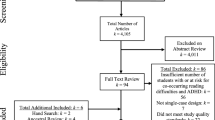
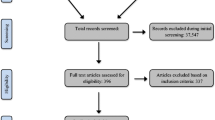
Abstract
This meta-analysis systematically identified reading intervention research for students with reading difficulties and problem behaviors in grades K–12 to determine the (a) impact of these reading interventions on reading outcomes and (b) extent to which reading outcomes varied based on student characteristics (e.g., grade, disability), intervention characteristics (e.g., group size, additional behavioral supports), and quality indicator characteristics. Follow-up analyses investigated three of the four hypothesized mechanisms underlying the high co-occurrence rate between reading difficulties and problem behaviors: (a) reading difficulties lead to future problem behaviors, (b) problem behaviors lead to future reading difficulties, and (c) a bi-directional association exists between reading difficulties and problem behaviors. Eleven studies were identified. There was a statistically significant main effect of reading interventions on reading outcomes (g = 0.86, p < .01). We did not find evidence to support either of the three stated hypotheses. The primary limitation of this study was a lack of reading intervention research for students with reading difficulties and problem behaviors. Due to the limited sample of intervention research to investigate the first three hypotheses, future intervention research is needed to better understand the relationship between reading and behavior difficulties. Furthermore, future reading intervention research is needed to better understand how to best develop a program of instruction for this population of students.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
References marked with an asterisk indicate studies included in the meta-analysis
Beaver, J. M., & Carter, M. A. (2003). Developmental reading assessment. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.
Benner, G. J., Nelson, J. R., & Epstein, M. H. (2002). Language skills of children with EBD: a literature review. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 10(1), 43–56. https://doi.org/10.1177/106342660201000105.
Benner, G. J., Nelson, J. R., Ralston, N. C., & Mooney, P. (2010). A meta-analysis of the effects of reading instruction on the reading skills of students with or at risk of behavioral disorders. Behavioral Disorders, 35, 86–102 Doi: jstor.org/stable/43153810.
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Introduction to meta-analysis. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd..
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R. (2014). Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (Version 3.3.070) [Computer software]. Englewood: Biostat.
*Cassar, A. G., & Jang, E. E. (2010). Investigating the effects of a game-based approach in teaching word recognition and spelling to students with reading disabilities and attention deficits. Australian Journal of Learning Difficulties, 15(2), 193–211. https://doi.org/10.1080/19404151003796516.
Chall, J. S., & Jacobs, V. A. (1983). Writing and reading in the elementary grades: developmental trends among low SES children. Language Arts, 60, 617–626 Doi: jstor.org.du.idm.oclc.org/stable/41961511.
Chow, J. C., & Ekholm, E. (2018). Do published studies yield larger effect sizes than unpublished studies in education and special education? A meta-review. Educational Psychology Review, 30, 727–744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-018-9437-7.
Chow, J. C., & Wehby, J. H. (2018). Associations between language and problem behavior: a systematic review and correlational meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 30(1), 61–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-016-9385-z.
Chronis, A. M., Jones, H. A., & Raggi, V. L. (2006). Evidence-based psychosocial treatments for children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clinical Psychology Review, 26(4), 486–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2006.01.002.
*Cochran, L., Feng, H., Cartledge, G., & Hamilton, S. (1993). The effects of cross-age tutoring on the academic achievement, social behaviors, and self-perceptions of low-achieving African-American males with behavioral disorders. Behavioral Disorders, 18, 292–302 Doi: jstor.org/stable/23887470.
Coleman, M., & Vaughn, S. (2000). Reading interventions for students with emotional/ behavioral disorders. Behavioral Disorders, 25(2), 93–104. https://doi.org/10.1177/019874290002500201.
Compton, D. L., Fuchs, D., Fuchs, L. S., Elleman, A. M., & Gilbert, J. K. (2008). Tracking children who fly below the radar: latent transition modeling of students with late-emerging reading disability. Learning and Individual Differences, 18(3), 329–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2008.04.003.
Cook, C. R., Dart, E., Collins, T., Restori, A., Daikos, C., & Delport, J. (2012). Preliminary study of the confined, collateral, and combined effects of reading and behavior interventions: evidence for a transactional relationship. Behavioral Disorders, 38(1), 38–56. https://doi.org/10.1177/019874291203800104.
Daley, D., Van der Oord, S., Ferrin, M., Danckaerts, M., Doepfner, M., Cortese, S., et al. (2014). Behavioral interventions in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials across multiple outcome domains. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 53(8), 835–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2014.05.013.
Dietz, S., & Montague, M. (2006). Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder comorbid with emotional and behavioral disorders and learning disabilities in adolescents. Exceptionality, 14(1), 19–33. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327035ex1401_3.
DuPaul, G. J., & Weyandt, L. L. (2006). School-based intervention for children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: effects on academic, social, and behavioral functioning. International Journal of Disability, Development and Education, 53(2), 161–176. https://doi.org/10.1080/10349120600716141.
DuPaul, G. J., Eckert, T. L., & Vilardo, B. (2012). The effects of school-based interventions for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis 1996-2010. School Psychology Review, 41, 387–412 Retrieved from: https://search.proquest.com/docview/1319240445?accountid=14608.
Durlak, J. A., Weissberg, R. P., Dymnicki, A. B., Taylor, R. D., & Schellinger, K. B. (2011). The impact of enhancing students’ social and emotional learning: a meta-analysis of school-based universal interventions. Child Development, 82(1), 405–432. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2010.01564.x.
Duval, S., & Tweedie, R. (2000). A nonparametric “trim and fill” method of accounting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 95(449), 89–98. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.2000.10473905.
Elliott, S., & Gresham, F. (1991). Social skills intervention guide: practical strategies for social skills training. Circle Pines: American Guidance Service.
Engelmann, S., & Bruner, E. C. (1988). Reading mastery I/II fast cycle: teacher’s guide. Chicago: Science Research Associates.
Engelmann, S., Carnine, L., & Johnson, G. (1988a). Corrective reading: word attack basics, decoding A. Chicago: Science Research Associates.
Engelmann, S., Johnson, G., Carnine, L., Meyer, L., Becker, W., & Eisele, J. (1988b). Corrective reading: decoding strategies, decoding B1. Chicago: Science Research Associates.
Fabiano, G. A., Pelham, W. E., Jr., Coles, E. K., Gnagy, E. M., Chronis-Tuscano, A., & O'Connor, B. C. (2009). A meta-analysis of behavioral treatments for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clinical Psychology Review, 29(2), 129–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2008.11.001.
Forness, S. R., Freeman, S. F., Paparella, T., Kauffman, J. M., & Walker, H. M. (2012a). Special education implications of point and cumulative prevalence for children with emotional or behavioral disorders. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 20(1), 4–18. https://doi.org/10.1177/1063426611401624.
Forness, S. R., Kim, J., & Walker, H. M. (2012b). Prevalence of students with EBD: impact on general education. Beyond Behavior, 21, 3–11 Doi. jstor.org/stable/24011810.
Froehlich, T. E., Lanphear, B. P., Epstein, J. N., Barbaresi, W. J., Katusic, S. K., & Kahn, R. S. (2007). Prevalence, recognition, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a national sample of US children. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 161(9), 857–864. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.161.9.857.
Froehlich, T. E., Fogler, J., Barbaresi, W. J., Elsayed, N. A., Evans, S. W., & Chan, E. (2018). Using ADHD medications to treat coexisting ADHD and reading disorders: a systematic review. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 104(4), 619–637. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.1192.
Garwood, J. D., Brunsting, N. C., & Fox, L. C. (2014). Improving reading comprehension and fluency outcomes for adolescents with emotional-behavioral disorders: recent research synthesized. Remedial and Special Education, 35(3), 181–194. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741932513514856.
Garwood, J. D., Varghese, C., & Vernon-Feagans, L. (2017). Internalizing behaviors and hyperactivity/inattention: consequences for young struggling readers, and especially boys. Journal of Early Intervention, 39(3), 218–235. https://doi.org/10.1177/1053815117706524.
Gaskins, I. W., Downer, M. A., & Gaskins, R. W. (1986). Introduction to the benchmark school word identification/vocabulary development program. Media: Benchmark School.
Gray, C., & Climie, E. A. (2016). Children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and reading disability: a review of the efficacy of medication treatments. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 988. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00988.
Hall, C., Roberts, G. J., Cho, E., McCulley, L. M., Carroll, M., & Vaughn, S. (2017). Reading instruction for English language learners in the middle grades: a synthesis of the research. Educational Psychology Review, 29(4), 763–794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-016-9372-4.
Hedges, L. V., Tipton, E., & Johnson, M. C. (2010). Robust variance estimation in meta-regression with dependent effect size estimates. Research Synthesis Methods, 1(1), 39–65. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.5.
Hinshaw, S. P. (1992). Externalizing behavior problems and academic underachievement in childhood and adolescence: causal relationships and underlying mechanisms. Psychological Bulletin, 111(1), 127–155. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.111.1.127.
Institute of Educational Sciences. (2017). What Works Clearinghouse procedures and standards handbook version 4.0. Retrieved from https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/Docs/referenceresources/wwc_procedures_handbook_v4.pdf Access: May 28, 2019
Jacobson, L. A., Ryan, M., Denckla, M. B., Mostofsky, S. H., & Mahone, E. M. (2013). Performance lapses in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder contribute to poor reading fluency. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 27(7), 672–683. https://doi.org/10.1093/arclin/act048.
Jitendra, A. K., DuPaul, G. J., Someki, F., & Tresco, K. E. (2008). Enhancing academic achievement for children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: evidence from school-based intervention research. Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 14(4), 325–330. https://doi.org/10.1002/ddrr.39.
Kauffman, J. M. (2015). The ‘B’ in EBD is not just for bullying. Journal of Research in Special Educational Needs, 15(3), 167–175. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-3802.12102.
Kauffman, J. M., & Landrum, T. J. (2017). Characteristics of emotional and behavioral disorders of children and youth (11th ed.). Upper Saddle River: Pearson.
*Lane, K. L. (1999). Young students at risk for antisocial behavior: the utility of academic and social skills interventions. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 7(4), 211–223. https://doi.org/10.1177/106342669900700403.
*Lane, K. L., Fletcher, T., Carter, E. W., Dejud, C., & Delorenzo, J. (2007). Paraprofessional-led phonological awareness training with youngsters at risk for reading and behavioral concerns. Remedial and Special Education, 28(5), 266–276. https://doi.org/10.1177/07419325070280050201.
Liberatti, A., Altman, D. G., Tetzlaff, J., Mulrow, C., Gotzsche, P. C., et al. (2009). The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Medicine, 6, 1–28.
Lim, H. J., & Kim, J. (2011). A longitudinal study of children’s social behaviors and their causal relationship to reading growth. Asia Pacific Education Review, 12(2), 197–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12564-010-9124-y.
Lin, Y. C., Morgan, P. L., Hillemeier, M., Cook, M., Maczuga, S., & Farkas, G. (2013). Reading, mathematics, and behavioral difficulties interrelate: Evidence from a cross-lagged panel design and population-based sample of US upper elementary students. Behavioral Disorders, 38, 212–227. https://doi.org/10.1177/019874291303800404.
Mastropieri, M. A., Emerick, K., & Scruggs, T. E. (1988). Mnemonic instruction of science concepts. Behavioral Disorders, 14(1), 48–56.
Mattison, R. E. (2008). Characteristics of reading disability types in middle school students classified ED. Behavioral Disorders, 34, 27–41 Doi: jstor.org/stable/43153799.
McGrath, L. M., Pennington, B. F., Shanahan, M. A., Santerre-Lemmon, L. E., Barnard, H. D., Willcutt, E. G., et al. (2011). A multiple deficit model of reading disability and attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder: searching for shared cognitive deficits. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 52(1), 547–557. https://doi.org/10.1037/spq0000037.
Mercer, C. D., & Campbell, K. U. (1998). Great leaps reading program. Gainsville: Diar Muid Inc..
Morgan, P. L., Farkas, G., & Wu, Q. (2009). Kindergarten predictors of recurring externalizing and internalizing psychopathology in the third and fifth grades. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 17(2), 67–79. https://doi.org/10.1177/1063426608324724.
Morgan, P. L., Farkas, G., Tufis, P. A., & Sperling, R. A. (2008). Are reading and behavior problems risk factors for each other? Journal of Learning Disabilities, 41(5), 417–436. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219408321123.
Mugnaini, D., Lassi, S., La Malfa, G., & Albertini, G. (2009). Internalizing correlates of dyslexia. World Journal of Pediatrics, 5(4), 255–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-009-0049-7.
*Nelson, J. R., Benner, G. J., & Gonzalez, J. (2005a). An investigation of the effects of a prereading intervention on the early literacy skills of children at risk of emotional disturbance and reading problems. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 13(1), 3–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/10634266050130010101.
Nelson, J. R., Benner, G., & Gonzalez, J. (2003). Learner characteristics that influence the treatment effectiveness of early literacy interventions: a meta-analytic review. Learning Disabilities Research and Practice, 18(4), 255–267. https://doi.org/10.1111/1540-5826.00080.
Nelson, J. R., Cooper, C., & Gonzalez, J. (2004). Stepping stones to literacy. Longmont: Sopris West.
Nelson, J. R., Lane, K. L., Benner, G. J., & Kim, O. (2011). A best evidence synthesis of literacy instruction on the social adjustment of students with or at-risk for behavior disorders. Education and Treatment of Children, 34, 141–162 Doi: jstor.org/stable/42900104.
*Nelson, J. R., Stage, S. A., Epstein, M. H., & Pierce, C. D. (2005b). Effects of a prereading intervention on the literacy and social skills of children. Exceptional Children, 72(1), 29–45. https://doi.org/10.1177/001440290507200102.
Peterson, R. L., Boada, R., McGrath, L. M., Willcutt, E. G., Olson, R. K., & Pennington, B. F. (2017). Cognitive prediction of reading, math, and attention: shared and unique influences. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 50(5), 408–421. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02346.x.
Prasad, V., Brogan, E., Mulvaney, C., Grainge, M., Stanton, W., & Sayal, K. (2013). How effective are drug treatments for children with ADHD at improving on-task behaviour and academic achievement in the school classroom? A systematic review and meta-analysis. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 22(4), 203–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-012-0346-x.
Rabiner, D. L., Malone, P. S., & Conduct Problems Prevention Research Group. (2004). The impact of tutoring on early reading achievement for children with and without attention problems. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 32(3), 273–284. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JACP.0000026141.20174.17.
Rapport, M. D., Orban, S. A., Kofler, M. J., & Friedman, L. M. (2013). Do programs designed to train working memory, other executive functions, and attention benefit children with ADHD? A meta-analytic review of cognitive, academic, and behavioral outcomes. Clinical Psychology Review, 33(8), 1237–1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2013.08.005.
Rivera, M. O., Al-Otaiba, S., & Koorland, M. A. (2006). Reading instruction for students with emotional and behavioral disorders and at risk of antisocial behaviors in primary grades: review of literature. Behavioral Disorders, 31(3), 323–339. https://doi.org/10.1177/019874290603100306.
Roberts, G. J., Solis, M., Ciullo, S., McKenna, J. W., & Vaughn, S. (2015a). Reading interventions with behavioral and social skill outcomes: a synthesis of research. Behavior Modification, 39(1), 8–42. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145445514561318.
Roberts, G., Rane, S., Fall, A.-M., Denton, C. A., Fletcher, J. M., & Vaughn, S. (2015b). The impact of intensive reading intervention on level of attention in middle school students. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 44(6), 942–953. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2014.913251.
*Rogevich, M. E., & Perin, D. (2008). Effects on science summarization of a reading comprehension intervention for adolescents with behavior and attention disorders. Exceptional Children, 74(2), 135–154. https://doi.org/10.1177/001440290807400201.
Sanford, C., Newman, L., Wagner, M., Cameto, R., Knokey, A. M., & Shaver, D. (2011). The post-high school outcomes of young adults with disabilities up to 6 years after high school: key findings from the National Longitudinal Transition Study-2 (NLTS2). NCSER 2011-3004. National Center for Special Education Research.
Scammacca, N. K., Roberts, G., Vaughn, S., & Stuebing, K. K. (2015). A meta-analysis of interventions for struggling readers in grades 4-12: 1980-2011. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 48(4), 369–390. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219413504995.
Sexton, C. C., Gelhorn, H. L., Bell, J. A., & Classi, P. M. (2012). The co-occurrence of reading disorder and ADHD: epidemiology, treatment, psychosocial impact, and economic burden. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 45(6), 538–564. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219411407772.
Sibley, M. H., Pelham, W. E., Jr., Molina, B. S., Gnagy, E. M., Waschbusch, D. A., Garefino, A. C., et al. (2012). Diagnosing ADHD in adolescence. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 80(1), 139–150. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026577.
Slavin, R. E. (1986). Best-evidence synthesis: an alternative to meta-analytic and traditional reviews. Educational Researcher, 19, 141–162 Doi: jstor.org/stable/42900104.
Spencer, V. G. (2006). Peer tutoring and students with emotional or behavioral disorders: a review of the literature. Behavioral Disorders, 31(2), 204–222. https://doi.org/10.1177/019874290603100206.
StataCorp. (2013). Stata Statistical Software: release 13. College Station: StataCorp LP.
*Tamm, L., Denton, C. A., Epstein, J. N., Schatschneider, C., Taylor, H., Arnold, L. E., et al. (2017). Comparing treatments for children with ADHD and word reading difficulties: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 85(5), 434–446. https://doi.org/10.1037/ccp0000170.
*Tannock, R., Frijters, J. C., Martinussen, R., White, E. J., Ickowicz, A., Benson, N. J., & Lovett, M. W. (2018). Combined modality intervention for ADHD with comorbid reading disorders: a proof of concept study. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 51(1), 55–72. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219416678409.
Tipton, E. (2015). Small sample adjustments for robust variance estimation with meta-regression. Psychological Methods, 20, 375–393. https://doi.org/10.1037/met0000011.
Tipton, E., & Pustejovsky, J. E. (2015). Small-sample adjustments for tests of moderators and model fit using robust variance estimation in meta-regression. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics, 40, 604–634. https://doi.org/10.3102/1076998615606099.
Torgesen, J. K., & Bryant, B. R. (1994). Phonological awareness training for reading. Austin: PRO-ED.
*Trout, A. L., Epstein, M. H., Mickelson, W. T., Nelson, J. R., & Lewis, L. M. (2003). Effects of a reading intervention for kindergarten students at risk for emotional disturbance and reading deficits. Behavioral Disorders, 28(3), 313–326.
Trzesniewski, K. H., Moffitt, T. E., Caspi, A., Taylor, A., & Maughan, B. (2006). Revisiting the association between reading achievement and antisocial behavior: new evidence of an environmental explanation from a twin study. Child Development, 77(1), 72–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2006.00857.x.
Vadasy, P. F., & Sanders, E. (2007). Sound Partners Plus. Seattle, WA: Washington Research Institute. Vocabulary development program. Media, PA: Benchmark School.
Vadasy, P. F., Wayne, S. K., O’Connor, R. E., Jenkins, J. R., Pool, K., Firebaugh, M., & Peyton, J. A. (2005). Sound partners: a tutoring program in phonics-based early reading. Longmont: Sopris West.
Wagner, M., & Cameto, R. (2004). The characteristics, experiences, and outcomes of youth with emotional disturbances. A report from the National Longitudinal Transition Study-2. Volume 3, issue 2. National Center on Secondary Education and Transition, University of Minnesota (NCSET). Retrieved from http://www.ncset.org/publications/viewdesc.asp?id=1687. Accessed 31 Jul 2018.
Wanzek, J., Stevens, E. A., Williams, K. J., Scammacca, N., Vaughn, S., & Sargent, K. (2018). Current evidence on the effects of intensive early reading interventions. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 51(6), 612–624. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219418775110.
Wanzek, J., Vaughn, S., Kim, A. H., & Cavanaugh, C. L. (2006). The effects of reading interventions on social outcomes for elementary students with reading difficulties: a synthesis. Reading and Writing Quarterly, 22(2), 121–138. https://doi.org/10.1080/10573560500242192.
Wanzek, J., Vaughn, S., Scammacca, N. K., Metz, K., Murray, C. S., Roberts, G., & Danielson, L. (2013). Extensive reading interventions for students with reading difficulties after grade 3. Review of Educational Research, 83, 163–195. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654313477212.
Wanzek, J., Vaughn, S., Scammacca, N., Gatlin, B., Walker, M. A., & Capin, P. (2016). Meta-analyses of the effects of tier 2 type reading interventions in grades k-3. Educational Psychology Review, 28(3), 551–576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-015-9321-7.
Wigfield, A., & Guthrie, J. T. (2000). Engagement and motivation in reading. Handbook of Reading Research, 3, 403–422.
Willcutt, E. G., Betjemann, R. S., McGrath, L. M., Chhabildas, N. A., Olson, R. K., DeFries, J. C., & Pennington, B. F. (2010). Etiology and neuropsychology of comorbidity between RD and ADHD: the case for multiple-deficit models. Cortex, 46, 1345–1361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2010.06.009.
Willcutt, E. G., Pennington, B. F., Olson, R. K., Chhabildas, N., & Hulslander, J. (2005). Neuropsychological analyses of comorbidity between reading disability and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: in search of the common deficit. Developmental Neuropsychology, 27(1), 35–78. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326942dn2701_3.
Woodcock, R. W. (1987). Woodcock reading mastery tests–revised. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service.
*Zeng, S., Benner, G. J., & Silva, R. M. (2016). Effects of a summer learning program for students at risk for emotional and behavioral disorders. Education and Treatment of Children, 39, 593–615. https://doi.org/10.1353/etc.2016.0026.
Funding
This study was funded by the University of Denver—2017 PROF Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberts, G.J., Cho, E., Garwood, J.D. et al. Reading Interventions for Students with Reading and Behavioral Difficulties: a Meta-analysis and Evaluation of Co-occurring Difficulties. Educ Psychol Rev 32, 17–47 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-019-09485-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-019-09485-1