Abstract
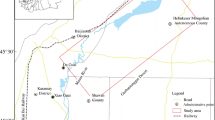
Shengjin Lake is a typical lake-type wetland in the lower of the Yangtze River, which is also an important national nature reserve in China. It is of great significance to evaluate the ecological risk of land use for promoting the coordinated development of land use and ecological environment. In this paper, according to the TM remote sensing images of Shengjin Lake wetland in Anhui province in 1986, 2002 and 2016, we used supervised classification method to divide the Shengjin Lake reserve into eight types of land use, and then we acquire land use information after the statistics of land utilization type and area, so as to analyze land use ecological risk indicator factors. Then we used analytic hierarchy process to calculate the weight of each index factor and established the land use ecological risk assessment index system. On this basis, the model of ecological risk assessment of land use was established by hierarchical analysis and fuzzy mathematics. The results showed that the overall ecological risk of Shengjin Lake wetland was intermediate in rank, from 1986 to 2016, the ecological risk of land use increased. Among them, the land use ecological risk index of the core area was relatively low, but it also showed a gradually increasing trend. The ecological risk index of the experimental area was higher. The ecological risk index of the buffer area changed obviously, and the ecological risk was serious.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, H., Liu, J., et al. (2006). Progresses of ecological risk assessment. Acta Ecologica Sinica,26(5), 1558–1566.
Ding, W., & Li, X. (2010). In recent 10 years danjiangkou hydroelectric watershed land use time and space dynamic evolution. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,27(11), 71–74.
Dong, B., Feng, Z., Du, L., et al. (2010). The Yellow River in Shandong province forest volume models for predicting the quantitative remote sensing research. Remote Sensing Technology and Application,20(4), 82–88.
Fu, Z., Xu, X., Lin, H., et al. (2001). Liaohe delta wetland regional ecological risk assessment. Acta Ecologica Sinica,21(3), 365–373.
Ji, Z. (2018). Risk analysis of land consolidation project based on fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. Project Management Technology,15(3), 57–62.
Josef, K. K., & Martin, H. (2006). Environment change in headwater peat wet lands. Netherlands: Springer.
Li, X., Bu, R., et al. (2004). The response of landscape metrics against pattern scenarios. Acta Ecologica Sinica,24(1), 123–134.
Li, D., Liao, T., Liu, H., et al. (2009). Leshan land ecological security early warning research. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition),131(13), 141–147.
Liu, X., Su, W., et al. (2012). Regional ecological risk assessment of land use in the flooding zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir area based on relative risk model. Acta Scientiae Cirumstantiae,26(5), 248–256.
Mao, X., & Ni, J. (2005). Recent progress of ecological risk assessment. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis,41(4), 646–654.
Peng, W., Dong, B., Zhang, S., et al. (2018). Research on rare cranes population response to land use change of nature wetland. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,46(11), 1795–1803.
Ren, Z., Yang, Q., Hu, Z., et al. (2009). Based on project driven by river watershed land use change of time and space dynamic analysis. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,27(3), 239–244.
Shanmugam, P., Ahn, Y. H., & Sanjeevi, S. (2006). A comparison of the classification of wetland characteristics by linear spectral mixture modelling and traditional hard classifiers on multispectral remotely sensed imagery in southern India. Ecological Modelling,194(4), 379–394.
Song, G., Li, Y., Fu, C., et al. (2010). Landscape pattern change in Yueqing Bay wetland based on RS and GIS. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 38(12), 80–83.
Su, H., & He, A. (2010). Analysis of land use based on RS and geostatistics in Fuzhou City. Journal of Natural Resources,25(1), 91–99.
Sun, H., Yang, G., Su, W., & Wan, S. (2009). The ecological risk assessment is reviewed. Chinese Journal of Ecology,28(2), 333–341.
Wang, C., Dong, B., et al. (2018). Influence of land-use change on the crane habitat and population in Shengjin Lake wetland. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University,38(3), 511–518.
Wu, C., Shi, C., Zhang, B., et al. (2007). North solid mountain wetland ecological evaluation AHP method. Yangzte River,38(1), 78–80.
Xu, M., & Fang, T. (2007). Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method with coupling AHP and Delphi method for reservoir social assessment. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University,29(2), 229–232.
Xu, X., Lin, H., Fu, Z., et al. (2001). The Yellow River delta wetland regional ecological risk assessment. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 37(1), 111–120.
Yang, L., Dong, B., Wang, Q., et al. (2015). Habitat suitability change of water birds in Shengjin Lake National Nature Reserve, Anhui Province. Journal of Lake Sciences,26(6), 1027–1034.
Yin, H., Wang, Y., et al. (2009). Regional ecological risk assessment: Its research progress and prospect. Chinese Journal of Ecology,28(05), 967–973.
Zang, S., Liang, X., & Zhang, S. (2005). GIS-based analysis of ecological risk on land-use in Daqing City. Journal of Natural Disasters,14(4), 142–145.
Zeng, H. (2005). Based on DEM and statistical analysis of the spatial pattern of forest resources to wuyi mountain as an example. Journal of Geo-Information Science,7(2), 82–88.
Zhou, L., Zhang, X., & Chen, S. (2009). Land use change and ecological risk assessment of Zhalong Natural Protection Area. Journal of Natural Disasters,18(2), 186–190.
Acknowledgements
This paper was funded by the project of LUCC in Anhui Province (2011-k-23; 2012-k-24; 2013-k-09); and the fund project of Anhui Agricultural University (wd2011-07; yj2012-03); and the project of the forest and land resources research in Anhui Province (KJ2012Z108); National Natural Science Foundation of China (41571101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, L., Dong, B., Wang, P. et al. Research on ecological risk assessment in land use model of Shengjin Lake in Anhui province, China. Environ Geochem Health 41, 2665–2679 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00322-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00322-6