Abstract
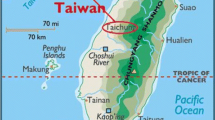
The purpose of this study is to characterize metallic elements associated with atmospheric particulate matter in the dry deposition plate, total suspended particulate, fine particles, and coarse particles at Taichung Harbor and Gong Ming Junior High School (airport) in central Taiwan at a sampling site from June 2013 to August 2013. The results indicated that: (1) the average concentrations of the metallic elements Cr and Cd were highest at the Gong Ming Junior High School (airport), and the average concentrations of the metallic elements Ni, Cu, and Pb were highest at the Taichung Harbor sampling site. (2) The high smelting industry density and export/import rate of heavily loaded cargos were the main reasons leading to these findings. (3) The average metallic element dry deposition and metallic element PM2.5–10 all followed the order of Pb > Cr > Cu > Ni > Cd at the two sampling sites. However, the average metallic elements Cu and Pb were found to have the highest dry deposition velocities and concentrations in PM2.5 for the two sampling sites in this study. (4) The correlation coefficients of ambient air particle dry deposition and concentration with wind speed at the airport were higher than those from the harbor sampling site. The wind and broad open spaces at Taichung Airport were the possible reasons for the increasing correlation coefficients for ambient air particle concentration and dry deposition with wind speed at the Taichung Airport sampling site.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aenab, A. M., Singh, S. K., & Lafta, A. J. (2013). Critical assessment of air pollution by ANOVA test and human health effects. Atmospheric Environment, 71, 84–91.
Al-Khashman, O. A. (2004). Heavy metal distribution in dust, street dust and soils from the work place in Karak Industrial Estate, Jordan. Atmospheric Environment, 38(39), 6803–6812.
Avery, C. L., Mills, K. T., Williams, R., Mcgraw, K. A., Poole, C., Smith, R. L., et al. (2010). Estimating error in using ambient PM2.5 concentrations as proxies for personal exposures: A review. Epidemiology, 21(2), 215–223.
Bell, M. L., & Hei Health review Committee. (2012). Assessment of the health impacts of particulate matter characteristics. Research report (Health Effects Institute), 161, 5–38.
Bencs, L., Ravindra, K., Hoog, J., Spolnika, Z., Bleux, N., Berghmans, P., et al. (2010). Appraisal of measurement methods, chemical composition and sources of fine atmospheric particles over six different areas of Northern Belgium. Environmental Pollution, 158, 3421–3430.
Boberly-kiss, I., Koltay, E., Szabo, G. Y., Bozo, L., & Tar, K. (1999). Composition and sources of urban and rural atmospheric aerosol in Eastern Hungary. Journal of Aerosol Science, 30, 369–391.
Cancio, J. L., Vera Castellano, A., & Chaar Herna’ndez, M. (2008). Metallic species in atmospheric particulate matter in Las Palmas de Gran Canaria. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 160, 521–528.
Celine, S. L., Lee, X. D., Li, G. Z., Li, J., Ding, A. J., & Wang, T. (2007). Heavy metals and Pb isotopic composition of aerosols in urban and suburban areas of Hong Kong and Guangzhou, South China—evidence of the long-range transport of air contaminants. Atmospheric Environment, 41, 432–447.
Chan, Y. C., Simpson, R. W., Mctainsh, G. H., Vowles, P. D., Cohen, D. D., & Bailey, G. M. (1999). Source apportionment of PM2.5 and PM10 aerosols in Brisbane (Australia) by receptor modeling. Atmospheric Environment, 33, 3251–3268.
Chen, L., Peng, S., Liu, J., & Hou, Qianqian. (2012). Dry deposition velocity of total suspended particles and meteorological influence in four locations in Guangzhou, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 24(4), 632–639.
Chu, C. C., Fang, G. C., Chen, J. C., & Lin, I. C. (2008). Ambient air dry deposition and ionic species analysis by using various deposition collectors in Shalu, central Taiwan. Atmos. Research, 88, 212–223.
Fabretti, J. F., Sauret, N., Gal, J. F., Maria, P. C., & Schärer, U. (2009). Elemental characterization and source identification of PM2.5 using positive matrix factorization: The Malraux road tunnel, nice, France. Atmospheric Research, 94, 320–329.
Faiz, Y., Tufail, M., Javed, M. T., Chaudhry, M. M., & Naila-Siddique, (2009). Road dust pollution of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn along Islamabad Expressway, Pakistan. Microchemical Journal, 92(2), 186–192.
Fang, G. C., Basu, N., Nam, D. H., & Yang, I. L. (2009). Characterization of ambient air particulates and particulate merrcury at Sha-Lu, central Taiwan. Environ Forensics, 10, 277–285.
Fang, G. C., Chang, C. N., Wu, Y. S., Fu, P. P. C., Yang, D. G., & Chu, C. C. (1999). Characterization of chemical species in PM2.5 and PM10 aerosols in suburban and rural sites of central Taiwan. The Science of the Total Environment, 234, 203–212.
Fang, G. C., Huang, Y. L., & Huang, J. H. (2010a). Study of atmospheric metallic elements pollution in Asia during 2000–2007. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 180, 115–121.
Fang, G. C., Huang, Y. L., Huang, J. H., & Liu, C. K. (2012). Dry deposition of Mn, Zn, Cr, Cu and Pb in particles of sizes of 3 μm, 5.6 μm and 10 μm in central Taiwan. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 203–204, 158–168.
Fang, G. C., Wu, Y. S., Fu, P. P. C., Chang, C. N., Chen, M. H., Ho, T. T., et al. (2005). Metallic elements study of fine and coarse particulates using a versatile air pollutant system at a traffic sampling site. Atmospheric Environment, 75, 1–14.
Fang, G., Yang, I., & Liu, C. (2010b). Measure and modeling the ambient air particles and particle bound mercury Hg(p) at a traffic sampling site. Atmospheric Research, 97(1–2), 97–105.
Geiser, L. H., Jovan, S. E., Glavich, D. A., & Porter, M. K. (2010). Lichen-based critical loads for atmospheric nitrogen deposition in Western Oregon and Washington Forests, USA. Environmental Pollution, 158(7), 2412–2421.
Geng, N., Wang, J., Xu, Y., Zhang, W., Chen, C., & Zhang, Ruiqin. (2013). PM2.5 in an industrial district of Zhengzhou. China: Chemical composition and source apportionment Particuology, 11, 99–109.
Gunawardena, Janaka., Egodawatta, Prasanna., Ayoko, Godwin. A., & Goonetilleke, Ashantha. (2013). Atmospheric deposition as a source of heavy metals in urban storm water. Atmospheric Environment, 68, 235–242.
Han, L., Zhuang, G., Cheng, S., Wang, Y., & Li, J. (2007). Characteristics of re-suspended road dust and its impact on the atmospheric environment in Beijing. Atmospheric Environment, 41(35), 7485–7499.
Herut, B., Nimmo, M., Medway, A., Chester, R., & Krom, M. D. (2001). Dry atmospheric inputs of trace metals at the Mediterranean coast of Israel (SE Mediterranean): Sourcesand fluxes. Atmospheric Environment, 35, 803–813.
Hien, P. D., Binh, N. T., Truong, Y., Ngo, N. T., & Sieu, L. N. (2001). Comparrtive receptor modelling study of TSP, PM2 and PM2-10 in Ho Chi Minh City. Atmospheric Environment, 35, 2669–2678.
Kelly, F. J., & Fussell, J. C. (2012). Size, source and chemical composition as determinants of toxicity attributable to ambient particulate matter. Atmospheric Environment, 60, 504–526.
Khillare, P. S., Balachandran, S., & Meena, B. R. (2004). Spatial and temporal variation of heavy metals in atmospheric aerosols of Delhi. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 90, 1–21.
Kim, K. H., Choi, G. H., Kang, C. H., Lee, J. H., Kim, J. Y., Youn, Y. H., et al. (2003). The chemical composition of fine and coarse particles in relation with the Asian Dust events. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 753–765.
Kim, K. H., Lee, J. H., & Jang, M. S. (2002). Metals in airborne particulate matter from the first and second industrial complex area of Taejon city, Korea. Environmental Pollution, 118, 41–51.
Kimbrough, D. E., Cohen, Y., Winer, A. M., Creelman, L., & Mabuni, C. (1999). A critical assessment of chromium in the environment. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 29(1), 1–46.
Kotchenruther, R. A. (2013). A regional assessment of marine vessel PM2.5 impacts in the U.S. Pacific Northwest using a receptor-based source apportionment method. Atmospheric Environment, 68, 103–111.
Künzli, N., Jerrett, M., Mack, W. J., Beckerman, B., Labree, L., Gilliland, F., et al. (2005). Ambient air pollution and atherosclerosis in Los Angeles. Environmental Health Perspectives, 113(2), 201–206.
Li, X., Poon, C., & Liu, P. S. (2001). Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and street dusts in Hong Kong. Applied Geochemistry, 16(11–12), 1361–1368.
Maté, T., Guaita, R., Pichiule, M., Linares, C., & Díaz, J. (2010). Short-term effect of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) on daily mortality due to diseases of the circulatory system in Madrid (Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 408, 5750–5757.
Matsumoto, K., Tominaga, S., & Igawa, M. (2011). Measurements of atmospheric aerosols with diameters greater than 10 mm and their contribution to fixed nitrogen deposition in coastal urban environment. Atmospheric Environment, 45, 6433–6438.
Mohapatr, J. K., Sanyal, A., Hemadri, D., Tosh, C., Palani, G., Rasool, T. J., et al. (2006). Development and comparison of genome detection assays for the diagnosis of foot-and-mouth disease suspected clinical samples. Journal of Virological Methods, 137(1), 14–20.
Odabasi, M., Muezzinoglu, A., & Bozlaker, A. (2002). Ambient concentrations and dry deposition fluxes of trace elements in Izmir, Turkey. Atmospheric Environment, 36(38), 5841–5851.
Okuda, T., Katsuno, M., Naoi, D., Nakao, S., Tanaka, S., He, K., et al. (2008). Trends in hazardous trace metal concentrations in aerosols collected in Beijing, China from 2001 to 2006. Chemosphere, 72(6), 917–924.
Olson, D. A., Turlington, J., Duvall, R. M., McDow, S. R., Stevens, C. D., & Williams, R. (2008). Indoor and outdoor concentrations of organic and inorganic molecular markers: Source apportionment of PM2.5 using low-volume samples. Atmospheric Environment, 42, 1742–1751.
Pedro, A., de Pereira, P., Lopes, W. A., Carvalho, L. S., da Rocha, G. O., de Carvalho Bahia, N., et al. (2007). Atmospheric concentrations and dry deposition fluxes of particulate trace metals in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. Atmospheric Environment, 41, 7837–7850.
Pope, C. A., I. I. I., & Dockery, D. W. (2006). Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: Lines that connect. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association, 56(6), 709–742.
Shahsavani, A., Naddafi, K., Jafarzade Haghighifard, N., Mesdaghinia, A., Yunesian, M., Nabizadeh, R., et al. (2012). The evaluation of PM10, PM2.5, and PM1 concentrations during the Middle Eastern Dust (MED) events in Ahvaz, Iran, from April through September 2010. Journal of Arid Environments, 77, 72–83.
Shaltout, A. A., Boman, J., Welz, B., Castilho, I. N. B., Al Ashkar, E. A., & Gaita, S. M. (2014). Method development for the determination of Cd, Cu, Ni and Pb in PM2.5 particles sampled in industrial and urban areas of Greater Cairo, Egypt, using high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchemical Journal, 113, 4–9.
Shen, Z., Cao, J., Arimoto, R., Han, Z., Zhang, R., & Han, Y. (2009). Ionic composition of TSP and PM2.5 during dust storms and air pollution episodes at Xi’an, China. Atmospheric Environment, 43, 2911–2918.
Stanek, L. W., Sacks, J. D., Dutton, S. J., & Dubois, J. J. B. (2011). Attributing health effects to apportioned components and sources of particulate matter: An evaluation of collective results. Atmospheric Environment, 45(32), 5655–5663.
Var, F., Narita, Y., & Tanaka, S. (2000). The concentration, trend and seasonal variation of metals in the atmosphere in 16 Japanese cities shown by the results of National Air Surveillance Network (NASN) from 1974to 1996. Atmospheric Environment, 34, 2755–2770.
Vardoulakis, S., Solazzo, E., & Lumbreras, J. (2011). Intra-urban and street scale variability of BTEX, NO2 and O3 in Birmingham, UK: Implications for exposure assessment. Atmospheric Environment, 45(29), 5069–5078.
Vardoulakisa, S., & Kassomenos, P. (2008). Sources and factors affecting PM10 levels in two European cities: Implications for local air quality management. Atmospheric Environment, 42(17), 3949–3963.
Wang, S., Feng, X., Zeng, X., Ma, Y., & Shang, K. (2009). A study on variations of concentrations of particulate matter with different sizes in Lanzhou, China. Atmospheric Environment, 43, 2823–2828.
Wu, Y. S., Fang, G. C., Chen, J. C., Lin, C. P., Huang, S. H., Rau, J. Y., et al. (2006). Ambient air particulate dry deposition, concentrations and metallic elements at Taichung Harbor near Taiwan Strait. Atmospheric Research, 79, 52–66.
Xu, L., Chen, X., Chen, J., Zhang, F., He, C., Zhao, J., et al. (2012). Seasonal variations and chemical compositions of PM2.5 aerosol in the urban area of Fuzhou, China. Atmospheric Research, 104–105, 264–272.
Yang, Y. J., Wang, Y. S., Wen, T. X., Li, W., Zhao, Y. N., & Li, L. (2009). Elemental composition of PM2.5 and PM10 at Mount Gongga in China during 2006. Atmospheric Research, 93, 801–810.
Yin, X., Liu, W., & Ni, J. (2014). Removal of coexisting Cr(VI) and 4-chlorophenol through reduction and Fenton reaction in a single system. Chemical Engineering Journal, 248, 89–97.
Yu, H. L., & Wang, C. H. (2010). Retrospective prediction of intraurban spatiotemporal distribution of PM2.5 in Taipei. Atmospheric Environment, 44, 3053–3065.
Zhang, N., Cao, J., Xua, H., & Zhua, C. (2013). Elemental compositions of PM2.5 and TSP in Lijiang, southeastern edge of Tibetan Plateau during pre-monsoon period. Particuology, 11, 63–69.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Science Council of the R.O.C (Taiwan) for financial support under project no. NSC 102-2815-C-241-013-E.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, GC., Chiang, HC., Chen, YC. et al. A measurement of summertime dry deposition of ambient air particulates and associated metallic pollutants in Central Taiwan. Environ Geochem Health 37, 233–249 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9642-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9642-3