Abstract
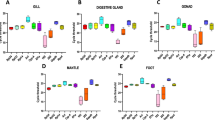
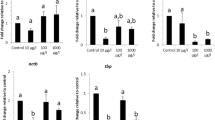
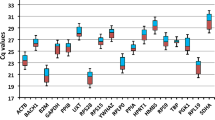
The annual killifish Austrolebias charrua is an endangered species, endemic to the southern region of South America, which inhabits temporary ponds that emerges in the rainy season. The main anthropogenic threat driving the extinction of A. charrua stems from extensive agriculture, primarily due to the widrespread use of glyphosate-based herbicides near their habitats. Annual killifishes have been used as models for ecotoxicological studies but, up to now, there are no studies about reference genes in any Austrolebias species. This represents an obstacle to the use of qPCR-based technologies, the standard method for gene expression quantification. The present study aimed to select and validate potential reference genes for qPCR normalization in the annual killifish Austrolebias charrua considering different tissues, gender and environmental conditions. The candidate reference genes 18 s, actb, gapdh, ef1a, shox, eif3g, and the control gene atp1a1 were evaluated in male and female individuals in three different tissues (brain, liver, and gills) under two experimental conditions (control and acute exposition to Roundup Transorb®). The collected tissues were submitted to RNA extraction, followed by cDNA synthesis, cloning, sequencing, and qPCR. Overall, 18 s was the most stable reference gene, and 18 s and ef1a were the most stable combination. Otherwise, considering all variables, gapdh and shox were the least stable candidate genes. Foremost, suitable reference genes were validated in A. charrua, facilitating accurate mRNA quantification in this species, which might be useful for developing molecular tools of ecotoxicological assessment based on gene expression analysis for environmental monitoring of annual killifish.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Ørntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Research 64(15):5245–5250. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-04-0496
Barber RD, Harmer DW, Coleman RA, Clark BJ (2005) GAPDH as a housekeeping gene: analysis of GAPDH mRNA expression in a panel of 72 human tissues. Physiol Genomics 21:389–395. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00025.2005
Berois N, García G, De Sá RO (2016) Annual Fishes - Life History Strategy, Diversity, and Evolution. CRC Press Taylor & Francis group, New York
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55(4):611–622. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797
Chapman JR, Waldenström J (2015) With Reference to Reference Genes: A Systematic Review of Endogenous Controls in Gene Expression Studies. PLoS One 10;10(11). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141853
Chovanec A, Hofer R, Schiemer F (2003) Chapter 18: Fish as bioindicators. Trace Metals and other Contaminants in the Environment 6:639–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-5215(03)80148-0
De Castro BD, Lanés LEK, Godoy RS, Maltchik L, Oliveira GT (2022) Development stage-dependent oxidative stress responses to the exposure to roundup original© in a neotropical annual killifish. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 95:103976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2022.103976
Ferrante M, Rapisarda P, Grasso A, Favara C, Oliveri Conti G (2023) Glyphosate and environmental toxicity with “One Health” approach, a review. Environ Res 235:116678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116678.
Forner-Piquer I, Faucherre A, Byram J, Blaquiere M, de Bock F, Gamet-Payrastre L, Ellero-Simatos S, Audinat E, Jopling C, Marchi N (2021) Differential impact of dose-range glyphosate on locomotor behavior, neuronal activity, glio-cerebrovascular structures, and transcript regulations in zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 267:128986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128986
Froese R, Pauly D (2021) Fishbase: World Wide Web Electronic Publication. Avaliable at: www.fishbase.org.version.(08/2021)
García G, Gutiérrez V, Ríos N (2022) Living in Temporary Ponds Loading Giant Genomes: The Neotropical Annual Killifish Genus Austrolebias as New Outstanding Evolutionary Model. Front Genet 20(13):90368. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.903683
García G, Ríos N, Gutiérrez V, Serra S, Loureiro M (2019) Transcriptome-Based SNP Discovery and Validation in the Hybrid Zone of the Neotropical Annual Fish Genus Austrolebias. Genes (Basel) 10(10):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100789. 11
Godoy RS, Lanés LEK, Castro BD, Weber V, Wingen N, Pires MM, Oliveira GT, Maltchik L (2020) Oxidative stress resistance in a short-lived neotropical annual killifish. Biogerontology 21(2):217–229
Harrison JB, Sunday JM, Rogers SM (2019) Predicting the fate of eDNA in the environment and implications for studying biodiversity. Proc Biol Sci 286(1915):20191409. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2019.1409
ICMBio (2018) Livro Vermelho da Fauna Brasileira Ameaçada de Extinção:. Volume VI Peixes, Instituto Chico Mendes de Conservação da Biodiversidade. Ministério do Meio Ambiente, Brasilia
Jaramillo ML, Pereira AG, Davico CE, Nezzi L, Ammar D, Müller YMR, Nazari EM (2018) Evaluation of reference genes for reverse transcription-quantitative PCR assays in organs of zebrafish exposed to glyphosate-based herbicide, Roundup. Animal 12(7):1424–1434. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1751731117003111
Kozera B, Rapacz M (2013) Reference genes in real-time PCR. J Appl Genet 54(4):391–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-013-0173-x
Kuchipudi SV, Tellabati M, Nelli RK, White GA, Perez BB, Sebastian S, Slomka MJ, Brookes SM, Brown IH, Dunham SP, Chang KC (2012) 18S rRNA is a reliable normalisation gene for real time PCR based on influenza virus infected cells. Virol J 9:230. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-9-230
Langiano VC, Martinez CB (2008) Toxicity and effects of a glyphosate-based herbicide on the Neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 147(2):222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2007.09.009
Li Y, Han J, Wu J, Li D, Yang X, Huang A, Du X (2020) Transcriptome-based evaluation and validation of suitable housekeeping gene for quantification real-time PCR under specific experiment condition in teleost fishes. Fish and Shel ImmunoL 98:218–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.01.018
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔct Method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lopes AR, Moraes JS, Martins CMG (2022) Effects of the herbicide glyphosate on fish from embryos to adults: a review addressing behavior patterns and mechanisms behind them. Aquat Toxicol 251:106281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2022.106281
Ma J, Zhu J, Wang W, Ruan P, Rajeshkumr S, Li X (2019) Biochemical and molecular impacts of glyphosate-based herbicide on the gills of common carp. Environmental Pollution 252:1288–1300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.040
Martins AWS, Silveira TLR, Remião MH, Domingues WB, Dellagostin EN, Varela Junior AS, Corcini CD, Costa PG, Bianchini A, Somoza GM, Robaldo RB, Campos VF (2021) Acute exposition to Roundup Transorb® induces systemic oxidative stress and alterations in the expression of newly sequenced genes in silverside fish (Odontesthes humensis). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 46:65127–65139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15239-w
Naumann B, Englert C (2018) Dispersion/reaggregation in early development of annual killifishes: Phylogenetic distribution and evolutionary significance of a unique feature. Dev Biol 442(1):69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.07.015
Nikinma M, Rytkönen KT (2011) Functional genomics in aquatic toxicology-do not forget the function. Aquat Toxicol 105(3):16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.05.019
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians TP (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper – Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnology Letters 26(6):509–515. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:bile.0000019559.84305.47
OECD (2019) Test No. 203: Fish, Acute Toxicity Test. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264069961-en
Pagano AD, Gonçalves NM, Domingues WB, da Silveira TLR, Kütter MT, Junior ASV, Corcini CD, Nascimento MC, Dos Reis LFV, Costa PG, Bianchini A, Volcan MV, Remião MH, Campos VF (2024) Assessment of oxidative stress biomarkers in the threatened annual killifish Austrolebias charrua exposed to Roundup. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 276:109787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2023.109787.
Reichard M, Polačik M (2019) Nothobranchius furzeri, an ‘instant’ fish from an ephemeral habitat. Elife 8:e41548.
Ribeiro YM, Moreira DP, Weber AA, Sales CF, Melo RMC, Bazzoli N, Rizzo E, Paschoalini AL (2022) Adverse effects of herbicides in freshwater Neotropical fish: A review. Aquat Toxicol 252:106293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2022.106293
Rocha DG, Castro TP, Aguiar ER, Pacheco LC (2020) Gene Expression Analysis in Bacteria by RT-qPCR. Methods in Mol. Biol. 2065:119–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9833-3_10
Saad D, Chauke P, Cukrowska E, Richards H, Nikiema J, Chimuka L, Tutu H (2022) First biomonitoring of microplastic pollution in the Vaal River using Carp fish (Cyprinus carpio) “as a bio-indicator”. Sci Total Environ 836:155623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155623.
Silveira TLR, Domingues WB, Remião MH, Santos L, Barreto B, Lessa IM, Varela Junior AS, Martins Pires D, Corcini C, Collares T, Seixas FK, Robaldo RB, Campos VF (2018) Evaluation of Reference Genes to Analyze Gene Expression in Silverside Odontesthes humensis Under Different Environmental Conditions. Front Genet 9:75. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00075
Silver N, Best S, Jiang J, Thein SL (2006) Selection of housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in human reticulocytes using real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 7:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-7-33
Smith CM, Vera MKM, Bhandari RK (2019) Developmental and epigenetic effects of Roundup and glyphosate exposure on Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Aquat Toxicol 210:215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.03.005
Sylvester F, Weichert FG, Lozano VL et al. (2023) Better integration of chemical pollution research will further our understanding of biodiversity loss. Nat Ecol Evol 7(10):1552–1555. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-023-02117-6
Tang R, Dodd A, Lai D, McNabb WC, Love DR (2007) Validation of zebrafish (Danio rerio) reference genes for quantitative real-time RT-PCR normalization. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 39(5):384–390. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7270.2007.00283.x~
Topal A, Atamanalp M, Uçar A, Oruç E, Kocaman EM, Sulukan E, Ceyhun SB (2015) Effects of glyphosate on juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Transcriptional and enzymatic analyses of antioxidant defence system, histopathological liver damage and swimming performance. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 111:206–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.09.027
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 18. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034
Volcan MV, Lanés LEK (2018) Brazilian killifishes risk extinction. Science 361(6400):340–341. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau5930
Xie F, Xiao P, Chen D, Xu L, Zhang B (2012) miRDeepFinder: a miRNA analysis tool for deep sequencing of plant small RNAs. Plant Mol Biol 80(1):75–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-012-9885-2
Yang C, Lim W, Song G (2021) Reproductive toxicity due to herbicide exposure in freshwater organisms. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2021.109103
Zebral YD, Lansini LR, Costa PG, Roza M, Bianchini A, Robaldo RB (2018) A glyphosate-based herbicide reduces fertility, embryonic upper thermal tolerance and alters embryonic diapause of the threatened annual fish Austrolebias nigrofasciatus. Chemosphere 196:260–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.196
Authors contributions
Matheus Volcan, Tony Silveira, Mariana Remião, Antônio Pagano, and Vinicius Campos conceived and designed the experiments. Tony Silveira and Mateus Kütter collected the animals. Antônio Pagano and Natiéli Gonçalves maintained the animals. Antônio Pagano, Lucas de Souza, William Domingues, Patrícia Costa and Adalto Bianchini carried out the laboratorial analyses. Antônio Pagano, Eduardo Blödorn, and Vinicius Campos contributed to the interpretation of the results. Antônio Pagano took the lead in writing the manuscript and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS-FAPESP #19/2551-0001323-0 and FAPERGS/SICT 06/2022 INOVA AGRO # 22/2551-0001645-6), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (Chamada CNPq/MCTI/CT-BIOTEC N° 31/2022, Processo # 440636/2022-1) and was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nivel Superior – Brasil (CAPES) Finance Code 001 and AUXPE #2537/2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The collection of animals was carried out through permit IBAMA/SISBIO 71072. The animal use and all handling practices were approved by the Ethics Committee on Animal Experimentation of the Federal University of Rio Grande (process no. 23116.003876/2019-24).
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pagano, A.D., Blödorn, E.B., Domingues, W.B. et al. Validation of qPCR reference genes in the endangered annual killifish Austrolebias charrua considering different tissues, gender and environmental conditions. Ecotoxicology (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-024-02752-0
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-024-02752-0