Abstract
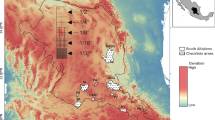
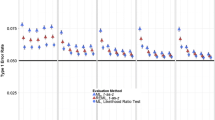
Monitoring stream networks through time provides important ecological information. The sampling design problem is to choose locations where measurements are taken so as to maximise information gathered about physicochemical and biological variables on the stream network. This paper uses a pseudo-Bayesian approach, averaging a utility function over a prior distribution, in finding a design which maximizes the average utility. We use models for correlations of observations on the stream network that are based on stream network distances and described by moving average error models. Utility functions used reflect the needs of the experimenter, such as prediction of location values or estimation of parameters. We propose an algorithmic approach to design with the mean utility of a design estimated using Monte Carlo techniques and an exchange algorithm to search for optimal sampling designs. In particular we focus on the problem of finding an optimal design from a set of fixed designs and finding an optimal subset of a given set of sampling locations. As there are many different variables to measure, such as chemical, physical and biological measurements at each location, designs are derived from models based on different types of response variables: continuous, counts and proportions. We apply the methodology to a synthetic example and the Lake Eacham stream network on the Atherton Tablelands in Queensland, Australia. We show that the optimal designs depend very much on the choice of utility function, varying from space filling to clustered designs and mixtures of these, but given the utility function, designs are relatively robust to the type of response variable.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caselton WF, Zidek JV (1984) Optimal monitoring network designs. Stat Probab Lett 2(4):223–227
Cressie N (1993) Statistics for spatial data. Wiley, New York
Cressie N, Frey J, Harch B, Smith M (2006) Spatial prediction on a river network. J Agric Biol Environ Stat 11(2):127–150
Diggle PJ, Lophaven S (2006) Bayesian geostatistical design. Scand J Stat 33(1):53–64
Diggle PJ, Ribeiro PJ (2007) Model based geostatistics. Springer, New York
Dobbie MJ, Henderson BL, Stevens DL (2008) Sparse sampling: spatial design for monitoring stream networks. Stat Surv 2(2008):113–153
Evangelou E, Zhu Z (2012) Optimal predictive design augmentation for spatial generalised linear mixed models. J Stat Plan Inf 142(12):3242–3253
Harville DA (1974) Bayesian inference for variance components using only error contrasts. Biometrika 61(2):383–385
Li J (2009) Spatial multivariate design in the plane and on stream networks. PhD thesis, University of Iowa
Muller P (1999) Simulation based optimal design. Bayesian Stat 6:459–474
Müller WG (1998) Collecting spatial data: optimum design of experiments for random fields. Heidelberg: Physica-Verlag
Peterson EE, Ver Hoef JM (2010) A mixed-model moving-average approach to geostatistical modeling in stream networks. Ecology 91(3):644–651
Royle JA (2002) Exchange algorithms for constructing large spatial designs. J Stat Plan Inf 100(2):121–134
Shreve RL (1967) Infinite topographically random channel networks. J Geol 75(1):178–186
Spatial Reporting Of Ecosystem Health Project. (2009) CSIRO and the Queensland Department of Environment and Resource Management. Included in SSN version 1.0 R package http://www.fs.fed.us/rm/boise/AWAE/projects/SpatialStreamNetworks
Ver Hoef JM, Peterson EE (2010) A moving average approach for spatial statistical models of stream networks. J Am Stat Assoc 105(489):6–18
Ver Hoef JM, Peterson EE, Clifford D, Shah R (2014) SSN: an R package for spatial statistical modelling on stream networks. J Stat Softw 56(3):1–45
Ver Hoef JM, Peterson EE, Theobald D (2006) Spatial statistical models that use flow and stream distance. Environ Ecol Stat 13(4):449–464
Wolfinger R, O’Connell M (1993) Generalized linear mixed models: a pseudo-likelihood approach. J Stat Comput Simul 48:233–243
Zhang H (2002) On estimation and prediction for spatial generalized linear mixed models. Biometrics 58(1):129–136
Zhu Z, Stein ML (2006) Spatial sampling design for prediction with estimated parameters. J Agric Biol Environ Stat 11(1):24–44
Zimmerman DL (2006) Optimal network design for spatial prediction, covariance parameter estimation, and empirical prediction. Environmetrics 17(6):635–652
Acknowledgments
The authors were supported by an Australian Research Council Discovery Grant. The authors would like to thank Dr. Erin Peterson and Associate Professor Zhengyuan Zhu for very helpful discussions. Additionally, the authors thank two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments which greatly improved this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Pierre Dutilleul.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falk, M.G., McGree, J.M. & Pettitt, A.N. Sampling designs on stream networks using the pseudo-Bayesian approach. Environ Ecol Stat 21, 751–773 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-014-0279-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-014-0279-2