Abstract
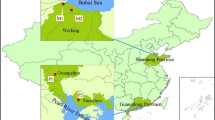
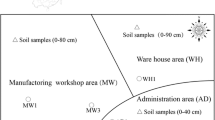
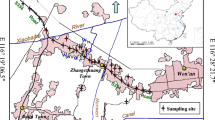
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) are a class of organic pollutants. They are used as flame retardants that caused worldwide environmental concern. This study investigated the occurrence of PBDEs in soils and dusts from three plastic manufacture plants and surrounding areas in Eastern China. A total of 13 PBDE congeners were detected using gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (electron impact ionization). The total concentrations of PBDEs range from 2.21 to 558, 19.7–4916, and 8.70–18,451 ng/g dry weight in the soils of three sampling areas, with mean of 1004 ng/g d w; in dusts, the concentrations range from 7240 to 10,469, 684–4482, and 193–3989 ng/g d w, with an overall mean of 3619 ng/g d w. The most abundant congener is the BDE-209, followed by BDE-153 and BDE-85. This indicates that the brominated flame retardant added in the plastic manufacture is mainly the commodity decabromodiphenyl ether. In comparison with other polluted areas around the world, the PBDE concentrations in the soils of the plastic manufacture plants are similar to those in soils of waste plastic disposal areas and PBDEs production sites, but orders of magnitude higher than those in agricultural soils, mountain soils and rural soils. Daily exposure was estimated using the average concentrations of the pollution sites. The hazard quotient shows that the PBDEs pose considerable human health risks, especially to children, to which attention should be paid.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, M. Y., Filley, T. R., Jafvert, C. T., Nies, L., Hua, I., & Bezares-Cruz, J. (2006). Photodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether adsorbed onto clay minerals, metal oxides, and sediment. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(1), 215–220.
Alexandre, K., Gilles, A., Brock, C., Alan, M., Robert, M., Dave, P., et al. (2008). Identification of the minor components of Great Lakes DE-71™ technical mix by means of 1 H NMR and GC/MS. Chemosphere, 73, 39–43.
Bondi, G., Abdul, N. G., Saif, U., Foday, M. J., Majed, B., & Jamal, Z. (2011). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in soils along a rural-urban- ruraltransect: Sources, concentration gradients, and profiles. Environmental Pollution, 159(12), 3666–3672.
Chen, T., Zhou, C., Mou, Y. J., & Yu, B. B. (2011). PBDEs pollution of soils in a typical e-waste disposal site and its surrounding area. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 27, 20–24.
Eljarrat, E., Marsh, G., Labandeira, A., & Barcelo, D. (2008). Effect of sewage sludges contaminated with polybrominated diphenylethers on agricultural soils. Chemosphere, 71, 1079–1086.
Eric, A., Olubiyi, I. O., Adegbenro, P. D., & Jonathan, O. O. (2017). Soil concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and trace metals from an electronic waste dump site in the Greater Accra Region, Ghana: Implications for human exposure. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 137, 247–255.
EU. (2002). The restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment.
GB 28481. (2012). The limit of harmful substances in plastic furniture.
Guardia, M. J. L., Hale, R. C., & Harvey, E. (2006). Detailed polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) congener composition of the widely used penta-, octa-, and deca-PBDE technical flameretardant mixtures. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(20), 6247–6254.
Hassanin, A., Breivik, K., Meijer, S. N., Steinnes, E., Thomas, G. O., & Jones, K. C. (2004). PBDEs in European background soils: levels and factors controlling their distribution. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 738–745. https://doi.org/10.1021/es035008y.
Jin, J., Wang, Y., Liu, W. Z., & Tang, X. Y. (2008). Level and distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soil from Laizhou Bay. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 28(7), 1463–1468.
Juan, B. C., Chad, T. J., & Inez, H. (2004). Solar photodecomposition of decabromodiphenyl ether: products and quantum yield. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(5), 4149–4156.
Kinani, S., Bouchonnet, S., Abjean, J., & Campargue, C. (2008). Determination of polybromodiphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in milk cream by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A, 25(8), 1007–1014.
Knoth, W., Mann, W., Meyer, R., & Nebhuth, J. (2007). Polybrominated diphenyl ether in sewage sludge in Germany. Chemosphere, 67, 1831–1837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.05.113.
Leung, A., Cai, Z. W., & Wong, M. H. (2006). Environmental contamination from electronic waste recycling at Guiyu, southeast China. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 8, 21–33.
Li, K., Fu, S., Yang, Z. Z., & Xu, X. B. (2008). Composition, distribution and characterization of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) in the soil in Taiyuan, China. Bulletin of Environment Contamination and Toxicology, 81, 588–593.
Liu, Q. L., Jiao, X. C., Wang, X. C., Lu, G. H., Gai, N., & Yang, Y. L. (2012). Spatial distribution of PBDEs in topsoils from electronic waste dismantling sites and the surrounding areas in Guiyu, Guangdong Province. Rock and mineral analysis, 31(6), 1006–1014.
Lyu, R. S., Huang, Q. F., Yang, Y. F., Tang, Z. W., Tian, S. L., He, J., et al. (2015). Distributions and risks of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in daily plastic products. Research of Environmental Sciences, 28(1), 74–81.
Marco, P., Niccolò, G., Roberto, C., Andrea, B., & Paolo, T. (2013). Background levels of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in soils from Mount Meru area, Arusha district (Tanzania). Science of the Total Environment, 452–453, 235–261.
Moon, H. B., Kannan, K., Lee, S. J., & Choi, M. (2007). Atmospheric deposition of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in coastal areas in Korea. Chemosphere, 66, 585–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.09.042.
Naert, C., Van Peteghem, C., Kupper, J., Jenni, L., & Naegeli, H. (2007). Distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in birds of prey from Switzerland. Chemosphere, 68, 977–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.01.009.
Ni, H. G., Cao, S. P., Chang, W. J., & Zeng, H. (2011). Incidence of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in central air conditioner filter dust from a new office building. Environmental Pollution, 159(7), 1957–1962.
Ni, K., Lu, Y. L., Wang, T. Y., Shi, Y. J., Kannan, K., Xu, L., et al. (2013). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in China: Policies and recommendations for sound management of plastic from electronic wastes. Journal of Environmental Management, 115, 114–123.
Ovokeroye, A. A., & Bice, S. M. (2016). Determination and human exposure assessment of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and tetrabromobisphenol A in indoor dust in South Africa. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 7038–7049.
Pirard, C., & Pauw, E. D. (2007). Absorption, disposition and excretion ofpolybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in chicken. Chemosphere, 66, 320–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.04.086.
Qin, P. H., Ni, H. G., Liu, Y. S., & Zeng, H. (2011). Spatial distribution and mass inventory of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in surface soil of Shenzhen, China. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 47(1), 127–132.
Qin, Q. L., Xu, X. J., Dai, Q. Y., Ye, K., & Wang, C. Y. (2018). Air pollution and body burden of persistent organic pollutants at an electronic waste recycling area of China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0176-y.
Qiu, X. H., Zhu, T., & Hu, J. X. (2010). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and other flame retardants in the atmosphere and water from Taihu Lake, East China. Chemosphere, 80(10), 1207–1212.
Shi, Y. M. (2010). Key problems in screening analysis of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in environmental monitoring and countermeasures. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 26(2), 178–184.
Tang, Z. W., Huang, Q. F., Cheng, J. L., Yang, Y. F., Yang, J., Guo, W., et al. (2014). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soils, sediments, and human hair in a plastic waste recycling area: A neglected heavily polluted area. Environmental Science and Technology, 48, 1508–1516.
Tian, H., Guo, Q., Mao, X. X., Huang, T., Ma, J. M., Wu, J. N., et al. (2014). Simulating the transfer and fate of typical PBDEs in Guangzhou. China Environmental Science, 34(3), 758–765.
Tiwari, M., Sahu, S. K., Bhangare, R. C., Ajmal, P. Y., & Pandit, G. G. (2018). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in core sediments from creek ecosystem: occurrence, geochronology, and source contribution. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0125-9.
USEPA. (2011). Exposure Factors Handbook. Washington, DC, Office of Research and Development: United States Environmental Protection Agency.
USEPA, 2015. Regional Screening Levels (RSL) for Chemical Contaminants at Superfund Sites (Accessed on 9 September, 2015). http://www.epa.gov/region9/superfund/prg/.
Wang, X. C., Jiao, X. C., Zhu, X. H., Liu, Q. L., Liu, J. C., Yin, X. C., et al. (2014). Distribution characteristics of PBDEs in surface and ground waters of electronic waste dismantling sites and surrounding area. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(6), 1027–1033.
Wang, Y., Luo, C. L., Li, J., Yin, H., Li, X. D., & Zhang, G. (2011). Characterization of PBDEs in soils and vegetations near an e-waste recycling site in South China. Environmental Pollution, 159, 2443–2448.
Wang, X. T., Wang, F., Jia, J. P., Li, Y. C., Sun, Y. Z., Wu, M. H., et al. (2010). Distribution and possible sources of PBDEs in agricultural soils from an electronic waste recycling area. China Environmental Science, 30(12), 1664–1669.
Wang, H. M., Yu, Y. J., Han, M., Yang, S. W., Li, Q., & Yang, Y. (2009). Estimated PBDE and PBB congeners in soil from an electronics waste disposal site. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 83(6), 789–793.
Wen, Q., Zhang, J. J., Guan, M., Liu, H. L., Su, G. Y., & Yu, H. X. (2012). Transformation and Metabolism of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers(PBDEs)in Environment. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 4(4), 34–41.
WHO. (1994). Brominated diphenyl ethers. Geneva.
WHO. (1997). Flame retardants: a general introduction. Geneva.
Wu, J. P., Luo, X. J., Zhang, Y., Luo, Y., Chen, S. J., Mai, B. X., et al. (2008). Bioaccumulation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in wild aquatic species from an electronic waste (e-waste) recycling site in South China. Environment International, 34, 1109–1113.
Wu, X. F., Tang, Z. W., Shen, H. Y., Huang, Q. F., & Tao, Y. (2013a). Characterization of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs)in dismantling and burning sites in electronic waste polluted area, south China. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(12), 84–89.
Wu, M. H., Tang, L., Xu, G., Ma, J., Liu, N., Wang, L., et al. (2013b). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface sediments from principal watersheds of Shanghai, China: levels, distribution, influencing factors, and risk assessment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 2651–2660.
Xu, J., Qian, W. Y., Kong, D. Y., & You, Z. Z. (2016). Pollution characteristics of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in water surrounding plastic enterprise. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 11(2), 900–905.
You, Z. Z., Kong, D. Y., Xu, J., He, J., Per, J. J., Fu, Y. J., et al. (2013). Determination of 13 polybrominated biphenyl ethers in soil and plant using accelerated solvent extraction and gas chromatography. Environmental Chemistry, 32(7), 1410–1416.
Yun, S. H., Addink, R., McCabe, J. M., Ostaszewski, A., Mackenzie-Taylor, D., Taylor, A. B., et al. (2008). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polybrominated biphenyls in sediment and floodplain soils of the Saginaw River watershed, Michigan, USA. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 55(1), 1–16.
Zeng, N., Yao, J., Tang, Z. W., Huang, Q. F., Jin, L., & He, J. (2013). Pollution characteristics of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soils from waste plastic recycling region in China. Research of Environmental Sciences, 26(4), 432–438.
Zhang, L., Wang, J. X., Xu, F., Zhang, G., Wang, Y. J., Zhang, W., et al. (2015). Distribution and Source Apportionment of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers(PBDEs)in Soils and Dusts in E-waste Recycling and Surrounding Areas. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 34(9), 1730–1736.
Zhao, X. H., Ta, N., Bao, J., Liu, W. W., & Wang, Y. R. (2015). Research Progress in Monitoring of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) in China. Environmental Science and Technology, 28(1), 65–69.
Zou, M. Y., Gong, J., & Ran, Y. (2009). The distribution and the environmental fate of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in watershed soils of PearlRiver Delta. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 18(1), 122–127.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Special Fund for Public Welfare Industry of National Environmental Protection (No. 201009026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Qian, W., Li, J. et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in soil and dust from plastic production and surrounding areas in eastern of China. Environ Geochem Health 41, 2315–2327 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00247-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00247-0