1421-2
Munteanu, C., Munteanu, D., Hoteteu, M., & Dogaru, G. (2019). Balneotherapy–medical, scientific, educational and economic relevance reflected by more than 250 articles published in Balneo Research Journal. Balneo Research Journal, 10(3), 174–203
Munteanu, C., Rotariu, M., Dogaru, G., Ionescu, E. V., Ciobanu, V., & Onose, G. (2021). Mud therapy and rehabilitation scientific relevance in the last six years (2015–2020): Systematic literature review and meta-analysis based on the PRISMA paradigm. Balneo and PRM Research Journal. https://doi.org/10.12680/balneo.2021.411
Nasermoaddeli, A., & Kagamimori, S. (2005). Balneotherapy in medicine: A review. Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02897707
Odabasi, E., Turan, M., Erdem, H., & Tekbas, F. (2008). Does mud pack treatment have any chemical effect? A randomized controlled clinical study. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2008.0003
Sato, D., Yamashiro, K., Onishi, H., Shimoyama, Y., Yoshida, T., & Maruyama, A. (2012). The effect of water immersion on short-latency somatosensory evoked potentials in human. BMC Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-13-13
Schlossmann, K. (1939). Estonian curative sea-muds and seaside health resorts. Boreas.
Shenkman, B. S., & Kozlovskaya, I. B. (2019). Cellular responses of human postural muscle to dry immersion. Frontiers in Physiology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00187
Šrámek, P., Šimečková, M., Janský, L., Šavlíková, J., & Vybíral, S. (2000). Human physiological responses to immersion into water of different temperatures. European Journal of Applied Physiology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050065
Swedish Council on Health Technology Assessment. (2006). Methods of treating chronic pain: A systematic review. Swedish Council on Health Technology Assessment (SBU). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK447986/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK447986.pdf. Accessed 9 June 2020.
Szabó, I., & Varga, C. (2020). Finding possible pharmacological effects of identified organic compounds in medicinal waters (BTEX and phenolic compounds). International Journal of Biometeorology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-019-01808-9
Tenti, S., Manica, P., Cheleschi, S., & Fioravanti, A. (2020). Sulfurous-arsenical-ferruginous balneotherapy for osteoarthritis of the hand: Results from a retrospective observational study. International Journal of Biometeorology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-020-01937-6
Terasmaa, J., Kapanen, G., Marzecova, A., & Rautam, S. (2017). Curative mud in Estonia 2013–2014: Värska Bay. http://terekk.ee/wp-content/uploads/Curative_mud_V%C3%A4rska_ENG_27022018.pdf. Accessed 9 June 2020.
Trink, R. (2000). Therapeutic effect of humic substances (humic, hymatomelanic and fulvic acid) Pärnu Institute of Health Resort Treatment and Medical Rehabilitation (in Estonian).
Tuulik, V.-R., Tuulik, V., Pille, V., Tamm, M., Saarik, S., Vare, T., & Tint, P. (2013). Laser-Doppler perfusion monitoring, myotonometry, and workplace risk evaluation as assessment methods of musculoskeletal overuse syndromes in industry workers. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. https://doi.org/10.2340/16501977-1223
Übner, M. (2015). Effect of different 6-day spa therapy courses on the quality of life in the knee osteoarthritis treatment, M Vinkel Eds In: Proceedings in the field of curative mud of the centre of excellence in health promotion and rehabilitation, Haapsalu College, Tallinn University, 44–49 (in Estonian).
Varzaityte, L., Kubilius, R., Rapoliene, L., Bartuseviciute, R., Balcius, A., Ramanauskas, K., & Nedzelskiene, I. (2020). The effect of balneotherapy and peloid therapy on changes in the functional state of patients with knee joint osteoarthritis: A randomized, controlled, single-blind pilot study. International Journal of Biometeorology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-019-01785-z
Viir, R., Laiho, K., Kramarenko, J., & Mikkelson, M. (2006a). Repeatability of trapezius muscle tone assessment by a myometric method. Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219519406001856
Viir, R., Vain, A., Virkus, A., Rajaleid, K., & Selart, A. (2006b). Skeletal muscle tone characteristics in upright, supine and partial water immersion conditions. In: Proceedings of the 57th International Astronautical Congress, 1, 132–141. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.IAC-06-A1.3.04.
Watenpaugh, D. E. (2016). Analogs of microgravity: head-down tilt and water immersion. Journal of Applied Physiology. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00986.2015
Wilcock, I. M., Cronin, J. B., & Hing, W. A. (2006). Physiological response to water immersion: A method for sport recovery? Sports Medicine. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200636090-00003
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Regional Competence Centre Development programme, European Regional Development Fund, project EU50286 – Centre of Excellence in Health Promotion and Rehabilitation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tuulik, VR., Kumm, M., Tuulik, V. et al. The therapeutic effect of Värska mud and Värska mineral water baths on the overuse pain and muscle tension syndromes in the working age population. Environ Geochem Health 44, 2101–2110 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00951-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00951-w