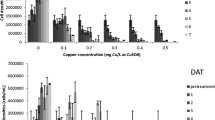
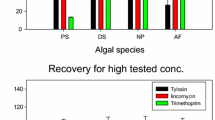
Abstract
Macroalgae are one of the main producers in marine environments. However, only a few toxicity test methods have been established that use reference strains of macroalgae to evaluate the effects of chemicals on the growth and reproduction of macroalgae to monitor water quality. We selected reference strains of Chlorophyta, Ulva aragoënsis; Phaeophyceae, Ectocarpus siliculosus; and wakame, Undaria pinnatifida, as test species to establish a microplate-based method to investigate the toxicity of potassium dichromate, 3,5-dichlorophenol, and two common herbicides (diuron and simazine). We determined the growth of the three macroalgae in their early life stages and during the sporangia formation stage in E. siliculosus under laboratory conditions. We observed that the growth and sporangia formation in these algae were impaired in a dose-dependent manner. Additionally, we investigated the sensitivity of these macroalgae by comparing the toxicity values of toxicants used in this study with those obtained from a database. Compared to other microalgae and plant species, macroalgae showed a relatively high sensitivity to organic compounds, including herbicides. Growth tests using U. aragoënsis and E. siliculosus produced reliable results at 0–32 and 25–32 practical salinity units (PSU), respectively. The tests established in this study could test the toxicity of chemical substances in macroalgae and are thus expected to contribute to a better understanding of the environmental risks of chemical substances on aquatic biota. The tests could be applied to all effluent toxicity tests used for the management of seawater and brackish water quality.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated or analyzed in this study can be procured on request from the corresponding author.
References
Afonso NC, Catarino MD, Silva AMS, Cardoso SM (2019) Brown macroalgae as valuable food ingredients. Antioxidants (Basel) 8:365. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090365
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals—concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075
Baba M (2008) Effects of temperature, irradiance and salinity on the growth of Undaria pinnatifida from Niigata Prefecture, Central Japan. Rep Mar Ecol Res Inst 11:7–15. https://kaiseiken.or.jp/publish/reports/lib/2008_11_02.pdf
Chapman G, Denton D, Lazorchak J (1995) Short-term methods for estimating the chronic toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to west coast marine and estuarine organisms. United States Environmental Protection Agency, EPA/600/R-95-136, (NTIS PB96261665). Washington, DC, https://cfpub.epa.gov/si/si_public_record_report.cfm?Lab=NERL&dirEntryId=46584 p 1995
Charrier B, Coelho SM, Le Bail A, Tonon T, Michel G, Potin P, Kloareg B, Boyen C, Peters AF, Cock JM (2008) Development and physiology of the brown alga Ectocarpus siliculosus: two centuries of research. New Phytol 177:319–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02304.x
Coelho SM, Scornet D, Rousvoal S, Peters NT, Dartevelle L, Peters AF, Cock JM (2012) Ectocarpus: a model organism for the brown algae. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2012:193–198. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.emo065821
Escher B, Leusch F (2011) Bioanalytical tools in water quality assessment. Water Intell Online 10:272. https://doi.org/10.2166/9781780400778
Fairman R, Mead CD, Williams WP (1998) Environmental risk assessment: approaches, experiences and information Environmental Issue Report, vol 4. http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/GH-07-97-595-EN-C2. Accessed 12 Oct 2022. EEA (European Environment Agency), pp. 252
Fourest E, Volesky B (1997) Alginate properties and heavy metal biosorption by marine algae. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 67:215–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02788799
Girling JA, Thomas KV, Brooks SJ, Smith DJ, Shahsavari E, Ball AS (2015) A macroalgal germling bioassay to assess biocide concentrations in marine waters. Mar Pollut Bull 91:82–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.12.025
Han T, Choi GW (2005) A novel marine algal toxicity bioassay based on sporulation inhibition in the green macroalga Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta). Aquat Toxicol 75:202–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.08.003
Han YS, Kumar AS, Han T (2009) Comparison of metal toxicity bioassays based on inhibition of sporulation and spore release in Ulva pertusa. Toxicol Environ Health Sci 1:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03216460
Hooten RL, Carr RS (1998) Development and application of a marine sediment pore-water toxicity test using Ulva fasciata zoospores. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:932–940. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620170524
Hothorn T, Bretz F, Westfall P (2008) Simultaneous inference in general parametric models. Biom J 50:346–363. https://doi.org/10.1002/bimj.200810425
Igbinosa EO, Odjadjare EE, Chigor VN, Igbinosa IH, Emoghene AO, Ekhaise FO, Igiehon NO, Idemudia OG (2013) Toxicological profile of chlorophenols and their derivatives in the environment: the public health perspective. Scientific World Journal 2013:460215. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/460215
Johansson P, Eriksson KM, Axelsson L, Blanck H (2012) Effects of seven antifouling compounds on photosynthesis and inorganic carbon use in sugar kelp Saccharina latissima (Linnaeus). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 63:365–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-012-9778-z
Karuppanapandian T, Moon JC, Kim C, Manoharan K, Kim W (2011) Reactive oxygen species in plants: their generation, signal transduction, and scavenging mechanisms. Aust J Crop Sci 5:709–725
Kılınç B, Cirik S, Turan G, Tekogul H, Koru E (2013) Seaweeds for food and industrial applications. In: Food Ind. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/53172
Lee H, Lee J, Brown MT, Park J, Vieira C, Han T (2019a) Toxicity testing of cosmetic ingredients using gametophyte beads of the brown alga Undaria pinnatifida (Laminariales, Phaeophyta). J Appl Phycol 31:2011–2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1669-x
Lee H, Brown MT, Choi S, Pandey LK, De Saeger J, Shin K, Kim JK, Depuydt S, Han T, Park J (2019b) Reappraisal of the toxicity test method using the green alga Ulva pertusa Kjellman (Chlorophyta). J Hazard Mater 369:763–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.076
Lee H, Depuydt S, Choi S, Han T, Park J (2020) Rapid toxicity assessment of six antifouling booster biocides using a microplate-based chlorophyll fluorescence in Undaria pinnatifida gametophytes. Ecotoxicology 29:559–570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02207-2
Mann KH (1973) Seaweeds: their productivity and strategy for growth: the role of large marine algae in coastal productivity is far more important than has been suspected. Science 182:975–981. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.182.4116.975
Niwa K (2016) Seedling production of Undaria pinnatifida using free-living gametophytes in a large indoor tank. Aquacult Sci 64:173–182. https://doi.org/10.11233/aquaculturesci.64.173. (in Japanese with English abstract)
Norberg-King TJ, Embry MR, Belanger SE, Braunbeck T, Butler JD, Dorn PB, Farr B, Guiney PD, Hughes SA, Jeffries M, Journel R, Lèonard M, McMaster M, Oris JT, Ryder K, Segner H, Senac T, Van Der Kraak G, Whale G, Wilson P (2018) An international perspective on the tools and concepts for effluent toxicity assessments in the context of animal alternatives: Reduction in vertebrate use. Environ Toxicol Chem 37:2745–2757. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4259
Norton SB, Rodier DJ, van der Schalie WH, Wood WP, Slimak MW, Gentile JH (1992) A framework for ecological risk assessment at the EPA. Environ Toxicol Chem 11:1663–1672. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620111202
OECD (2004) Test No. 202: Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilisation Test, OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. Section 2, Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264069947-en
OECD (2011) Test No. 201: freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test, OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. Section 2, Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264069923-en
OECD (2019) Test No. 203: Fish Acute Toxicity Test, OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. Section 2, Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264069961-en
Park J, Park J, Jin G, Hwang MS, Brown MT, Han T (2016) Toxicity tests using the kelp Undaria pinnatifida for heavy metal risk assessment. Toxicol Environ Health Sci 8:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-016-0265-1
Peters AF, Marie D, Scornet D, Kloareg B, Mark Cock J (2004) Proposal of Ectocarpus siliculosus (Ectocarpales, Phaeophyceae) as a model organism for brown algal genetics and genomics. J Phycol 40:1079–1088. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2004.04058.x
Provasoli L (1966) Media and prospects for the cultivation of marine algae. In: Watanabe A, Hattori A (eds) (end) Cultures and collections of algae Proceedings of the US-Jpn conference held at Hakone, 12-15 Sept 1966. Jpn Soc Plant Physiol, pp 63–75
Quinn B, Gagné F, Blaise C (2009) Evaluation of the acute, chronic and teratogenic effects of a mixture of eleven pharmaceuticals on the cnidarian, Hydra attenuata. Sci Total Environ 407:1072–1079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.10.022
R Core Team (2022) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, http://www.R-project.org 2022
Ritz C, Baty F, Streibig JC, Gerhard D (2015) Dose–response analysis using R. PLOS ONE 10:e0146021. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146021
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2089
Shimada Y, Masakiyo Y, Shimada S (2018) Thallus fragmentation and culture temperature and salinity conditions for induction of maturation of Ulva mediterranea. Aquac Sci 66:117–122. https://doi.org/10.11233/aquaculturesci.66.117. (in Japanese with English abstract)
Skriptsova A, Khomenko V, Isakov V (2004) Seasonal changes in growth rate, morphology and alginate content in Undaria pinnatifida at the northern limit in the Sea of Japan (Russia). J Appl Phycol 16:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JAPH.0000019049.74140.61
Softcheck KA (2021) Marine algal sensitivity to source and weathered oils. Environ Toxicol Chem 40:2742–2754. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5128
United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) (2002) Red microalga, Champia parvula, sexual reproduction test Method 1009.0. In: Short-term methods for estimating the chronic toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to marine and estuarine organisms. https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-08/documents/short-term-chronic-marine-and-estuarine-wet-manual_2002.pdf. Accessed 12 Oct 2022. EPA, Washington DC-821-R-02-014
Wang X, Shan T, Pang S (2019) Effects of cobalt on spore germination, gametophyte growth and gametogenesis of Undaria pinnatifida (Phaeophyceae). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102:784–788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02614-0
Wendt I, Arrhenius Å, Backhaus T, Hilvarsson A, Holm K, Langford K, Tunovic T, Blanck H (2013) Effects of five antifouling biocides on settlement and growth of zoospores from the marine macroalga Ulva lactuca L. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91:426–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1057-9
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Goro Yoshida (Nagasaki Field Station, Fisheries Technology Institute, Japan Fisheries Research and Education Agency) for his guidance on culturing wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) and Ms. Mika Momosaki and Ms. Yuko Makimoto (Hatsukaichi Field Station, Fisheries Technology Institute, Japan Fisheries Research and Education Agency) for their assistance. We thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing. This study was supported by the Environment Research and Technology Development Fund (JPMEERF20185003) of the Environmental Restoration and Conservation Agency of Japan.
Author contributions
The study was conceptualized by TO and KM. The data was curated and analyzed by TO and RS. HY and KM acquired the funds for the study. TO, RS, and TY were involved in the experimental investigations. The methodology to be adopted was decided upon by TO and RS. HY and KM were responsible for project administration and supervision. TO and RS participated in the validation of the tests. TO prepared the original draft and was also involved in the review and editing along with RS, TY, TH, HY, and KM.
Funding
This work was supported by the Environment Research and Technology Development Fund (Grant number JPMEERF20185003) of the Environmental Restoration and Conservation Agency of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Onduka, T., Somiya, R., Yamagishi, T. et al. Development of a microplate-based novel toxicity bioassay using Chlorophyta and Phaeophyceae macroalgae. Ecotoxicology 32, 824–836 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-023-02692-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-023-02692-1