Abstract
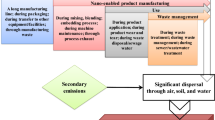
Nanoscale zero-valent iron particles (NZVI) are widely used in a variety of industries owing to their advantageous mechanical, physical, and chemical properties. These particles can be released into environmental media, including water, soil, and air, through several pathways. NZVI in the ecosystem can be taken up, excreted and distributed within organisms, which is harmful to plants, animals and humans. Plants play a significant role as producers in the ecological circle and can both positively and negatively affect the ecological behavior of NZVI. Therefore, understanding the relationship between plants and NZVI is likely to be of great value for the assessment of NZVI-associated risks and future research directions. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge on the uptake, distribution, and accumulation of NZVI in plants; the phytotoxicity triggered by NZVI exposure at the physiological, biochemical, and molecular levels; and the defense mechanism used by plants to defend against NZVI-induced insults. We further discuss the toxic effects of NZVI on soil animals and microorganisms as well as the risk posed by the presence of NZVI in the food chain.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. The data has not been modified in anyway.
References
Asli S, Neumann PM (2009) Colloidal suspensions of clay or titanium dioxide nanoparticles can inhibit leaf growth and transpiration via physical effects on root water transport. Plant Cell Environ 32(5):577–584
Auffan M, Achouak W, Rose J, Roncato M-A, Chaneac C, Waite DT, Masion A, Woicik JC, Wiesner MR, Bottero J-YJES (2008) Relation between the redox state of iron-based nanoparticles and their cytotoxicity toward Escherichia coli. Environ Sci Technol 42(17):6730–6735
Barnes RJ, van der Gast CJ, Riba O, Lehtovirta LE, Prosser JI, Dobson PJ, Thompson IPJJOHM (2010) The impact of zero-valent iron nanoparticles on a river water bacterial community. J Hazard Mater 184(1-3):73–80
Barrena R, Casals E, Colón J, Font X, Sánchez A, Puntes VJC (2009) Evaluation of the ecotoxicity of model nanoparticles. Chemosphere 75(7):850–857
Bennett RN, Wallsgrove RMJNP (1994) Secondary metabolites in plant defence mechanisms. New Phytol 127(4):617–633
Briat J-F, Lobréaux, SJTIPS (1997). Iron transport and storage in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2(5):187–193
Cabiscol Català E, Tamarit Sumalla J, Ros Salvador JJIM (2000) Oxidative stress in bacteria and protein damage by reactive oxygen species. Int Microbiol 3(1):3–8
Cao J, Elliott D, Zhang W-XJJONR (2005) Perchlorate reduction by nanoscale iron particles. J Nanopart Res. 7(4):499–506
Cao J, Zhang W-XJJOHM (2006) Stabilization of chromium ore processing residue (COPR) with nanoscale iron particles. J Hazard Mater 132(2-3):213–219
Cape JN (1994) Evaluation of pollutant critical levels from leaf surface characteristics, Air pollutants and the leaf cuticle. Springer, 123–138
Chang MC, Kang HY (2009) Remediation of pyrene-contaminated soil by synthesized nanoscale zero-valent iron particles. J Environ Sci Health Part a-Toxic/Hazardous Substances Environ Eng 44(6):576–582
Chang Y-N, Zhang M, Xia L, Zhang J, Xing GJM (2012) The toxic effects and mechanisms of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles. Materials 5(12):2850–2871
Chaudière J, Ferrari-Iliou RJF (1999) Intracellular antioxidants: from chemical to biochemical mechanisms. Food Chem Toxicol 37(9-10):949–962
Chen PJ, Tan SW, Wu WL (2012) Stabilization or oxidation of nanoscale zerovalent iron at environmentally relevant exposure changes bioavailability and toxicity in medaka fish. Environ Sci Technol 46(15):8431–8439
Curie C, Alonso JM, JEAN ML, Ecker JR, Briat J-FJBJ (2000) Involvement of NRAMP1 from Arabidopsis thaliana in iron transport. Involvement of NRAMP1 from Arabidopsis Thaliana in Iron Transport 347(3):749–755
Da Silva LC, Oliva MA, Azevedo AA, De Araujo JMJW (2006) Responses of restinga plant species to pollution from an iron pelletization factory. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 175(1):241–256
Dawes C, Chan M, Chinn R, Koch E, Lazar A, Tomasko DJAB (1987) Proximate composition, photosynthetic and respiratory responses of the seagrass Halophila engelmannii from Florida. Aquatic Botany 27(2):195–201
De Jong WH, Hagens WI, Krystek P, Burger MC, Sips AJ, Geertsma REJB (2008) Particle size-dependent organ distribution of gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration. Biomaterials 29(12):1912–1919
de la Rosa G, García-Castañeda C, Vázquez-Núñez E, Alonso-Castro ÁJ, Basurto-Islas G, Mendoza Á, Cruz-Jiménez G, Molina CJPP (2017) Physiological and biochemical response of plants to engineered NMs: Implications on future design. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:226–235
Diao M, Yao MJWR (2009) Use of zero-valent iron nanoparticles in inactivating microbes. Water Res 43(20):5243–5251
El-Temsah YS, Joner EJJC (2012) Ecotoxicological effects on earthworms of fresh and aged nano-sized zero-valent iron (nZVI) in soil. Chemosphere 89(1):76–82
El-Temsah YS, Joner EJJC (2013) Effects of nano-sized zero-valent iron (nZVI) on DDT degradation in soil and its toxicity to collembola and ostracods. Chemosphere 92(1):131–137
El‐Temsah YS, Joner EJJET (2012) Impact of Fe and Ag nanoparticles on seed germination and differences in bioavailability during exposure in aqueous suspension and soil. Environ Toxicol 27(1):42–49
Fangel JU, Ulvskov P, Knox JP, Mikkelsen MD, Harholt J, Popper ZA, Willats WGTJFips (2012) Cell wall evolution and diversity. Front Plant Sci 3:152
Frei M, Tetteh RN, Razafindrazaka AL, Fuh MA, Wu LB, Becker M (2016) Responses of rice to chronic and acute iron toxicity: genotypic differences and biofortification aspects. Plant & Soil 408(1-2):1–13
Genon J, De Hepcée N, Delvaux B, Dufey J, Hennebert PJP (1994a) Redox conditions and iron chemistry in highland swamps of Burundi. Plant and Soil 166(2):165–171
Genon J, De Hepcee N, Duffy J, Delvaux B, Hennebert PJP (1994b) Iron toxicity and other chemical soil constraints to rice in highland swamps of Burundi. Plant and Soil 166(1):109–115
Ghafariyan MH, Malakouti MJ, Dadpour MR, Stroeve P, Mahmoudi MJES (2013) Effects of magnetite nanoparticles on soybean chlorophyll. Environ Sci Technol 47(18):10645–10652
Ghauch AJC (2001) Degradation of benomyl, picloram, and dicamba in a conical apparatus by zero-valent iron powder. Chemosphere 43(8):1109–1117
Ghosh I, Mukherjee A, Mukherjee AJM (2017) In planta genotoxicity of nZVI: influence of colloidal stability on uptake, DNA damage, oxidative stress and cell death. Mutagenesis 32(3):371–387
Ghosh I, Sadhu A, Moriyasu Y, Bandyopadhyay M, Mukherjee A (2019) Genotoxicity of nanoscale zerovalent iron particles in tobacco BY-2 cells. Nucleus (India) 62(3)
Ghosh M, Bandyopadhyay M, Mukherjee AJC (2010) Genotoxicity of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles at two trophic levels: plant and human lymphocytes. Chemosphere 81(10):1253–1262
Gill SS, Tuteja NJPP (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(12):909–930
Gong X, Huang D, Liu Y, Zeng G, Wang R, Wan J, Zhang C, Cheng M, Qin X, Xue WJES (2017) Stabilized nanoscale zerovalent iron mediated cadmium accumulation and oxidative damage of Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaudich cultivated in cadmium contaminated sediments. Environ Sci Technol 51(19):11308–11316
Grantz D, Garner J, Johnson DJEI (2003) Ecological effects of particulate matter. Environ Int 29(2-3):213–239
Green MA, Fry SCJN (2005) Vitamin C degradation in plant cells via enzymatic hydrolysis of 4-O-oxalyl-L-threonate. Nature 433(7021):83–87
Grieger KD, Fjordbøge A, Hartmann NB, Eriksson E, Bjerg PL, Baun AJJOCH (2010) Environmental benefits and risks of zero-valent iron nanoparticles (nZVI) for in situ remediation: risk mitigation or trade-off? J Contam Hydrol 118(3-4):165–183
Guha T, Ravikumar K, Mukherjee A, Mukherjee A, Kundu RJPP (2018a) Nanopriming with zero valent iron (nZVI) enhances germination and growth in aromatic rice cultivar (Oryza sativa cv. Gobindabhog L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 127:403–413
Guha T, Ravikumar KVG, Mukherjee A, Mukherjee A, Kundu R (2018b) Nanopriming with zero valent iron (nZVI) enhances germination and growth in aromatic rice cultivar (Oryza sativa cv. Gobindabhog L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 127:403
Howeler RHJSSSOAJ (1973) Iron-induced oranging disease of rice in relation to physico-chemical changes in a flooded oxisol. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 37(6):898–903
Huber DL (2005) Synthesis, properties, and applications of iron nanoparticles. Small 1(5):482–501
Jiamjitrpanich W, Parkpian P, Polprasert C, Laurent F, Kosanlavit RJJOES (2012) The tolerance efficiency of Panicum maximum and Helianthus annuus in TNT-contaminated soil and nZVI-contaminated soil. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 47(11):1506–1513
Johnson TL, Scherer MM, Tratnyek PGJES (1996) Kinetics of halogenated organic compound degradation by iron metal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30(8):2634–2640
Kadar E, Rooks P, Lakey C, White DAJSOTTE (2012) The effect of engineered iron nanoparticles on growth and metabolic status of marine microalgae cultures. The effect of engineered iron nanoparticles on growth and metabolic status of marine microalgae cultures. Sci Total Environ 439:8–17
Kadar E, Tarran GA, Jha AN, Al-Subiai SNJES (2011) Stabilization of engineered zero-valent nanoiron with Na-acrylic copolymer enhances spermiotoxicity. Environ Sci Technol 45(8):3245–3251
Kim CKJ-YATY (2018) Activation of Persulfate by Nanosized Zero-Valent Iron (NZVI): mechanisms and transformation products of NZVI. Environ Sci Technol 52(6):3625–3633
Kim H, Hong H-J, Jung J, Kim S-H, Yang J-WJJOHM (2010) Degradation of trichloroethylene (TCE) by nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) immobilized in alginate bead. J Hazard Mater 176(1-3):1038–1043
Kim J-H, Lee Y, Kim E-J, Gu S, Sohn EJ, Seo YS, An HJ, Chang Y-SJES (2014) Exposure of iron nanoparticles to Arabidopsis thaliana enhances root elongation by triggering cell wall loosening. Environ Sci Technol 48(6):3477–3485
Kim JH, Kim D, Seo SM, Kim D (2019) Physiological effects of zero-valent iron nanoparticles in rhizosphere on edible crop, Medicago sativa (Alfalfa), grown in soil. Ecotoxicology 28(8):869–877
Kim JY, Park H-J, Lee C, Nelson KL, Sedlak DL, Yoon JJA (2010) Inactivation of Escherichia coli by nanoparticulate zerovalent iron and ferrous ion. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(22):7668–7670
Kirschling TL, Gregory KB, Minkley J, Edwin G, Lowry GV, Tilton RDJES (2010) Impact of nanoscale zero valent iron on geochemistry and microbial populations in trichloroethylene contaminated aquifer materials. Environ Sci Technol 44(9):3474–3480
Kotchaplai P, Khan E, Vangnai ASJES (2017) Membrane alterations in Pseudomonas putida F1 exposed to nanoscale zerovalent iron: Effects of short-term and repetitive nZVI exposure. Environ Sci Technol 51(14):7804–7813
Kreyling W, Semmler M, Erbe F, Mayer P, Takenaka S, Schulz H, Oberdörster G, Ziesenis AJJOT (2002) Translocation of ultrafine insoluble iridium particles from lung epithelium to extrapulmonary organs is size dependent but very low. J Toxicol Environ Health A 65(20):1513–1530
Lee C, Kim JY, Lee WI, Nelson KL, Yoon J, Sedlak DLJES (2008) Bactericidal effect of zero-valent iron nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Environ Sci Technol 42(13):4927–4933
Lefevre E, Bossa N, Wiesner MR, Gunsch CKJSOTTE (2016) A review of the environmental implications of in situ remediation by nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI): behavior, transport and impacts on microbial communities. Sci Total Environ 565:889–901
Li S, Wang W, Yan W, Zhang W-X (2014) Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) for the treatment of concentrated Cu(II) wastewater: a field demonstration. Environ Sci Processes Impacts 16(3):524–533
Li X, Yang Y, Gao B, Zhang MJPO (2015) Stimulation of peanut seedling development and growth by zero-valent iron nanoparticles at low concentrations, Stimulation of peanut seedling development and growth by zero-valent iron nanoparticles at low concentrations. PLoS One 10(4):e0122884
Li X-Q, Elliott DW, Zhang W-XJCRISS (2006) Zero-valent iron nanoparticles for abatement of environmental pollutants: materials and engineering aspects. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. 31(4):111–122
Li X-Q, Zhang W-XJL (2006) Iron nanoparticles: The core− shell structure and unique properties for Ni (II) sequestration. Langmuir 22(10):4638–4642
Li Y, Li J, Zhang YJJOHM (2012) Mechanism insights into enhanced Cr (VI) removal using nanoscale zerovalent iron supported on the pillared bentonite by macroscopic and spectroscopic studies. J Hazard Mater 227:211–218
Li Z, Greden K, Alvarez PJ, Gregory KB, Lowry GVJES (2010) Adsorbed polymer and NOM limits adhesion and toxicity of nano scale zerovalent iron to E. coli. Environ Sci Technol 44(9):3462–3467
Liang J, Xia X, Yuan L, Zhang W, Lin K, Zhou B, Hu SJEP (2018) The reproductive responses of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in the presence of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE209). Environ Pollut 237:784–791
Libralato G, Devoti AC, Zanella M, Sabbioni E, Mičetić I, Manodori L, Pigozzo A, Manenti S, Groppi F, Ghirardini AVJE, Safety E (2016) Phytotoxicity of ionic, micro- and nano-sized iron in three plant species. Phytotoxicity of Ionic, Micro-and Nano-sized Iron in Three Plant Species 123:81–88
Lien H-L, Zhang W-XJC (2001) Nanoscale iron particles for complete reduction of chlorinated ethenes. Physicochemical Aspects 191(1-2):97–105
Lin S, Reppert J, Hu Q, Hudson JS, Reid ML, Ratnikova TA, Rao AM, Luo H, Ke PCJS (2009) Uptake, translocation, and transmission of carbon nanomaterials in rice plants. Small 5(10):1128–1132
Lütz-Meindl U, Lütz CJM (2006) Analysis of element accumulation in cell wall attached and intracellular particles of snow algae by EELS and ESI. Micron 37(5):452–458
Ma B, Yu W, Jefferson WA, Liu H, Qu JJWR (2015a) Modification of ultrafiltration membrane with nanoscale zerovalent iron layers for humic acid fouling reduction. Water Res 71:140–149
Ma C, White JC, Dhankher OP, Xing B (2015b) Metal-Based Nanotoxicity and Detoxification Pathways in Higher Plants. Environ Sci Technol 49(12):7109–22
Ma C, White JC, Dhankher OP, Xing BJES (2015c) Metal-based nanotoxicity and detoxification pathways in higher plants. Environ Sci Technol 49(12):7109–7122
Ma X, Gurung A, Deng YJSOTTE (2013) Phytotoxicity and uptake of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) by two plant species. Sci Total Environ 443:844–849
Marsalek B, Jancula D, Marsalkova E, Mashlan M, Safarova K, Tucek J, Zboril RJES (2012) Multimodal action and selective toxicity of zerovalent iron nanoparticles against cyanobacteria. Environ Sci Technol 46(4):2316–2323
Marusenko Y, Shipp J, Hamilton GA, Morgan JL, Keebaugh M, Hill H, Dutta A, Zhuo X, Upadhyay N, Hutchings JJEP (2013) Bioavailability of nanoparticulate hematite to Arabidopsis thaliana. Bioavailability of Nanoparticulate Hematite to Arabidopsis Thaliana 174:150–156
Mengel KJP (1994) Iron availability in plant tissues-iron chlorosis on calcareous soils. Plant and Soil. 165(2):275–283
Müller K, Linkies A, Vreeburg RA, Fry SC, Krieger-Liszkay A, Leubner-Metzger GJPP (2009) In vivo cell wall loosening by hydroxyl radicals during cress seed germination and elongation growth. Plant Physiol 150(4):1855–1865
Navarro E, Baun A, Behra R, Hartmann NB, Filser J, Miao A-J, Quigg A, Santschi PH, Sigg LJE (2008) Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. Ecotoxicology 17(5):372–386
Ottow J, Benckiser G, Watanabe I, Santiago SJTA (1983) Multiple nutritional soil stress as the prerequisite for iron toxicity of wetland rice (Oryza sativa L.)
Rico CM, Majumdar S, Duarte-Gardea M, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JLJJOA (2011) Interaction of nanoparticles with edible plants and their possible implications in the food chain. J Agric Food Chem 59(8):3485–3498
Rico CM, Morales MI, Barrios AC, McCreary R, Hong J, Lee W-Y, Nunez J, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JLJJOA (2013) Effect of cerium oxide nanoparticles on the quality of rice (Oryza sativa L.) grains. J Agric Food Chem 61(47):11278–11285
Sarwani M, Jumberi A, Noor AJFLIFE (1995) Management of rainfed wetland with iron toxicity problem for rice production in Indonesia. Fragile Lives Fragile Ecosyst. 299–312
Schopfer PJTPJ (2001) Hydroxyl radical-induced cell‐wall loosening in vitro and in vivo: implications for the control of elongation growth. Plant J 28(6):679–688
Semerad J, Pacheco NIN, Grasserova A, Prochazkova P, Pivokonsky M, Pivokonska L, Cajthaml T (2020) In vitro study of the toxicity mechanisms of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) and released iron ions using earthworm cells. Nanomaterials (Basel) 10(11):2189
Shao G, Chen M, Wang W, Mou R, Zhang GJPGR (2007) Iron nutrition affects cadmium accumulation and toxicity in rice plants. Plant Growth Regul. 53(1):33–42
Snowden RED, Wheeler BD (2014) Iron toxicity to fen plant species.
Sohn K, Kang SW, Ahn S, Woo M, Yang S-KJES (2006) Fe (0) nanoparticles for nitrate reduction: stability, reactivity, and transformation. Environ Sci Technol 40(17):5514–5519
Stampoulis D, Sinha SK, White JCJES (2009) Assay-dependent phytotoxicity of nanoparticles to plants. Environ Sci Technol 43(24):9473–9479
Su C, Puls RWJES (2001) Arsenate and arsenite removal by zerovalent iron: kinetics, redox transformation, and implications for in situ groundwater remediation. Environ Sci Technol 35(7):1487–1492
Tanaka A, Loe R, Navasero SA (1966) Some mechanisms involved in the development of iron toxicity symptoms in the rice plant. Soil Sci Plant Nutri 12(4):32–38
Tanaka A, Tadano TJPR (1972) Potassium in relation to iron toxicity of the rice plant. 21:1–12
Tripathi DK, Shweta, Singh S, Singh S, Pandey R, Singh VP, Sharma NC, Prasad SM, Dubey NK, Chauhan DK (2017) An overview on manufactured nanoparticles in plants: Uptake, translocation, accumulation and phytotoxicity. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:2–12
Varotto C, Maiwald D, Pesaresi P, Jahns P, Salamini F, Leister DJTPJ (2002) The metal ion transporter IRT1 is necessary for iron homeostasis and efficient photosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 31(5):589–599
Wang C-B, Zhang W-XJES (1997) Synthesizing nanoscale iron particles for rapid and complete dechlorination of TCE and PCBs. 31(7):2154–2156
Wang J, Fang Z, Cheng W, Yan X, Tsang PE, Zhao DJEP (2016) Higher concentrations of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in soil induced rice chlorosis due to inhibited active iron transportation. Environ Pollut 210:338–345
Wang Y, Fang Z, Kang Y, Tsang EPJJOHM (2014) Immobilization and phytotoxicity of chromium in contaminated soil remediated by CMC-stabilized nZVI. J Hazard Mater 275:230–237
Xu Y, Zhang W-XJI (2000) Subcolloidal Fe/Ag particles for reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated benzenes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 39(7):2238–2244
Yamauchi M, Peng XJP (1995) Iron toxicity and stress-induced ethylene production in rice leaves. Plant Soil 173(1):21–28
Yan W, Herzing AA, Kiely CJ, Zhang W-X (2010) Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI): Aspects of the core-shell structure and reactions with inorganic species in water. J Contaminant Hydrology 118(3-4):96–104
Yu X, Amrhein C, Deshusses MA, Matsumoto MRJES (2007) Perchlorate reduction by autotrophic bacteria attached to zerovalent iron in a flow-through reactor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41(3):990–997
Yue CS, Du HL, Li Y, Yin NY, Peng B, Cui YS (2021) Stabilization of soil arsenic with iron and nano-iron materials: a review. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 21(1):10–21
Zhang S, Li J, Lykotrafitis G, Bao G, Suresh SJAM (2009) Size-dependent endocytosis of nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 21(4):419–424
Zhu H, Han J, Xiao JQ, Jin YJJOEM (2008) Uptake, translocation, and accumulation of manufactured iron oxide nanoparticles by pumpkin plants. J Environ Monit 10(6):713–717
Funding
This research was supported by the Hunan Province Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2021JJ30357) and the Key Research and Development Program of Hunan Province (2022NK2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SZ and KY conceived the idea and SL developed the format of the manuscript. SZ and AC performed the literature review and drafted the manuscript with input from SZ. JS and LP critically evaluated the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Yi, K., Chen, A. et al. Toxicity of zero-valent iron nanoparticles to soil organisms and the associated defense mechanisms: a review. Ecotoxicology 31, 873–883 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-022-02565-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-022-02565-z