Abstract
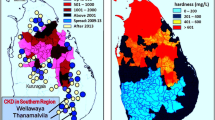
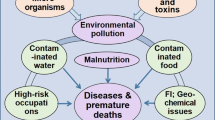
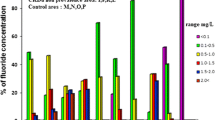
High incidence of chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDU) prevalent in many countries (e.g., Sri Lanka, equatorial America) is reviewed in the context of recent experimental work and using our understanding of the hydration of ions and proteins. Qualitative considerations based on Hofmeister-type action of these ions, as well as quantitative electrochemical models for the Gibbs free energy change for ionpair formation, are used to explain why (1) fluoride and water hardness due to magnesium ions (but not due to calcium ions) and similarly (2) cadmium ions in the presence of suitable pairing ions can be expected to be more nephrotoxic, while arsenite in the presence of fluoride and hardness may be expected to be less nephrotoxic. No synergy of arsenic with calcium hardness is found. The analysis is applied to a variety of ionic species that may be found in typical water sources to predict their likely combined electrochemical action. These results clarify the origins of chronic kidney disease that has reached epidemic proportions in the North Central Province of Sri Lanka as being most likely due to the joint presence of fluoride and magnesium ions in drinking water. The conclusion is further strengthened by a study of the dietary load of Cd and other toxins in the affected regions and in the healthy regions where the dietary toxin loads and lifestyles are similar, and found to be safe especially when the mitigating effects of micronutrient ionic forms of Zn, Se, as well as corrections for bioavailability are taken into account. The resulting etiological picture is consistent with the views of most workers in the field who have suspected that fluoride and other ions found in the hard water stagnant in shallow household wells were the major causative factors of the disease. Similar incidence of CKDu found in other hot tropical climates is likely to have similar origins.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
ADA. (2005). Fluoridation facts. Technical report, American Dental Association. www.ada.org/~/media/ADA/Member%20Center/FIles/fluoridation_facts.ashx.
Agriculture Dept Sl. (2013). Crop recommendations. http://www.agridept.gov.lk/index.php/si/crop-recommendations/903.
Amarasooriya, A. A. G. D., & Dharmagunawardhane, H. A. (2014). Leaching of aluminum and its incorporation to rice during cooking under different fluoride concentrations in water. In SAITM Research Symposium on Engineering Advancements, Malabe, Sri Lanka. http://www.saitm.edu.lk/fac_of_eng/RSEA/SAITM_RSEA_2014/imagenesweb/12.pdf.
ARL. (2012). Technical report, Analytical Research Labs, Inc., Phoenix, Arizona, USA. http://www.arltma.com/Articles/CadmiumToxDoc.htm.
ASTDR U. (2008). Notice of the revised priority list of hazardous substances that will be the subject of toxicological profiles. https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/ToxProfiles/TP.asp?id=191&tid=34.
ASTDR U. (2013). Cadmium toxicity what are the U.S. standards for cadmium exposure? https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/csem/csem.asp?csem=6&po=7.
Ben-Naim, A. (1992). Statistical thermodynamics for chemists and biochemists. New York: Plenum Press.
Brzóska, M. M., & Moniuszko-Jkoniuk, J. (2001). Interactions between cadmium and zinc in the organism. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 39, 967–980.
Bustamante, M., & Feraille, E. (2007). Sodium in health and disease. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Chandrajith, R., Dissanayake, C. B., & Tobschall, H. J. (2005). Geochemistry of trace elements in paddy (rice) soils of Sri Lanka—Implications for iodine deficiency disorders. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 27, 55–64.
Collins, K. D. (1997). Charge density-dependent strength of hydration and biological structure. Biophysical Journal, 72, 65–76.
Dahanayake, K. S., Wijewardahana, K. M. R. C., Jayasumana, M. A. C. S., & Paranagama, P. (2012). Presence of high levels of arsenic in internal organs of deceased patients with chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology (CKDu): Three case reports. In: Proceedings of the research symposium on chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology (CKDu), Sri Lanka Medical Association, Colombo, Sri Lanka. https://issuu.com/slmanews/docs/ckdu_abstract_book.html.
Dharma-wardana, M. W. C., Amarasiri, S., Dharmawardene, N., & Panabokke, C. R. (2015). Chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology and ground-water ionicity: Study based on Sri Lanka. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 37, 221–231.
Diyabalanage, S., Abekoon, S., Watanabe, I., et al. (2016a). Has irrigated water from Mahaweli River contributed to the kidney disease of uncertain etiology in the dry zone of Sri Lanka? Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 38, 439–454. doi:10.1007/s10653-015-9749-1.
Diyabalanage, S., Navarathna, T., Abeysundara, T. A., et al. (2016b). Trace elements in native and improved paddy rice from different climatic regions of Sri Lanka: Implications for public health. SpringerPlus, 5, 1684. doi:10.1186/s40064-016-3547-9.
EPA. (2011). S-environmental protection agency, drinking water regulations on fluoride. Technical report, Environmental Protection Agency, USA. https://safewater.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/212076577-4-What-are-EPA-s-drinking-water-regulations-for-fluoride-.
Fox, M. (2011). U.S. lowers limits for fluoride in water. http://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-fluoride-idUSTRE7064CM20110108.
Gracia-Tabanino, R., Dominguez, J., & Oliver, J. A. (2005). Proteinuria and chronic renal failure in the coast of El Salvador: Detection with low cost methods and associated factors. Nefrologia, 25(1), 31–38.
Illeperuma, O. A. (2011). Geo-environmental factors associated in the Rajarata kidney disease. http://www.sundaytimes.lk/110731/Plus/plus_11.html.
Illeperuma, O. A., Dharmagunawardhane, H. A., & Herath, K. R. P. (2009). Dissolution of aluminium from substandard utensils under high fluoride stress: A possible risk factor for chronic renal failures in the North-Central province. Journal of the National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka, 37, 219–222.
ITFG. (2014). Glyphosate and chronic kidney disease—Sri Lanka. Technical report, Industry Task Force on Glyphosate. http://www.glyphosate.eu/glyphosate-and-chronic-kidney-disease-sri-lanka.
Jayasekara, J. M. K. B., Dissanayake, D. M., Adhikari, S. B., & Bandara, P. (2013). Geographical distribution of chronic kidney disease of unknown origin in North Central Region of Sri Lanka. Ceylon Medical Journal, 58, 6–9.
Jayasinghe, P., Herath, B., & Wickremasinghe, N. (2015). Technical review report based on visit to Anuradhapura CKDu affected areas; Review of input–output water of reverse-osmosis installations. Technical report, COSTI (Coordinating Office for Science and Technology Innovation, Sri Lanka). https://dh-web.org/placenames/posts/COSTI-Jaysinghe-RO.pdf.
Jayasumana, C., Parangama, P., & Amarasinghe, M. (2011). Chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu) and arsenic in ground water in Sri Lanka. presence of arsenic in pesticides used in Sri Lanka. In: Proceedings on workshop on challenges in groundwater management in Sri Lanka. http://www.wrb.gov.lk/web/images/stories/downloads/Scientific_Reportsproceeding_07_april_11.pdf.
Jayasumana, C., Gunatilake, S., & Senanayake, P. (2014). Glyphosate, hard water and nephrotoxic metals: Are they the culprits behind the epidemic of chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Sri Lanka? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11, 2125–2147.
Jayasumana, C., Fonseka, S., Fernando, A., Jayalath, K., Amarasinghe, M., Siribaddana, S., et al. (2015). Phosphate fertilizer is a main source of arsenic in areas affected with chronic kidney of unknown etiology in Sri Lanka. SpringerPlus, 4, 90. doi:10.1186/s40064-015-0868-z.
Jayasumana, M. A. C. S., Paranagama, P. A., Amarasinghe, M. D., Wijewardane, K. M. R. C., Dahanayake, K. S., Fonseka, S. I., et al. (2013). Possible link of chronic arsenic toxicity with chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Sri Lanka. Journal of Natural Science Research, 3(1), 64–73.
Jayatilake, N., Mendis, S., Maheepala, P., & Metha, R. F. (2013). Chronic kidney disease of uncertain aetiology, prevalence and causative factors in a developing country. BMC Nephrology, 14, 180.
JECFA. (2011). Joint FAO/WHO food standards programme codex committee on contaminants in foods fifth session. Technical report, WHO-FAO, Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). ftp://ftp.fao.org/codex/meetings/CCCF/cccf5/cf05_INF.pdf.
Jessani, S., Bux, R., & Jafar, T. (2014). Prevalence, determinants, and management of chronic kidney disease in Karachi, Pakistan—A community based cross-sectional study. BMC Nephrology, 15, 90.
Koneshan, S., Rasaiah, J. C., Lynden-Bell, R. M., & Lee, S. H. (1998). Solvent structure, dynamics, and ion mobility in aqueous solutions at 25 °C. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 102, 4193–4204. doi:10.1021/jp980642x.
Lin, B., Shao, L., Luo, Q., Ou-yang, L., Zhou, F., Du, B., et al. (2014). Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and its association with metabolic diseases: A cross-sectional survey in Zhejiang Province, Eastern China. BMC Nephrology, 15, 36–36.
Loganathan, P., Headly, M. J., & Grace, N. D. (2008). Pasture soils contaminated with fertilizer-derived cadmium and fluorine. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 129, 29–66.
Manthrithilake, H. (2016). CKDu: Are we shooting the right target? http://dh-web.org/place.names/posts/Manthithilake-CKDu.pdf. Accessed November 12, 2016.
Marcus, I. (1991). Part 5—Gibbs free energy of hydration at 298.15 K. Journal of the Chemical Society, Faraday Transactions, 87, 2995–2999.
Matović, V., Buha, A., Bulat, Z., & Dukić-Ćosić, D. (2011). Cadmium toxicity revisited: Focus on oxidative stress induction and interactions with zinc and magnesium. Arhiv za Higijenu Rada i Toksikologiju, 62, 65–76.
McWilliams, J. E. (2009). Just food: Where locavores get it wrong and how we can truly eat responsibly. New York: Little, Brown and Co.
Meharg, A.A., Williams, P.N., Adomako, E., Lawgali, Y.Y., Deacon, C., Villada, A., et al. (2009) Geographical variation in total and inorganic arsenic content of polished (white) rice. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 1612–1617.
Meharg, A. A., Norton, G., Deacon, V., Williams, P., Adomako, E., Price, A., et al. (2013). Variation in rice cadmium related to human exposure. Environmental Science & Technology, 47, 5613–5618.
Nanayakkara, S., Senevirathna, S., Abeysekera, T., Chandrajith, R., Ratnatunga, N., Gunarathne, E., et al. (2014). An integrative study of the genetic, social and environmental determinants of chronic kidney disease characterized by tubulointerstitial damages in the North Central Region of Sri Lanka. Journal of Occupational Health, 56, 28–38.
Panabokke, C. R. (2007). Groundwater conditions in Sri Lanka. Colombo: National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka.
Premarathne, H. M. P. L. (2006). Soil and crop contamination by toxic trace elements. Master’s thesis, Post Graduate Institute of Agriculture, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, Technical Report.
Ramãres Solis, S., Mukopdhyay, R., Rosen, B. M., et al. (2004). Experimental and theoretical characterization of arsenite in water: Insights into the coordination environment of arsenite. Inorganic Chemistry, 43, 2954–2959. doi:10.1021/ic0351592.
Reddy, D. V., & Gunasekar, A. (2013). Chronic kidney disease in two coastal districts of Andhra Pradesh, India: Role of drinking water. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 35, 439–454. doi:10.1007/s10653-012-9506-7.
Salis, A., & Ninham, B. W. (2014). Models and mechanisms of Hofmeister effects in electrolyte solutions, and colloid and protein systems revisited. Chemical Society Reviews, 43, 7358–7377.
Shannon, R. D. (1976). Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances; Electronic table of Shannon ionic radii, J. David van Horn, 2001. Acta Crystallographica Section A, 32, 751–767. http://v.web.umkc.edu/vanhornj/shannonradii.htm.
Smith, P. E. (2004). Cosolvent interactions with biomolecules: Relating computer simulation data to experimental thermodynamic data. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 108, 18716–18724.
Smith, P. H., & Raymond, K. N. (1988). Solid-state and solution chemistry of calcium N-(phosphonomethyl) glycinate. Inorganic Chemistry, 27, 1056–1061.
Stritsis, C., & Claassen, N. (2013). Cadmium uptake kinetics and plants factors of shoot Cd concentration. Plant and Soil, 367, 591–603.
Tegegne, B., Chandravanshi, S. B., & Zewge, F. (2013). Fluoride levels in commercially available rice in Ethiopia. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Ethiopia, 27, 179–189.
Tomljenovic, L., & Shaw, C. (2012). Aluminum vaccine adjuvants: Are they safe? Current Medicinal Chemistry, 17, 2630–2637.
Tòth, G., Hermann, T., Da Silva, M. R., & Montanarella, L. (2016). Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environment International, 88, 299239.
Wanigasuriya, K.P., Peiris-John, R. J., & Wickremasinghe, R. (2011). Chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology in Sri Lanka: Is cadmium a likely cause? BMC Nephrology, 12, 32. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2369/12/32, downloaded November 21, 2013.
Wasana, H. M. S., Perera, G. D. R. K., De Panduka, S., Gunawardena, P. D. S., Fernando, P. S., & Bandara, J. (2017). Who water quality standards vs synergic effect(s) of fluoride, heavy metals and hardness in drinking water on kidney tissues. Nature Scientific Reports. doi:10.1038/srep42516.
Weave, V. M., Fadrowski, G. F., & Jaar, B. G. (2015). Global dimensions of chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu): A modern era environmental and/or occupational nephropathy? BMC Nephrology, 16(1), 1. doi:10.1186/s12882-015-0105-6.
WHO-SL-reports. (2013). Chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology (CKDu): A new threat to health. http://dh-web.org/place.names/posts/index.html#ckdu. Accessed November 12, 2013.
World-Bank. (2016). Fertilizer consumption (kilograms per hectare of arable land). Technical report, Food and Agriculture Organization. http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/AG.CON.FERT.ZS.
Yeo, W. K., Tan, K. L., Koh, S. B., Khan, M., Nilar, S., & Go, M. L. (2012). Exploration and optimization of structure–activity relationships in drug design using the Taguchi method. ChemMedChem, 7, 977–982.
Yu, R., Xia, T., Wang, A., & Chen, X. (2006). Effects of selenium and zinc on renal oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by fluoride in rats. Biomedical and Environmental Sciences, 19, 439–444.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dharma-wardana, M.W.C. Chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology and the effect of multiple-ion interactions. Environ Geochem Health 40, 705–719 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0017-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0017-4