Abstract
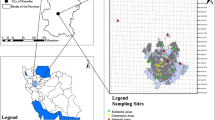
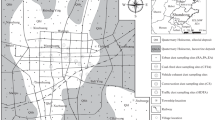
This study aimed to investigate spatial distribution, correlations among elements and ecological and probabilistic health risk assessment in smaller than 75 μm street dust in Kerman city, Iran. Street dust samples were collected from 35 different points. Elements were detected by ICP-AES. Pollution degree was characterized through Enrichment Factor (EF), Contamination Factor (CF), Geo-accumulation Index (Igeo) and Potential Ecological Risk (PER). The health risk was assessed using the Monte Carlo simulation method. The mean values of elements were in the order of Al > Mn > Zn > Cu > V > Pb > Cr > Ni > Li > As > Co > Mo > Sb > Cd > Ag. The results of Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA) showed that Al, As, Co, Li, Mn and V were possibly derived from natural sources (local soil), while traffic and mining activities were proposed as the main source of Cd, Cr, Cu, Mo, Ni, Pb, Sb and Zn. The order of EF and CF mean values decreased as follows: Mn > Ag > Cu > Zn > Pb > Sb > Mo > Li > Co > V > Cd > As > Cr > Ni. In addition, 73% of Cu and 35% of Zn, Ag and Mn had significant enrichment in the street dust samples. Also, Ag and Mn were categorized in the significant and very significant pollution category. In terms of the PER index, all samples could be classified at low-risk category. Ingestion of street dust was the significant route for exposure of residents of Kerman to the elements studied. No significant ecological hazards and health risks were observed from street dust in the study area in the period of the study. The improvement in the fuels quality and development of green spaces can be suggested to control natural and anthropogenic street dust pollution sources in the Kerman city.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasnejad, A., & Abbasnejad, B. (2019). Distribution, sources and pollution status of Pb in indoor and outdoor dusts of Kerman City, SE Iran. Environmental Forensics., 20(1), 106–119.
Abbasnejad, B., Keshavarzi, B., Mohammadi, Z., Moore, F., Abbasnejad, A. (2019). Characteristics, distribution, source apportionment, and potential health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban street dust of Kerman metropolis, Iran. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, pp 1–18.
Agency USEP. (2001). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Volume III—Part A, Process for Conducting Probabilistic Risk Assessment. Author Washington, DC.
Atapour, H. (2015). Geochemistry of potentially harmful elements in topsoils around Kerman city, southeastern Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(7), 5605–5624.
Bartholomew, C. J., Li, N., Li, Y., Dai, W., Nibagwire, D., & Guo, T. (2020). Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in street dust for children in Jinhua, china. China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(5), 5042–5055.
Boomeri, M., Nakashima, K., & Lentz, D. R. (2010). The Sarcheshmeh porphyry copper deposit, Kerman, Iran: A mineralogical analysis of the igneous rocks and alteration zones including halogen element systematics related to Cu mineralization processes. Ore Geology Reviews, 38(4), 367–381.
Chang, X., Li, Y. X. (2020). Lead distribution in urban street dust and the relationship with mining, gross domestic product GDP and transportation and health risk assessment. Environmental Pollution, 2 , 62.
Chenery, S. R. N., Sarkar, S. K., Chatterjee, M., Marriott, A. L., Watts, M. J. (2020). Heavy metals in urban road dusts from Kolkata and Bengaluru, India: implications for human health. Environmental Geochemical Health.
Dehghani, S., Moore, F., Keshavarzi, B., & Hale, B. A. (2017). Health risk implications of potentially toxic metals in street dust and surface soil of Tehran, Iran. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 136, 92–103.
Dehghanzadeh, R., Hir, N. S., Sis, J. S., & Taghipour, H. (2015). Integrated assessment of spatial and temporal variations of groundwater quality in the eastern area of Urmia Salt Lake Basin using multivariate statistical analysis. Water Resources Management, 29(4), 1351–1364.
Eslami, F., Yaghmaeian, K., Mohammadi, A., Salari, M., & Faraji, M. (2019). An integrated evaluation of groundwater quality using drinking water quality indices and hydrochemical characteristics: a case study in Jiroft, Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(10), 314.
Ferrante, M., & Conti, G. O. (2017). Environment and neurodegenerative diseases: an update on miRNA role. Microrna, 6(3), 157–165.
Fiore, M., Oliveri Conti, G., Caltabiano, R., Buffone, A., Zuccarello, P., Cormaci, L., et al. (2019). Role of emerging environmental risk factors in thyroid cancer: a brief review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(7), 1185.
Ghanavati, N., Nazarpour, A., & De Vivo, B. (2019). Ecological and human health risk assessment of toxic metals in street dusts and surface soils in Ahvaz, Iran. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 41(2), 875–891.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001.
Hamzeh, M. A., Aftabi, A., & Mirzaee, M. (2011). Assessing geochemical influence of traffic and other vehicle-related activities on heavy metal contamination in urban soils of Kerman city, using a GIS-based approach. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33(6), 577.
Hou, S., Zheng, N., Tang, L., Ji, X., Li, Y., & Hua, X. (2019). Pollution characteristics, sources, and health risk assessment of human exposure to Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb pollution in urban street dust across China between 2009 and 2018. Environment International, 128, 430–437.
Huang, S., Tu, J., Liu, H., Hua, M., Liao, Q., Feng, J., et al. (2009). Multivariate analysis of trace element concentrations in atmospheric deposition in the Yangtze River Delta, East China. Atmospheric Environment, 43(36), 5781–5790.
Jonidi Jafari, A., Kermani, M., Kalantary, R. R., & Arfaeinia, H. (2018). The effect of traffic on levels, distribution and chemical partitioning of harmful metals in the street dust and surface soil from urban areas of Tehran, Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77(2), 38.
Kamani, H., Mirzaei, N., Ghaderpoori, M., Bazrafshan, E., Rezaei, S., & Mahvi, A. H. (2018). Concentration and ecological risk of heavy metal in street dusts of Eslamshahr, Iran. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 24(4), 961–970.
Khademi, H., Gabarrón, M., Abbaspour, A., Martínez-Martínez, S., Faz, A., & Acosta, J. A. (2019). Environmental impact assessment of industrial activities on heavy metals distribution in street dust and soil. Chemosphere, 217, 695–705.
Khaldari, F., Khanjani, N., Bahrampour, A., Ravandi, M. R. G., Mianroodi, A. A. A. A. (2016). The time of hearing loss onset among workers in the copper by-industry and its effective factors. International Journal of Occupational Hygiene, 8(3), 172–178.
Krewski, D., Yokel, R. A., Nieboer, E., Borchelt, D., Cohen, J., Harry, J., et al. (2007). Human health risk assessment for aluminium, aluminium oxide, and aluminium hydroxide. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health Part B: Critical Reviews,10 (Suppl 1), 1–269.
Li, N., Han, W., Tang, J., Bian, J., Sun, S., & Song, T. (2018). Pollution Characteristics and Human Health Risks of Elements in Road Dust in Changchun, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(9), 1843.
Liu, L., Liu, A., Li, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, G., & Guan, Y. (2016). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with road deposited solid and their ecological risk: Implications for road stormwater reuse. Science of the Total Environment, 563–564, 190–198.
Liu, E., Wang, X., Liu, H., Liang, M., Zhu, Y., & Li, Z. (2019). Chemical speciation, pollution and ecological risk of toxic metals in readily washed off road dust in a megacity (Nanjing), China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 173, 381–392.
Lu, X., Shi, D., Yin, N., Pan, H., & Smith, P. (2017). Risk assessment of heavy metals in finer than 63-μm dust particles from various functional areas in Xi'an. Air Quality, Atmosphere, and Health, 10, 907–915.
Miri, M., Alahabadi, A., Ehrampoush, M. H., Ghaffari, H. R., Sakhvidi, M. J. Z., Eskandari, M., et al. (2018). Environmental determinants of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons exposure at home, at kindergartens and during a commute. Environment International, 118, 266–273.
Mirzaei Aminiyan, M., Baalousha, M., Mousavi, R., Mirzaei Aminiyan, F., Hosseini, H., & Heydariyan, A. (2018). The ecological risk, source identification, and pollution assessment of heavy metals in road dust: a case study in Rafsanjan, SE Iran. Environmental Science Pollution Research, 25(14), 13382–13395.
Mohammadi, A., Mokhtari, M., Arani, A. M., Taghipour, H., Hajizadeh, Y., & Fallahzadeh, H. (2018). Biomonitoring levels of airborne metals around Urmia Lake using deciduous trees and evaluation of their tolerance for greenbelt development. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(21), 21138–21148.
Mohammadi, A., Hajizadeh, Y., Taghipour, H., Arani, A. M., Mokhtari, M., Fallahzadeh, H. (2018). Assessment of metals in agricultural soil of surrounding areas of Urmia Lake, northwest Iran: a preliminary ecological risk assessment and source identification. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal.
Mohammadi, A., Ghassoun, Y., Löwner, M.-O., Behmanesh, M., Faraji, M., Nemati, S., et al. (2020). Spatial analysis and risk assessment of urban BTEX compounds in Urmia, Iran. Chemosphere, 246, 125769.
Mun’im Mohd Han N, Latif MT, Othman M, Dominick D, Mohamad N, Juahir H, et al. Composition of selected heavy metals in road dust from Kuala Lumpur city centre. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72(3), 849–859.
Musa, A. A., Hamza, S. M., & Kidak, R. (2019). Street dust heavy metal pollution implication on human health in Nicosia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research: North Cyprus.
Nkansah, M. A., Darko, G., Dodd, M., Opoku, F., Bentum Essuman, T., & Antwi-Boasiako, J. (2017). Assessment of pollution levels, potential ecological risk and human health risk of heavy metals/metalloids in dust around fuel filling stations from the Kumasi Metropolis, Ghana. Environmental Science, 3(1), 1412153.
Peng, T., O'Connor, D., Zhao, B., Jin, Y., Zhang, Y., Tian, L., et al. (2019). Spatial distribution of lead contamination in soil and equipment dust at children's playgrounds in Beijing, China. Environmental Pollution., 245, 363–370.
Safiur Rahman, M., Khan, M. D. H., Jolly, Y. N., Kabir, J., Akter, S., & Salam, A. (2019). Assessing risk to human health for heavy metal contamination through street dust in the Southeast Asian Megacity: Dhaka, Bangladesh. Science of The Total Environment, 660, 1610–1622.
Salminen, R., Batista, M., Bidovec, M., Demetriades, A., De Vivo, B., De Vos, W., et al. (2005) FOREGS Geochemical Atlas of Europe, Part 1: Background Information. Methodology and Maps.
Santo Salvatore, S., Gea, O. C., Antonella, Z., Andrea, B., & Maria, F., Margherita, F. (2019). Effect of particulate matter-bound metals exposure on prothrombotic biomarkers: a systematic review. Environmental Research, p. 108573.
Shi, D., & Lu, X. (2018). Accumulation degree and source apportionment of trace metals in smaller than 63 μm road dust from the areas with different land uses: a case study of Xi'an, China. Science of The Total Environment, 636, 1211–1218.
Statistical Center of Iran Natinal Portal et al. (2016). Available from: https://www.amar.org.ir/.
Sun, G., Feng, X., Yang, C., Zhang, L., Yin, R., Li, Z., et al. (2020). Levels, sources, isotope signatures, and health risks of mercury in street dust across China. Journal of Hazardous Material, p 392.
Sun, G., Li, Z., Liu, T., Chen, J., Wu, T., & Feng, X. (2017). Rare earth elements in street dust and associated health risk in a municipal industrial base of central China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health., 39(6), 1469–1486.
Taghavi, S., Kamani, H., Dehghani, M. H., Nabizadeh, R., Afshari, N., Mahvi, A. (2019a) Assessment of heavy metals in street dusts of Tehran using enrichment factor and geo-accumulation index: a. health scope (In Press).
Taghavi, S. N., Kamani, H., Dehghani, M. H., Nabizadeh, R., Afshari, N., & Mahvi, A. H. (2019b). Assessment of Heavy Metals in Street Dusts of Tehran Using Enrichment Factor and Geo-Accumulation Index., 8(1), e57879.
Taylor, S. (1964). Abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust: a new table. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 28(8), 1273–1285.
Tokalıoğlu, Ş., & Kartal, Ş. (2006). Multivariate analysis of the data and speciation of heavy metals in street dust samples from the Organized Industrial District in Kayseri (Turkey). Atmospheric Environment, 40(16), 2797–2805.
Trojanowska, M., Świetlik, R. (2020). Investigations of the chemical distribution of heavy metals in street dust and its impact on risk assessment for human health, case study of Radom (Poland). Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, pp 1–20.
Trujillo-González, J. M., Torres-Mora, M. A., Keesstra, S., Brevik, E. C., & Jiménez-Ballesta, R. (2016). Heavy metal accumulation related to population density in road dust samples taken from urban sites under different land uses. Science of the Total Environment, 553, 636–642.
(USEPA) UEPA, editor Guidelines for carcinogen risk assessment (2005). Risk Assessment Forum, US Environmental Protection Agency.
(USEPA) UEPA Method 6010C (SW-846): Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry, Revision 3 (2007). Available from: https://www.epa.gov/homeland-security-research/epa-method-6010c-sw-846-inductively-coupled-plasma-atomic-emission.
van der Does, M., Knippertz, P., Zschenderlein, P., Harrison, R. G., Stuut, J.-B. W. (2018) The mysterious long-range transport of giant mineral dust particles. Science Advances, 4(12), eaau2768.
Wahab, M. I. A., Razak, W. M. A. A., Sahani, M., Khan, M. F. (2020) Characteristics and health effect of heavy metals on non-exhaust road dusts in Kuala Lumpur. Science of the Total Environment, p. 703.
Weerasundara, L., Magana-Arachchi, D. N., Ziyath, A. M., Goonetilleke, A., & Vithanage, M. (2018). Health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in a congested city environment in a developing country: Kandy City, Sri Lanka. Journal of Environmental Management, 220, 198–206.
Weiss, J. M., Gustafsson, Å., Gerde, P., Bergman, Å., Lindh, C. H., & Krais, A. M. (2018). Daily intake of phthalates, MEHP, and DINCH by ingestion and inhalation. Chemosphere, 208, 40–49.
Yarmoradi, Z., Nasiri, B., Mohammadi, G. H., & Karampour, M. (2020). Long-term characteristics of the observed dusty days and its relationship with climatic parameters in East Iran. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13(6), 1–11.
Zafra, C., Temprano, J., & Suárez, J. (2017). A simplified method for determining potential heavy metal loads washed-off by stormwater runoff from road-deposited sediments. Science of The Total Environment, 601–602, 260–270.
Zhang, J., Hua, P., & Krebs, P. (2017). Influences of land use and antecedent dry-weather period on pollution level and ecological risk of heavy metals in road-deposited sediment. Environmental Pollution, 228, 158–168.
Zhaoyong, Z., Mamat, A., & Simayi, Z. (2019). Pollution assessment and health risks evaluation of (metalloid) heavy metals in urban street dust of 58 cities in China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(1), 126–140.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Vice-Chancellor for Research and Technology of Kerman University of Medical Sciences under grant number 98000337 and the code of research ethics certificate IR.KMU.REC.1398.312. The authors would like to acknowledge the Environmental Health Engineering Research Center of Kerman University of Medical Sciences. Also, the authors are grateful to the Physiology Research Center of Kerman University of Medical Sciences for technically support and staff collaboration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malakootian, M., Mohammadi, A., Nasiri, A. et al. Spatial distribution and correlations among elements in smaller than 75 μm street dust: ecological and probabilistic health risk assessment. Environ Geochem Health 43, 567–583 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00694-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00694-0