Abstract
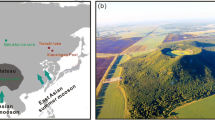
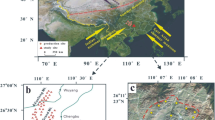
A new 210Pb-dated record of Hg accumulation derived from a sediment core from a Hg-enriched area in Huguangyan Lake (HGY) in South China is presented. Based on synthetic analyses of multi-proxy records including chemical composition, total organic matter, and grain-size distribution in surface sediments and nearby soil samples, it is inferred that the influx of Hg into the lake is mainly a result of atmospheric deposition, with no or minor hydroclimate-induced lithogenic input from the catchment and limited adsorption effects of organic matter and clay. Significantly enhanced anthropogenic input of Hg started in the early 1900s. Since then, several anomalies of Hg accumulation have been the results of wars or intensified economic activities in China. HGY sediments provide a rare and reliable natural archive for detecting atmospheric Hg deposition, which is closely related to anthropogenic activities.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data will be provided from the authors upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Agnieszka, J., Magdalena, B., & Marcelina, Z. (2019). The role of benthic macrofauna in the trophic transfer of mercury in a low-diversity temperate coastal ecosystem (Puck Lagoon, southern Baltic Sea). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 137.
Amos, H. M., Jacob, D. J., & Holmes, C. D. (2012). Gas-particle partitioning of atmospheric Hg (II) and its effect on global mercury deposition. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12, 591–603.
Appleby, P. G. (2004). Environmental change and atmospheric contamination on Svalbard: Sediment chronology. Journal of Paleolimnology, 31, 433–443.
Appleby, P. G., Nolan, P. J., Gifford, D. W., Godfrey, M. J., Oldfield, F., Anderson, N. J., et al. (1986). 210 pb dating by low background gamma counting. Hydrobiologia, 143(1), 21–27.
Ashokkumar, R., Srinivasalu, S., Jayaprakash, M., & Gopal, V. (2016). Geochemical weathering indices of core sediments from the off-Cuddalore Region, Tamil Nadu, India. International Journal of Earth Sciences and Engineering, 08(1), 43–51.
Biester, H., Bindler, R., Martinez-Cortizas, A., & Engstrom, D. R. (2007). Critical review: modelling the past atmospheric deposition of mercury using natural archives. Environmental Science and Technology., 41, 4851–4860.
Birks, H. J. B., Jones, V. J., & Rose, N. L. (2004). Recent environmental change and atmospheric contamination on svalbard as recorded in lake sediments: An introduction. Journal of Paleolimnology., 31(4), 403–410.
Boës, X., Rydberg, J., Martínez-Cortizas, A., Bindler, R., & Renberg, I. (2011). Evaluation of conservative lithogenic elements (Ti, Zr, AlandRb) to study anthropogenic element enrichments in lake sediments. Journal of Paleolimnology, 46, 75–87.
Bookman, R., Driscoll, C. T., Effler, S. W., & Engstrom, D. R. (2010). Anthropogenic impacts recorded in recent sediments from Otisco Lake, New York, USA. Journal of Paleolimnology, 43, 449–462.
Brazeau, M. L., Poulain, A. J., & Paterson, A. M. (2013). Recent changes in mercury deposition and primary productivity inferred from sediments of lakes from the Hudson Bay Lowlands, Ontario, Canada. Environmental Pollution, 173, 52–60.
Carrie, J., Sanei, H., Goodarzi, F., Stern, G., & Wang, F. Y. (2009). Characterization of organic matter in surface sediments of the Mackenzie River Basin, Canada. International Journal of Coal Geology, 77, 416–423.
Chu, G. Q., Liu, J. Q., Sun, Q., Lu, H. Y., Gu, Z. Y., Wang, W. Y., & Liu, T. S. (2002). The “Mediaeval Warm Period” drought recorded in Lake Huguangyan, tropical South China. Holocene, 12, 511–516.
Chu, G., Sun, Q., Zhu, Q., Shan, Y., Shang, W., Ling, Y., Su, Y., Xie, M., Wang, X., & Liu, J. (2017). The role of the Asian winter monsoon in the rapid propagation of abrupt climate changes during the last deglaciation. Quaternary Science Reviews, 177, 120–129.
Conaway, C. H., Swarzenski, P. W., & Cohen, A. S. (2012). Recent paleorecords document rising mercury contamination in Lake Tanganyika. Applied Geochemistry, 27, 352–359.
Demers, J. D., Blum, J. D., & Zak, D. R. (2013). Mercury isotopes in a forested ecosystem: Implications for air-surface exchange dynamics and the global mercury cycle. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 27, 222–238.
Driscoll, C. T., Blette, V., Yan, C., Schofield, C. L., Munson, R., & Holsapple, J. (1995). The role of dissolved organic carbon in the chemistry and bioavailability of mercury in remote Adirondack lakes. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 80, 499–508.
Duan, Z., Liu, Q., Yang, X., Gao, X., & Su, Y. (2014). Magnetism of the Huguangyan Maar Lake sediments, Southeast China and its paleoenvironmental implications. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 395, 158–167.
Engstrom, D. R., Balogh, S. J., & Swain, E. B. (2007). History of mercury inputs to Minnesota lakes: Influences of watershed disturbance and localized atmosphericde position. Limnology and Oceanography, 52, 2467–2483.
Engstrom, D. R., Fitzgerald, W. F., & Cooke, C. A. (2014). Atmospheric Hg emissions from preindustrial gold and silver extraction in the Americas: A reevaluation from lake-sediment archives. Environmental Science and Technology, 48, 6533–6543.
Ericksen, J. A., Gustin, M. S., Schorran, D. E., & Johnson, D. W. (2003). Accumulation of atmospheric mercury in forest foliage. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 1613–1622.
Feng, X. B., Bai, W. Y., Shang, L. H., He, T. R., Qiu, G. L., & Yan, H. Y. (2011). Mercury speciation and distribution in Aha Reservoir which was contaminated by coal mining activities in Guiyang, Guizhou, China. Applied Geochemistry, 26, 213–221.
Fitzgerald, W. F. (1995). Is mercury increasing in the atmosphere? The need for an atmospheric mercury network (AMNET). Water Air and Soil Pollution, 80, 245–254.
Fitzgerald, W. F., Engstrom, D. R., Mason, R. P., & Nater, E. A. (1998). The case for atmospheric mercury contamination in remote areas. Environment Science and Technology, 32, 1–7.
Fitzgerald, W. F., Engstrom, D. R., Lamborg, C. H., Tseng, C. M., Balcom, P. H., & Hammerschmidt, C. R. (2005). Modern and historic atmospheric mercury fluxes in northern Alaska: Global sources and Arctic depletion. Environment Science and Technology, 39, 557–568.
Fuhrmann, A., Mingram, J., Lucke, A., Lu, H. Y., Horsfield, B., Liu, J. Q., Negendank, J. F. W., Schleser, G. H., & Wilkes, H. (2003). Variations in organic matter composition in sediments from Lake Huguang Maar (Huguangyan), South China during the last 68 ka: implications for environmental and climatic change. Organic Geochemistry, 34, 1497–1515.
Gao, Y., Xu, S., Guo, Q., & Zhang, M. (1962). Monsoon region and regional climate in China. In Y. Gao & S. Xu (Eds.), Some problems of East Asian Monsoon (pp. 49–63). Science Press.
Graydon, J. A., Louis, V. L. S., & Lindberg, S. E. (2006). Investigation of mercury exchange between forest canopy vegetation and the atmosphere using a new dynamic chamber. Environment Science and Technology, 40(15), 4680–4688.
Graydon, J., Louis, V. L. S., Hintelmann, H., Lindberg, S., Sandilands, K., Rudd, J., Kelly, C., Hall, B., & Mowat, L. (2008). Long-term wet and dry deposition of total and methyl mercury in the remote boreal ecoregion of Canada. Environment Science and Technology, 42, 8345–8351.
Hao, L., Sun, L., Zhao, Y., & Lu, J. (2013). Sedimentary records of evolution of heavy metals in Songhua Lake, Northeast China. Clean-Soil Air Water, 41, 1010–1017.
Hermanns, Y. M., & Biester, H. (2013). A 17300-year record of mercury accumulation in a pristine lake in southern Chile. Journal of Paleolimnology, 49, 547–561.
Hintelmann, H. R., Harris, A., Heyes, J., Hurley, P., Kelly, D., Krabbenhoft, S., Lindberg, J., Rudd, W. M., Scott, K. J., & Louis, S. (2002). Reactivity and mobility of new and old mercury deposition in a boreal forest ecosystem during the first year of the METAALICUS study. Environment Science and Technology, 36, 5034–5040.
Horowitz, H. M., Jacob, D. J., Amos, H. M., et al. (2014). Historical Mercury releases from commercial products: Global environmental implications. Environment Science and Technology, 48(17), 10242–10250.
Jackson, T. A. (1997). Long-range atmospheric transport of mercury to ecosystems, and the importance of anthropogenic emissions-a critical review and evaluation of the published evidence. Environment Reviews, 5, 99–120.
Janssens, J. A. (1983). A quantitative method for stratigraphic analysis of bryophytes in Holocene peat. Journal of Ecology, 171, 189–196.
Kang, S., Huang, J., & Wang, F. (2016). Atmospheric mercury depositional chronology reconstructed from lake sediment and ice cores in the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau. Environment Science and Technology, 50, 2859–2869.
Lamborg, C. H., Fitzgerald, W. F., Dammann, A. W. H., Benoit, J. M., Balcom, P. H., & Engstrom, D. R. (2002). Modern and historic atmospheric mercury fluxes in both hemispheres: Gobal and regional mercury cycling implications. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 16, 1104–1115.
Li, H. B., Yu, S., Li, G. L., Deng, H., Xu, B., Ding, J., Gao, J. B., Hong, Y. W., & Wong, M. H. (2013). Spatial distribution and historical records of mercury sedimentation in urban lakes under urbanization impacts. Science of the Total Environment, 445, 117–125.
Li, Y. P., Ma, C. M., & Zhu, C. (2016). Historical anthropogenic contributions to mercury accumulation recorded by a peat core from Dajiuhu montane mire, central China. Environmental Pollution, 216, 332–339.
Lindqvist, O., Johansson, K., Aastrup, M., Andersson, A., Bringmark, L., Hovsenius, G., Hakanson, L., & Iverfeldt, A. (1991). Mercury in Swedish environment: Recent research on causes consequences and corrective methods. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 55, 23–32.
Liu, D. S., Liu, J. Q., & Lu, H. Y. (1998). Progress in high-resolution paleoenvironment research from Maar Lake. Quaternary Science Reviews, 4, 289–296. (in Chinese).
Mao, H., Ye, Z., & Driscoll, C. (2017). Meteorological effects on hg wet deposition in a forested site in the Adirondack region of New York during 2000–2015. Atmospheric Environment, 168, 90–100.
Mingram, J., Schettler, G., Nowaczyk, N., Luo, X. J., Lu, H. Y., Liu, J. Q., & Negendank, J. F. W. (2004). The Huguang maar lake: A high-resolution record of palaeoenvironmental and palaeoclimatic changes over the last 78,000 years from South China. Quaternary International, 122, 85–107.
Mowat, L. D., Louis, V. L. S., Graydon, J. A., & Lehnherr, I. (2011). Influence of forest canopies on the deposition of methylmercury to boreal ecosystem watersheds. Environmental Science and Technology, 45, 5178–5185.
Norton, S. A., Jacobson, G. L., Kopacek, J., & Tomas, N. (2015). A comparative study of long-term Hg and Pb sediment archives. Environmental Chemistry, 13, 517–527.
Obrist, D., Agnan, Y., & Jiskra, M. (2007). Tundra uptake of atmospheric elemental mercury drives Arctic mercury pollution. Nature, 547, 201–204.
Obrist, D., Kirk, J. L., Zhang, L., Sunderland, E. M., Jiskra, M., & Selin, N. E. (2018). A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: Changes of emissions, climate, and land use. Ambio, 47, 116–140.
Perry, E., Norton, S. A., Kamman, N. C., Lorey, P. M., & Driscoll, C. T. (2005). Deconstruction of historic mercury accumulation in lake sediments, northeastern states. Ecotoxicology, 14, 85–99.
Price, J. R., & Velbel, M. A. (2003). Chemical weathering indices applied to weathering profiles developed on heterogeneous felsic metamorphic parent rocks. Chemical Geology, 202(3–4), 397–416.
Roos-Barraclough, F., Martinez-Cortizas, A., García-Rodedja, E., & Shotyk, W. (2002). A 14500 year record of the accumulation of atmospheric mercury in peat: Volcanic signals, anthropogenic influences and a correlation to bromine accumulation. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 202, 435–451.
Roos-Barraclough, F., Givelet, N., Cheburkin, A. K., Shotyk, W., & Norton, S. A. (2006). Use of Br and se in peat to reconstruct the natural and anthropogenic fluxes of atmospheric hg: a 10000-year record from Caribou bog, Maine. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 3188–3194.
Rydberg, J., Klaminder, J., Rosen, P., & Bindler, R. (2010). Climate driven release of carbon and mercury from permafrost mires increases mercury loading to sub-arctic lakes. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 4778–4783.
Saniewska, D., & Bełdowska, M. (2017). Mercury fractionation in soil and sediment samples using thermo-desorption method. Talanta, 168, 152–161.
Shi, J. B., Carman, C. M. I., Zhang, G., Jiang, G. B., & Li, X. D. (2010). Mercury profiles in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary and the surrounding coastal area of South China. Environmental Pollution, 158(5), 1974–1979.
Siqueira, G. W., Fabio, A., Georg, I., & Braga, E. S. (2018). Mercury in the amazon basin: Human influence or natural geological pattern? Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 86, 193–199.
Stern, G. A., Sanei, H., Roach, P., Delaronde, J., & Outridge, P. M. (2009). Historical interrelated variations of mercury and aquatic organic matter in lake sediment cores from a subarctic lake in Yukon, Canada: Further evidence toward the algalmercury scavenging hypothesis. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 7684–7690.
Streets, D. G., Devane, M. K., Lu, Z., Bond, T. C., Sunderland, E. M., & Jacob, D. J. (2011). All-time releases of mercury to the atmosphere from human activities. Environmental Science and Technology, 45, 10485–10491.
Streets, D. G., Hao, J., Wu, Y., et al. (2005). Anthropogenic mercury emissions in China. Atmospheric Environment, 39(40), 7789–7806.
Sun, Q. L., Wang, S. M., Zhou, J., Chen, Z. Y., Shen, J., Xie, X. P., Wu, F., & Chen, P. (2010). Sediment geochemistry of Lake Daihai, north-central China, implications for catchments weathering and climate change during the Holocene. Journal of Paleolimnology, 43, 75–87.
Teisserenc, R., Lucotte, M., & Houel, S. (2011). Terrestrial organic matter biomarkers as tracers of Hg sources in lake sediments. Biogeochemistry, 103, 235–244.
Wang, X. S., Chu, G. Q., Sheng, M., Zhang, S. Q., Li, J. H., Chen, Y., Tang, L., Su, Y. L., PeiJ, L., & Yang, Z. Y. (2016). Millennial-scale Asian summer monsoon variations in South China since the last deglaciation. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 451, 22–30.
Weiss, D., Shotyk, W., Appleby, P. G., Kramers, J. D., & Cheburkin, A. K. (1999). Atmospheric Pb deposition since the industrial revolution recorded by five Swiss peat profiles: Enrichment factors, fluxes, isotopic composition, and sources. Environmental Science and Technology, 33, 1340–1352.
Xia, K. (1999). X-ray absorption spectroscopic evidence for the complexation of Hg (II) by reduced sulfur in soil humic substances. Environmental Science and Technology, 33, 257–261.
Yang, H., & Rose, N. (2003). Distribution of mercury in six lake sediment cores across the UK. Science of the Total Environment., 36, 1383–1388.
Yang, H., & Smyntek, P. (2014). Use of the mercury record in Red Tarn sediments to reveal air pollution history and the implications of catchment erosion. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts, 16, 2554–2563.
Yang, H., Turner, S., & Rose, N. L. (2016). Mercury pollution in the lake sediments and catchment soils of anthropogenically-disturbed sites across England. Environmental Pollution, 219, 1092–1101.
Zeng, Y., Chen, J. A., Zhu, Z. J., Li, J., Wang, J. F., & Wan, G. J. (2012). The wet Little Ice Age recorded by sediments in Huguangyan Lake, tropical South China. Quaternary International, 263, 55–62.
Zeng, Y., Chen, J., Yang, Y., & Wang, J. (2017). Huguangyan Maar Lake (SE China): A solid record of atmospheric mercury pollution history in a non-remote region. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 147, 1–8.
Zhang, H., Zhang, N., & Zhong, L. (2011). A 1955–2004 record of Hg contamination in Dianshan Lake sediments, Shanghai. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 9(4), 479–484.
Zhao, K. N. (1984). The evolution in extracting hg from cinnabar and related achievements in chemistry in ancient China. Historical Studies in the Natural Sciences, 3, 11–23.
Acknowledgements
We thank Bing Liu, Lixue Tian, Susu Ye, and Xiaowen Tang for their help in field investigation and laboratory measurements. We are grateful to two anonymous reviewers and the editor for their valuable and constructive comments. This work was supported by the NSF of China (Grant Nos. 41971101, 41571187 and 41071137), and the Fund of Scientific innovation and cultivation in Climbing Program for college student of Guangdong Province (Grant No. Pdjh2020b0169). Thanks are also given to Mogoedit for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tianhang Li and Wei Zhong organized this study, including conception of the study, sampling, measurement and manuscript writing. Zhiqiang Wei, Shengtan Shang and Susu Ye took part in sampling, performed the experiment and contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation. Yuanhan Chen and Junyu Pan helped perform the analysis and the preparation of the manuscript in format and citations. Xiaojun Wang helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. Manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Animal research
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Zhong, W., Wei, Z. et al. Response of mercury accumulation to anthropogenic pollution in the past 1000 years based on Lake Huguangyan sediments, Southern China. Environ Geochem Health 43, 3921–3933 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00878-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00878-2