Abstract
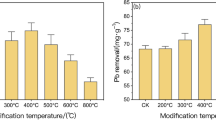
Biosorption properties of arsenate [As(V)] onto activated sludge were investigated in batch systems. The adsorption of As(V) onto sludge increased from 23 to 266 μg/g dry weight through the methylation of the activated sludge. This increase resulted from neutralization of carboxylic groups via the methylation process. The pH effect of As(V) uptake was also investigated and As(V) adsorption by methylated sludge decreased significantly at high pH (pH > 11) due to competition between As(V) and OH− ions for binding sites distributed on sludge surfaces. In contrast, low pH favored As(V) adsorption by methylated sludge because of the elevated quantities of positively charged functional groups. The results suggest that methylated activated sludge may provide promising applications for the simultaneous removal and separation of As(V) from aqueous effluents.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu, Z., Kutsal, T., Gün, S., Haciosmanoglu, N., & Gholaminejad, M. (1991). Investigation of biosorption of Cu(II), Ni(II) and Cr(VI) ions to activated sludge bacteria. Environmental Technology, 12, 915–921.
Alam, M. G. M., Tokunaga, S., & Maekawa, T. (2001). Extraction of arsenic in a synthetic arsenic-contaminated soil using phosphate. Chemosphere, 43, 1035–1041.
Brandhuber, P., & Amy, G. (1998). Alternative methods for membrane filtration of arsenic from drinking water. Desalination, 117, 1–10.
Drake, L. R., Lin, S., Rayson, G. D., & Jackson, P. J. (1996). Chemical modification and metal binding studies of Datura innoxia. Environmental Science & Technology, 30, 110–114.
Fraenkel-Conrat, H., & Olcott, H. S. (1945). Esterification of proteins with alcohols of low molecular weight. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 161, 259–268.
Gardea-Torresdey, J., Becker-Hapak, M. K., Hosea, J. M., & Darnall, D. W. (1990). Effect of chemical modification of algal carboxyl groups on metal ion binding. Environmental Science & Technology, 24, 1372–1378.
Gecol, H., Ergican, E., & Fuchs, A. (2004). Molecular level separation of arsenic (V) from water using cationic surfactant micelles and ultrafiltration membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 241, 105–119.
Kapoor, A., & Viraraghavan, T. (1997). Heavy metal biosorption sites in Aspergillus niger. Bioresource Technology, 61, 221–227.
Kang, S. Y., Lee, J. U., & Kim, K. W. (2005a). Metal removal from wastewater by bacterial biosorption: Kinetics and competition studies. Environmental Technology, 26, 615–624.
Kang, S. Y., Bremer, P. J., Kim, K. W., & McQuillan, A. J. (2005b). Monitoring metal ion binding in single layer Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms using ATR-IR spectroscopy. Langmuir, 22, 286–291.
Kim, J. Y., Davis, A., & Kim, K. W. (2003). Stabilization of available arsenic in highly contaminated mine tailings using iron. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 189–195.
Kim, K.W., & Kang, S.Y. (2006). Bacterial biosorption of trace elements, In: Trace Elements in the Environment: Biogeochemistry, Biotechnology, and Bioremediation (pp. 325–340). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Ko, I. W., Kim, J. Y., & Kim, K. W. (2004). Arsenic speciation and sorption kinetics in the As-hematite-humic acid system. Colloid Surface A, 234, 43–50.
Ko, I. W., Chang, Y. Y., Lee, C. H., & Kim, K. W. (2005). Assessment of pilot-scale acid washing of soil contaminated with As, Zn and Ni using the BCR three-step sequential extraction. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 127, 1–13.
Korngold, E., Belayev, N., & Aronov, L. (2001). Removal of arsenic from drinking water by anion exchangers. Desalination, 141, 81–84.
Lee, J. -U., & Park, H. S. (2005). Arsenic adsorption onto Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell surface. Economical Environmental Geology, 38, 525–534.
Lin, T. F., & Wu, J. K. (2001). Adsorption of arsenite and arsenate within activated alumina grains: Equilibrium and kinetics. Water Resource, 35, 2049–2057.
Loukidou, M. X., Matis, K. A., Zouboulis, A. I., & Liakopoulou-Kyriakidou, M. (2003). Removal of As(V) from wastewaters by chemically modified fungal biomass. Water Resource, 37, 4544–4552.
Maity, S., Chakravarty, S., Bhattacharjee, S., & Roy, B. C. (2005). A study on arsenic adsorption on polymetallic sea nodule in aqueous medium. Water Resource, 39, 2579–2590.
Nordstrom, D. K. (2002). Worldwide occurrences of arsenic in ground water. Science, 296, 2143–2144.
Oremland, R. S., & Stolz, J. F. (2003). The ecology of arsenic. Science, 300, 939–944.
Sağ, Y., Tatar, B., & Kutsal, T. (2003). Biosorption of Pb(II) and Cu(II) by activated sludge in batch and continuous-flow stirred reactors. Bioresource Technology, 87, 27–33.
Saxena, V. K., Kumar, S., & Singh, V. S. (2004). Occurrence, behavior and speciation of arsenic in groundwater. Current Science, 86, 281–284.
Schecher, W. D., & McAvoy, D. C. (1998). MINEQL+: A Chemical Equilibrium Modeling System. Environmental Research Software. Maine: Hallowell.
Tüzün, İ., Bayramoğlu, G., Yalçin, E., Başaran, G., Çelik, G., & Arica, M. Y. (2005). Equilibrium and kinetic studies on biosorption of Hg(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions onto microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Journal of Environmental Management, 77, 85–92.
USEPA. (2002). National Primary Drinking Water Regulations. United States Environmental Protection Agency No. 815-z−02–001.
Utgikar, V., Chen, B. Y., Tabak, H. H., Bishop, D. F., & Govind, R. (2000). Treatment of acid mine drainage: I. Equilibrium biosorption of zinc and copper on non-viable activated sludge. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 46, 19–28.
Vandecasteele, C., Dutré, V., Geysen, D., & Wauters, G. (2002). Solidification/stabilization of arsenic bearing fly ash from the metallurgical industry. Immobilisation mechanism of arsenic. Waste Management, 22, 143–146.
Volesky B. (1990). Removal and recovery of heavy metals by biosorption. In B. Volesky (Ed.), Biosorption of Heavy Metals (pp. 7–43) Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Yee, N., Benning, L. G., Phoenix, V. R., & Ferris, F. G. (2004). Characterization of metal-cyanobacteria sorption reactions: A combined macroscopic and infrared spectroscopic investigation. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 775–782.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) Research Fund and National Research Laboratory Project (Arsenic Geoenvironment Laboratory) to K.-W. Kim.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, SY., Kim, DW. & Kim, KW. Enhancement of As(V) adsorption onto activated sludge by methylation treatment. Environ Geochem Health 29, 313–318 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-007-9096-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-007-9096-y