Abstract
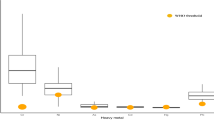
Owing to its unique nutritional and immunological characteristics, human milk is the most important food source for infants. Breast milk can, however, also be a pathway of maternal excretion of toxic elements. Selected toxic elements (As, Pb, Mn,a Hg and Cd) were determined in human breast milk and blood samples obtained from 120 subjects related to an integrated steel plant environment located in central India. Samples of breast milk and blood from subjects living outside the steel plant environment were also analyzed for comparative study. Higher levels of these toxic elements were found in blood samples as compared to breast milk samples. Plant workers showed the higher presence of these metals in their breast milk and blood samples compared to the residents of the area and the subjects living outside the industrial environment, respectively. Mn, Pb and Hg have shown a higher tendency to associate with blood and breast milk than As and Cd. The order of occurrence of these metals in blood and milk samples thus found is Mn > Pb > Hg > As > Cd.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G Concha et al. (1998) ArticleTitleLow level arsenic excretion to breast milk of native andean women exposed to high levels of arsenic in the drinking water International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health 71 42–46 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004200050248
Environmental Protection Agency: 2002, Third external review draft of air quality criteria for particulate matter Volume I and II.
J Golding (1997) Unnatural constituents of breast milk-Medication, lifestyle, pollutants, viruses, early human development 49 IssueIDSuppl S29–S43
P Grandjean PJ Jorgensen P Weihe (1994) ArticleTitleHuman milk as a source of methylmercury exposure of infants Environmental Health Perspective Journal 102 IssueID1 74–77
P Grandjean P Weihe R White (1995) ArticleTitleMilestone development in infants exposed to methylmercury from human milk Neuro Toxicology 16 IssueID1 27–34
BL Gulson CW Jameson KR Mahaffey KJ Mizon MJ Korsch G Vimpani (1997) ArticleTitlePregnancy increases mobilization of lead from maternal skeleton Journal of Laboratory Clinical Medicine 130 51–62 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-2143(97)90058-5
BL Gulson CW Jameson KR Mahaffey KJ Mizon AJ Law MJ Korsch MA Salter (1998) ArticleTitleRelationships of lead in breast milk to lead in blood, urine, and diet of the infant and mother Environmental Health Perspective 106 667–674
BL Gulson KR Mahaffey KJ Mizon MJ Korsch M Cameron G Vimpani (1995) ArticleTitleContribution of tissue lead to blood lead in adult female subjects based on stable lead isotope methods Journal of Laboratory Clinical Medicine 125 703–712
IP Hallen L Jorhem BJ Lagerkvist A Oskarsson (1995) ArticleTitleLead and cadmium levels in human milk and blood Science of Total Environment 166 149–155 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0048-9697(95)04523-4
CS Kim TC Kang (1997) ArticleTitleComparative measurement of lung deposition of inhaled fine particulate in normal subjects and patients with obstructive air-way disease American Journal of Respiratory Critical Care Medicine 155 899–905
PJ Landrigan B Sonawane D Mattison M McCally A Garg (2002) ArticleTitleChemical contaminants in breast milk and their impacts on children’s health: an overview Environmental Health Perspectives 110 IssueID6 A313–A315
U Mukherjee K Nandi KK De (1997) ArticleTitleToxic metal absorption by human population in critically polluted areas Chemical Environmental Research 6 IssueID3&4 277–290
A Oskarsson HI Palminger J Sundberg (1995) ArticleTitleExposure to toxic elements via milk Analyst 120 IssueID3 765–770 Occurrence Handle10.1039/an9952000765 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqB2MbnvFc%3D Occurrence Handle7741226
A Oskarsson HI Palminger J Sundberg (1998) ArticleTitleRisk assessment in relation to neonatal metal exposure Analyst 123 IssueID1 19–23 Occurrence Handle10.1039/a705136k Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmtlKntA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9581014
PK Pandey KS Patel P Subrt (1998) ArticleTitleTrace elemental composition of atmospheric particulate at Bhilai in central-east India The Science of the Total Environment 215 123–134 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0048-9697(98)00111-9
S Pervez GS Pandey (1994) ArticleTitleToxic metals in kidneys and gallstones of workers in a steel plant environment Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 32 93–99 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00547130
Quraishi YF. 1997 Study of physico-chemical characteristics of fugitive dusts in relation to respiratory ailments, PhD thesis, Pt. Ravishankar Shukla University, Raipur, India.
YF Quraishi GS Pandey (1995) ArticleTitleBronchial contamination with toxic metals in mineral-based industrial areas of India Environmental Geochemistry and Health 17 25–28 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00188628
M Rabinowitz A Leviton H Needleman (1985) ArticleTitleLead in milk and infant blood: a dose-response model Archives of Environmental Health 40 IssueID5 283–286
B Radisch W Luck H Nau (1987) ArticleTitleCadmium concentration in milk and blood in smoking mothers Toxicology Letters 36 147–152 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-4274(87)90178-0
R Raghunath RM Tripathi RN Khandekar KSV Nambi (1997) ArticleTitleRetention times of Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn in children’s blood Science of the Total Environment 207 IssueID2&3 133–139 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0048-9697(97)00255-6
Roosli M. 2001. Spatial variability of air pollutants in the Basel area and carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic health risk, PhD thesis, University of Basel, Switzerland.
Sharma RK. 2002 Characterization and impact assessment of emitted dusts in selected environments, PhD thesis, Pt. Ravishankar Shukla University, Raipur, India.
JC Van Loon (1980) Analytical Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy for Selected Metals Academics press New York 60–70
arian publication: 1989, Flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry – analytical methods, Varian techtron Pvt. Ltd., Publn. No. 85-10000-00, Mulgrave Victoria (Australia).
Welcher FJ. 1963 Standard Methods of Chemical Analysis, 6th Edition, Vol. 2, D. Van Nostrand Co., Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, R., Pervez, S. Toxic metals status in human blood and breast milk samples in an integrated steel plant environment in Central India. Environ Geochem Health 27, 39–45 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-004-1628-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-004-1628-0