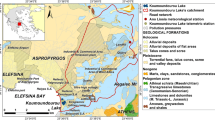
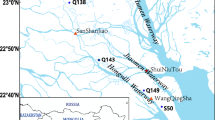
Abstract
Considering the current poor understanding of the seawater–freshwater (SW–FW) interaction pattern at dynamic hydro-geological boundary of coastal aquifers, this work strives to study tidal effect on groundwater quality using chemical tracers combined with environmental isotopes. In situ measurement data of electrical conductivity and groundwater level along with laboratory measurement data of hydro-chemical species were compared with tidal level data measured by Hydrographic and Oceanographic Department, Saijo City, Japan for time series analysis. Result shows that diurnal tides have significant effect on groundwater level as well as its chemical characteristics; however, the magnitude of effect is different in case of different aquifers. Various scatter diagrams were plotted in order to infer mechanisms responsible for water quality change with tidal phase, and results show that cations exchange, selective movement and local SW–FW mixing were likely to be the main processes responsible for water quality changes. It was also found that geological structure of the aquifers is the most important factor affecting the intensity of tidal effect on water quality.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2005). Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution (2nd edn, p. 649). Balkema. The Netherland.
Beck, A. J., Cochran, J. K., & Sanudo-Wilhelmy, S. A. (2010). The distribution and speciation of dissolved trace metals in a shallow subterranean estuary. Marine Chemistry, 121, 145–156.
Bullen, T. D., & Kendall, C. (1998). Tracing of weathering reactions and water flowpaths: A multi-isotope approach. In C. Kendall & J. J. McDonnell (Eds.), Isotope tracers in catchment hydrology (pp. 611–646). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Carr, P. A., & Kamp, G. S. V. D. (1969). Determining aquifer characteristics by the tidal method. Water Resources Research, 5, 5.
Erskine, A. D. (1992). The effect of tidal fluctuation on a coastal aquifer in the UK. Groundwater, 29, 4.
Faure, G., & Mensing, T. M. (2005). Isotopes: Principles and applications (3rd ed., pp. 347–362). New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Freeze, R. A., & Cherry, J. A. (1979). Groundwater. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Gibbes, B., Robinson, C., Li, L., & Lockington, D. (2007). Measurement of hydrodynamics and pore water chemistry in intertidal groundwater systems. Journal of Coastal Research SI, 50, 884–894.
Grant, U. S. (1948). Influence of the water table on beach aggradation and degradation. Journal of Marine Research, 7, 655–660.
Gregg, D. O. (1966). An analysis of groundwater fluctuation caused by the ocean tides in Glynn country, Georgia. Ground Water, 29(3), 24–32.
Harbison, P. (1986). Diurnal variation in the chemical environment of a shallow tidal inlet, Gulf St Vincent, South Australia: Implication for water quality and trace metal migration. Marine Environment Research, 20, 161–195.
Jha, M. K., Namgial, D., Kamii, Y., & Peiffer, S. (2008). Hydraulic parameters of coastal aquifer systems by direct methods and an extended tide–aquifer interaction technique. Water Resource Management, 22, 1899–1923.
Jorgensen, N. O., Andersen, M. S., & Engesgaard, P. (2008). Investigation of a dynamic seawater intrusion event using strontium isotopes (87Sr/86Sr). Journal of Hydrology, 348, 257–269.
Kim, J., Lee, J., Cheong, T., Kim, R., Koh, D., Ryu, J., et al. (2005). Use of time series analysis for the identification of tidal effect on groundwater in the coastal area of Kimje, Korea. Journal of Hydrology, 300, 188–198.
Kim, K. Y., Seong, H., Kim, T., Park, K., Woo, N., Park, Y., et al. (2006). Tidal effects on variations of fresh–saltwater interface and groundwater flow in a multilayered coastal aquifer on a volcanic island (Jeju Island, Korea). Journal of Hydrology, 330, 525–542.
Kumar, P., Kumar, M., Ramanathan, A. L., & Tsujimura, M. (2010). Tracing the factors responsible for arsenic enrichment in groundwater of the middle Gangetic Plain, India: A source identification perspective. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 32, 129–146.
Kumasaka, H. (2010). Estimation of groundwater residence time using CFCs as tracer in Saijo and Shuso plain. Master thesis. Tsukuba: University of Tsukuba.
Kurihara, G. (1972). Geology of the alluvial plains of the southern coastal area of Setouchi. Tohoku University Institute of Geology and Paleontology Center, 73, 31–65. (in Japanese with English abstract).
Langman, J. B., & Ellis, A. S. (2010). A multi-isotope (δD, δ18O, 87Sr/86Sr, and δ11B) approach for identifying saltwater intrusion and resolving groundwater evolution along the Western Caprock Escarpment of the Southern High Plains, New Mexico. Applied Geochemistry, 25, 159–174.
Langmuir, C. H., Vocke, R. D., Hanson, G. N., & Hart, S. R. (1978). General mixing equation with applications to Icelandic basalts. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 37, 380–392.
Li, L., Barry, D. A., Parlange, J. Y., & Pattiaratchi, C. B. (1997). Beach water table fluctuation due to wave run-up: Capillary effects. Water Resources Research, 33(5), 935–945.
Li, L., Barry, D. A., Stagnitti, F., & Parlange, J. Y. (1999). Tidal along-shore groundwater flow in a coastal aquifer. Environmental Modeling and Assessment, 4, 179–188.
Lu, J. C. S., & Chen, K. Y. (1977). Migration of trace metals in interfaces of seawater and polluted surficial sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 11, 174–182.
Nakamura, Y., Hosokawa, T., Jinno, K., & Iwamitu, K. (2005). Estimation of residence time of fresh water and salt water in coastal aquifers and their characteristics. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 49, 103–108. (in Japanese with English abstract).
Nakano, T., Saitoh, Y., & Tokumasu, M. (2008). Geological and human impacts on the aquifer system of the Saijo basin, western Japan. Proceedings of 36th IAH Congress.
Nielsen, P. (1990). Tidal dynamics of the water table in beaches. Water Resources Research, 26, 2127–2134.
Parkhurst, D. L., & Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). User’s guide to PHREEQC: a computer program for speciation, reaction-path, 1-D transport, and inverse geochemical calculations (pp. 99–4259). Report: U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations.
Robinson, C., Li, L., & Barry, D. A. (2007). Effect of tidal forcing on a subterranean estuary. Advances in Water Resources, 30, 851–865.
Saijo City. (2008). Survey of groundwater resources in Dozen plain (p. 94). Nippon Koei Co., Ltd. Japan (in Japanese).
Shalev, E., Lazar, A., Wollman, S., Kington, S., Yechieli, Y., & Gvirtzman, H. (2009). Biased monitoring of fresh water-salt water mixing zone in coastal aquifers. Ground Water, 47(1), 49–56.
Spiteri, C., Regnier, P., Slomp, C. P., & Charette, M. A. (2006). pH-dependent iron oxide precipitation in a subterranean estuary. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 88, 399–403.
Steyl, G., & Dennis, I. (2010). Review of coastal-area aquifers in Africa. Hydrogeology Journal, 18, 217–225.
Stuyfzand, P. J. (2008). Base exchange indices as indicators of salinization or freshening of (coastal) aquifers. Proceedings of the 20th salt water intrusion meeting, Naples, Florida, USA.
Tanikawa, S. (1998). Comparative study of the salinization affect to groundwater quality—case study in Saijo Plain, Ehime Pref. Proceedings of the General Meeting of the Association of Japanese Geographers, 54, 76–77.
Turner, I. (1993). The total water content of sandy beaches. Journal of Coastal Research, 15, 11–26.
Weisman, R. N., Seidel, G. S., & Ogden, M. R. (1995). Effect of watertable manipulation on beach profiles. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal and Ocean Engineering, 121(2), 134–142.
Woods, T. L., Fullagar, P. D., Spruill, R. K., & Sutton, L. C. (2000). Strontium isotopes and major elements as tracers of groundwater evolution: example from the upper Castle Hayne aquifer of North Carolina. Ground Water, 38(5), 762–771.
Acknowledgments
The authors are highly thankful to the Monbu-kagakusho (MEXT) Japanese Government fellowship which helped to pursue research. Authors also want to put on record contribution of Dr. Ki-Cheo Shin for providing the necessary logistic support to conduct experiments at RIHN, Kyoto, Japan. Authors also want to give their gratitude to Mr. Koichi Sakakibara, Mr. Wataru Yamada and all members of life and environment section, Municipal office of Saijo City for their valuable help to our field work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P., Tsujimura, M., Nakano, T. et al. Time series analysis for the estimation of tidal fluctuation effect on different aquifers in a small coastal area of Saijo plain, Ehime prefecture, Japan. Environ Geochem Health 35, 239–250 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-012-9479-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-012-9479-6