Abstract
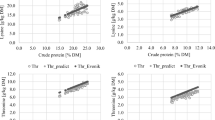
Eighteen representative sites for the Austrian grain-growing and eight for the potato-growing zones (soils and crops) were investigated. On each site, total element contents (B, Ba, Ca, Cd, Co, Cu, Fe, K, Li, Mg, Mn, Mo, Na, P, Sr and Zn) were determined in 4–12 varieties of winter wheat (n = 136), 6 varieties of spring durum wheat (n = 30), 5 varieties of winter durum wheat (n = 15), 7 varieties of rye (n = 49), 5 varieties of spring barley (n = 30) and 5 varieties of potatoes (n = 40). Element accumulations in grain species and potato tubers varied significantly with site conditions, with the main exceptions for B in potatoes and wheat as well as for Zn, Cu and Co in durum wheat. On average, across all investigated sites, differences in varieties occurred concerning the elements Ca, Cd, Ba, Sr and Zn (except Zn in potatoes and winter durum). A rough estimation revealed that an average Austrian consumer of wheat, rye and potatoes meets more than 50% of the needs of daily element intake for K, P and Mg, between 36 and 72% for Fe, Zn and Cu, and more than 100% for Co, Mo and Mn. In particular, the elements Ca and Na have to be added from other sources.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C. (2001). Trace elements in terrestrial environments: Biogeochemistry, bioavailability and risks of metals (2nd ed.). New York: Springer.
Anke M., Jaritz M., Dorn W., Seifert M., Müller R., Hoppe Ch. (2000): The biological importance of barium in the food chain of humans. In Z. Garban et al. (Eds.), Metal elements in environment, medicine and biology, band 5, Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Metal Elements in Environment, Medicine and Biology, Timisoara.
Bell, M. J., McLaughlin, M. J., Wright, G. C., & Cruickshank, A. (1997). Inter- and intra-specific variation in accumulation of cadmium by peanut, soybean, and navybean. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 48, 1151–1160.
Blum, W. E. H., Spiegel, H., & Wenzel, W. W. (1996). Bodenzustandsinventur, Konzeption, Durchführung, Bewertung (2nd ed.). Wien: Institut für Bodenforschung.
BMLFUW. (2003). 2. Lebensmittelbericht Österreich. Wien: Bundesministerium für Land- und Forstwirtschaft, Umwelt und Wasserwirtschaft.
Brüggemann, J., & Kumpulainen, J. (1995a). The status of trace elements in staple foods from the former Federal Republic of Germany. Zeitschrift fur Lebensmittel-untersuchung und -forschung, 201, 1–6.
Brüggemann, J., & Kumpulainen, J. (1995b). The status of trace elements in staple foods. Some effects of cereal and potato processing. Zeitschrift fur Lebensmittel-untersuchung und -forschung, 201, 7–11.
DGE. (2001). Referenzwerte für die Nährstoffzufuhr, 1. Auflage; Hrs. DGE, ÖGE, SGE und SVE. Frankfurt/Main: Umschau/Braus.
Elmadfa, I., Freisling, H., König, J., et al. (2003). Österreichischer Ernährungsbericht 2003, (1. Ed.). Wien: Institut für Ernährungswissenschaften, Universität Wien. ISBN 3-901861-01-7.
Friesl, W., Friedl, J., Platzer, K., Horak, O., & Gerzabek, M. H. (2006). Remediation of contaminated agricultural soils near a former Pb/Zn smelter in Austria: Batch, pot and field experiments. Environmental Pollution, 144, 40–50.
Frossard, E., Bucher, E., Mächler, F., Mozafar, A., & Hurrell, R. (2000). Potential for increasing the content and bioavailability of Fe, Zn, and Ca in plants for human nutrition. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 80, 861–879.
Kabata Pendias, A., & Pendias, H. (1992). Trace elements in soils and plants (2nd ed.). London: CRC Press.
Kirchmann, H., Mattsson, L., & Eriksson, J. (2009). Trace element concentration in wheat grain: results from the Swedish long-term soil fertility experiments and national monitoring program. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. doi:10.1007/s10653-009-9251-8.
Kurz, H., Schulz, R., & Römheld, V. (1999). Selection of cultivars to reduce the concentration of cadmium and thallium in food and fodder plants. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 162, 323–328.
Marschner, H. (1995). Mineral nutrition of higher plants (2nd ed., p. 889). London: Academic Press.
Öborn, I., Jansson, G., & Johnsson, L. (1995). A field study on the influence of soil pH on trace element levels in spring wheat, potatoes and carrots. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 85, 835–840.
ÖNORM L1061-2. (2002). Physikalische Bodenuntersuchungen—Bestimmung der Korngrößenverteilung des Mineralbodens—Teil 2: Feinboden. Wien: Austrian Standards plus.
Pfannhauser, W., Riediger, K., Messner, C., Breitschädel, R. (2004). Magnesium uptake in Austria—is there a need for action? 2nd International IUPAC Symposium—Trace elements in food, Brussels/Belgium.
Puschenreiter, M., & Horak, O. (2000). Influence of different soil parameters on the transfer factor soil to plant of Cd, Cu and Zn for wheat and rye. Die Bodenkultur, 51(1), 3–10.
Puschenreiter, M., Horak, O., Friesl, W., & Hartl, W. (2005). Low-cost agricultural measures to reduce the heavy metal transfer into human food chain e a review. Plant, Soil and Environment, 51, 1–11.
Richter, C. (2005). Agrikulturchemie und Pflanzenernährung. Weikersheim: Margraf Publishers.
Schubert, S. (2006). Pflanzenernährung. UTB 2802. Stuttgart: Eugen Ulmer.
Seifert, M., Jaritz, M., Holzinger, S., Seeber, O., & Anke, M. (2000). Alimentary strontium intake: First results in Germany. Trace Elements and Electrolytes, 17(3), 112–118.
Souci, S. W., Fachmann, W., & Kraut, H. (2000). Food composition and nutrition tables (6th ed.). Stuttgart: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsges. mbH.
Spiegel, H., & Sager, M. (2008): Elementzusammensetzung von Weizen und Kartoffeln in Österreich unter Berücksichtigung des Einflusses von Sorte und Standort. ERNÄHRUNG/NUTRITION, 32, 7/8-2008, 297-308. ISSN 0250-1554.
Wenzel, W. W., Blum, W. E. H., Brandstetter, A., Jockwer, F., Köchl, A., Oberforster, M., et al. (1996). Effects of soil properties and cultivar on cadmium accumulation in wheat grain. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 159, 609–614.
WHO. (2004). Cadmium in drinking-water. Background document for development of WHO Guidelines for drinking-water quality. WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/80.
Ysart, G., Miller, P., Crews, H., Robb, P., Baxter, M., De L’Argy, C., et al. (1999). Dietary exposure estimates of 30 elements from the UK—total diet study. Food Additives and Contaminants, 16(9), 391–403.
Zeng, F., Mao, Y., Cheng, W., Wu, F., & Zhang, G. (2008). Genotypic and environmental variation in chromium, cadmium and lead concentrations in rice. Environmental Pollution, 153, 309–314.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spiegel, H., Sager, M., Oberforster, M. et al. Nutritionally relevant elements in staple foods: influence of arable site versus choice of variety. Environ Geochem Health 31, 549–560 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-009-9254-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-009-9254-5