Abstract
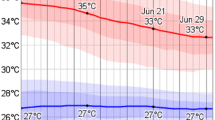
How to mitigate the effect of the urban heat island has become a hot research problem in the field of the environment, landscape engineering, and the architectural design. The heat island of the micro-climate, such as the residence community, has much more impact on the people’s life, and should be paid more attentions. In this paper, the experiment and simulation methods are combined to study the heat island of residence community. Four sensitivity factors (wind velocity, underlying and building surface, anthropogenic heating and landscape) are chosen to study their influences on the urban heat island (UHI). The results show that the correlation coefficients of the above four sensitivity factors on the UHI are −0.718, 0.521, 0.251 and −0.229, respectively. And the sequence of the above factors to reduce UHI from strong to weak is wind velocity, underlying and the building surface, anthropogenic heating and the landscape.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen XL, Zhao HM, Li PX, Yin ZY (2006) Remote sensing image-based analysis of the relationship between urban heat island and land use/cover changes. Remote Sens Environ 104(2):133–146. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2005.11.016
Alexandri E, Jones P (2008) Temperature decreases in an urban canyon due to green walls and green roofs in diverse climates. Build Environ 43(4):480–493. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2006.10.055
Mathew A, Sreekumar S, Khandelwal S, Kaul N, Kumar R (2016) Prediction of surface temperatures for the assessment of urban heat island effect over Ahmedabad city using linear time series model. Energy Build 128:605–616. doi:10.1016/j.enbuild.2016.07.004
Zheng S, Zhao L, Li Q (2016) Numerical simulation of the impact of different vegetation species on the outdoor thermal environment. Urban For Urban Green 18:138–150. doi:10.1016/j.ufug.2016.05.008
Fan H, Sailor DJ (2005) Modeling the impacts of anthropogenic heating on the urban climate of Philadelphia: a comparison of implementations in two PBL schemes. Atmos Environ 39(1):73–84. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.09.031
Chen H, Ooka R, Huang H, Tsuchiya T (2009) Study on mitigation measures for outdoor thermal environment on present urban blocks in Tokyo using coupled simulation. Build Environ 44(11):2290–2299. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2009.03.012
Lin BR, Tan G, Wang P, Song L, Zhu YX, Zhai GK (2004) Study on the thermal performance of the Chinese traditional vernacular dwellings in Summer. Energy Build 36(1):73–79. doi:10.1016/s0378-7788(03)00090-2
Ward K, Lauf S, Kleinschmit B, Endlicher W (2016) Heat waves and urban heat islands in Europe: a review of relevant drivers. Sci Total Environ 569–570:527–539. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.119
Kakoniti A, Georgiou G, Marakkos K, Kumar P, Neophytou MKA (2016) The role of materials selection in the urban heat island effect in dry mid-latitude climates. Environ Fluid Mech 16(2):347–371. doi:10.1007/s10652-015-9426-z
Klein PM, Galvez JM (2015) Flow and turbulence characteristics in a suburban street canyon. Environ Fluid Mech 15(2):419–438. doi:10.1007/s10652-014-9352-5
Constantinescu D, Cheval S, Caracaş G, Dumitrescu A (2016) Effective monitoring and warning of urban heat island effect on the indoor thermal risk in Bucharest (Romania). Energy Build 127:452–468. doi:10.1016/j.enbuild.2016.05.068
Gómez F, Cueva AP, Valcuende M, Matzarakis A (2013) Research on ecological design to enhance comfort in open spaces of a city (Valencia, Spain). Utility of the physiological equivalent temperature (PET). Ecol Eng 57:27–39. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.04.034
Jim CY, He H (2011) Estimating heat flux transmission of vertical greenery ecosystem. Ecol Eng 37(8):1112–1122. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.02.005
Eksi M, Rowe DB, Fernández-Cañero R, Cregg BM (2015) Effect of substrate compost percentage on green roof vegetable production. Urban For Urban Green 14(2):315–322. doi:10.1016/j.ufug.2015.03.006
Ratanachotinun J, Kasayapanand N, Hirunlabh J, Visitsak S, Teekasap S, Khedari J (2016) A design and assessment of solar chimney of bioclimatic house wall and roof for construction in the housing market of Thailand. Build Serv Eng Res Technol 37(6):694–709. doi:10.1177/0143624416647761
Wang Y, Ma Z, Zhou Y, Zhu H, Huang Y, Yang Y (2016) Experimental investigation on the airflow characteristics of an attachment-based personalized ventilation method. Build Serv Eng Res Technol 37(6):710–729. doi:10.1177/0143624416658088
Buyantuyev A, Wu J (2010) Urban heat islands and landscape heterogeneity: linking spatiotemporal variations in surface temperatures to land-cover and socioeconomic patterns. Landsc Ecol 25(1):17–33. doi:10.1007/s10980-009-9402-4
Yuan J, Emura K, Sakai H, Farnham C, Lu S (2016) Optical analysis of glass bead retro-reflective materials for urban heat island mitigation. Sol Energy 132:203–213. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2016.03.011
Pei Z, Lin B, Liu Y, Zhu Y (2015) Comparative study on the indoor environment quality of green office buildings in China with a long-term field measurement and investigation. Build Environ 84:80–88. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2014.10.015
Kalogirou SA (2004) Solar thermal collectors and applications. Prog Energy Combust Sci 30(3):231–295. doi:10.1016/j.pecs.2004.02.001
Gizińska-Górna M, Czekała W, Jóźwiakowski K, Lewicki A, Dach J, Marzec M, Pytka A, Janczak D, Kowalczyk-Juśko A, Listosz A (2016) The possibility of using plants from hybrid constructed wetland wastewater treatment plant for energy purposes. Ecol Eng 95:534–541. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.055
Grudzińska M (2016) Glazed balconies as passive greenhouse systems—potential of their use in Poland. Build Serv Eng Res Technol 37(5):555–572. doi:10.1177/0143624416641294
Elsayed K, Lacor C (2013) CFD modeling and multi-objective optimization of cyclone geometry using desirability function, Artificial neural networks and genetic algorithms. Appl Math Model 37(8):5680–5704. doi:10.1016/j.apm.2012.11.010
Acknowledgements
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, W., Xue, Y. Numerical and experimental study of sensitivity factors on heat island of residence community. Environ Fluid Mech 17, 1189–1205 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10652-017-9544-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10652-017-9544-x