Abstract
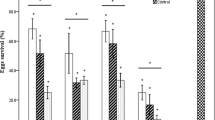
Carmoisine belongs to a water-soluble synthetic dye and is often used as a food additive. Previous research has shown that carmoisine is toxic to rats and zebrafish, but there have been few reports on the effect of carmoisine on soil-dwelling social insects. The present study evaluated carmoisine toxicity in Polyrhachis vicina Roger. We found that the effects of different concentrations of carmoisine on the mortality of workers were dose-dependent. The 10% lethal dose (LD10), 50% lethal dose (LD50) and 90% lethal dose (LD90) of carmoisine to workers at 96 h was calculated to be 0.504, 5.491 and 10.478 g/L, respectivily. LD10 of workers were selected to treat the fourth instar larvae, pupae and adults for 10 days. The results showed that the survival rate of all ants, except for females, was significantly reduced, especially larvae and workers. The body weight of larvae, pupae and males decreased significantly, while weight gain was observed in the females and workers. The appearance of larvae, pupae and workers changed after carmoisine treatment, such as body darkening and epidermis shrinking of larvae and pupae, as well as body segment expansion of workers. Furthermore, carmoisine altered the expression of the estrogen-related receptor, tailless and homothorax of P. vicina (Pv-ERR, Pv-tll and Pv-hth) to varying degrees in larvae and adults. We believe that variations in body weight can lead to a decrease in survival rate and appearance changes in the ants, which may be related to abnormal gene expressions caused by carmoisine treatment. Therefore, we confirm that carmoisine has negative effects on the growth and development of P. vicina.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Abbott WS (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/18.2.265a
Abril S, Gómez C (2013) Rapid assessment of ant assemblages in public pine forests of the central Iberian Peninsula. Forest Ecol Manag 293:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2012.12.036
Ahlström LH, Eskilsson C, Björklund E (2005) Determination of banned azo dyes in consumer goods. Trend Anal Chem 24(1):49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2004.09.004
Ahmed MA, Al-Khalifa AS, Al-Nouri D, El-Din M (2021) Dietary intake of artificial food color additives containing food products by school-going children. Saudi J Biol Sci 28(1):27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.08.025
Aldaz S, Morata G, Azpiazu N (2005) Patterning function of homothorax/extradenticle in the thorax of Drosophila. Development 132(3):439–446. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.01585
Ali MO, Al-Ghor A, Sharaf AK, Mekkawy H, Montaser MM (1998) Genotoxic effects of the food color (carmoisine) on the chromosome of bone marrow cells of rat. Toxicol Lett 95(S1):44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(98)80172-0
Amin KA, Abdel Hameid H, Abd Elsttar AH (2010) Effect of food azo dyes tartrazine and carmoisine on biochemical parameters related to renal, hepatic function and oxidative stress biomarkers in young male rats. Food Chem Toxicol 48(10):2994–2999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.07.039
Ando M, Totani Y, Walldorf U, Furukubo-Tokunaga K (2011) Tale-class homeodomain transcription factors, homothorax and extradenticle, control dendritic and axonal targeting of olfactory projection neurons in the Drosophila brain. Dev Biol 358(1):122–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.07.018
Angelini DR, Kaufman TC (2004) Functional analyses in the hemipteran Oncopeltus fasciatus reveal conserved and derived aspects of appendage patterning in insects. Dev Biol 271(2):306–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.04.005
Arshad F, Sharma A, Lu C, Gulia-Nuss M (2021) RNAi by soaking Aedes aegypti pupae in dsRNA. Insects 12(7):634. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12070634
Atlı-Şekeroğlu Z, Güneş B, Kontaş Yedier S, Şekeroğlu V, Aydın B (2017) Effects of tartrazine on proliferation and genetic damage in human lymphocytes. Toxicol Mech Method 27(5):370–375. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2017.1296051
Azpiazu N, Morata G (2000) Function and regulation of homothorax in the wing imaginal disc of Drosophila. Development 127(12):2685–2693. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.127.12.2685
Baek M, Enriquez J, Mann RS (2013) Dual role for Hox genes and Hox co-factors in conferring leg motoneuron survival and identity in Drosophila. Development 140(9):2027–2038. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.090902
Beebe K, Robins MM, Hernandez EJ et al. (2020) Drosophila estrogen-related receptor directs a transcriptional switch that supports adult glycolysis and lipogenesis. Genes Dev 34(9-10):701–714. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.335281.119
Bessa J, Gebelein B, Pichaud F, Casares F, Mann RS (2002) Combinatorial control of Drosophila eye development by eyeless, homothorax, and teashirt. Gene Dev 16(18):2415–2427. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1009002
Bhulaidok S, Sihamala O, Shen L, Li D (2010) Nutritional and fatty acid profiles of sun-dried edible black ants (Polyrhachis vicina Roger). Maejo Int J Sci Tech 4(1):101–112
Bodofsky S, Koitz F, Wightman B (2017) Conserved and exapted functions of nuclear receptors in animal development. Nucl Receptor Res 4:101305. https://doi.org/10.11131/2017/101305
Bryantsev AL, Duong S, Brunetti TM et al. (2012) Extradenticle and homothorax control adult muscle fiber identity in Drosophila. Dev Cell 23(3):664–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2012.08.004
Casares F, Mann RS (1998) Control of antennal versus leg development in Drosophila. Nature 392(6677):723–726. https://doi.org/10.1038/33706
Chen J, Rashid T, Feng G (2012) Toxicity of formic acid to red imported fire ants, Solenopsis invicta Buren. Pest Manag Sci 68(10):1393–1399. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.3319
Chung KT, Stevens JR, Cerniglia CE (1992) The reduction of azo dyes by the intestinal microflora. Crit Rev Microbiol 18(3):175–190 https://doi.org/10.3109/10408419209114557
Corsetti E, Azpiazu N (2013) Functional dissection of the splice variants of the Drosophila gene homothorax (hth). Dev Biol 384(1):72–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.09.018
Cuvillier-Hot V, Salin K, Devers S et al. (2014) Impact of ecological doses of the most widespread phthalate on a terrestrial species, the ant Lasius niger. Environ Res 131:104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.03.016
Daniel A, Dumstrei K, Lengyel JA, Hartenstein V (1999) The control of cell fate in the embryonic visual system by atonal, tailless and EGFR signaling. Development 126(13):2945–2954. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.126.13.2945
Das A, Mukherjee A (2004) Genotoxicity testing of the food colours amaranth and tartrazine. Int J Hum Genet 4(4):277–280. https://doi.org/10.1080/09723757.2004.11885906
Davis SM, Thomas AL, Nomie KJ, Huang L, Dierick HA (2014) Tailless and atrophin control Drosophila aggression by regulating neuropeptide signalling in the pars intercerebralis. Nat Commun 5:3177. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4177
Dias NP, Cagliari D, Dos Santos EA et al. (2020) Insecticidal gene silencing by RNAi in the neotropical region. Neotrop Entomol 49(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-019-00722-4
Diaz RJ, Harbecke R, Singer JB et al. (1996) Graded effect of tailless on posterior gut development: molecular basis of an allelic series of a nuclear receptor gene. Mech Dev 54(1):119–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-4773(95)00467-x
Dondero F, Banni M, Negri A, Boatti L, Viarengo A (2011) Interactions of a pesticide/heavy metal mixture in marine bivalves: a transcriptomic assessment. BMC Genomics 12(1):195. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-195
Elekima I, Horsfall OL, Adimefe IG et al. (2020) Assessment of ovarian integrity, reproductive hormones, and oxidative stress in Albino rats exposed to tartrazine azo dye. Asian Journal of Biochemistry Genetics and Molecular Biology 5:9–19. https://doi.org/10.9734/AJBGMB/2020/v5i430136
El-Borm HT, Badawy GM, El-Nabi SH, El-Sherif WA, Atallah MN (2020) The ameliorative effect of curcumin extract on the morphological and skeletal abnormalities induced by sunset yellow and tartrazine in the developing chick embryo gallus domesticus. Heliyon 6(1):e03305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03305
El-Wahab HM, Moram GS (2013) Toxic effects of some synthetic food colorants and/or flavor additives on male rats. Toxicol Ind Health 29(2):224–232. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233711433935
Ford GP, Stevenson BI, Evans JG (1987) Long-term toxicity study of carmoisine in rats using animals exposed in utero. Food Chem Toxicol 25(12):919–925. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-6915(87)90285-7
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J et al. (2011) Effect of food azo dye tartrazine on learning and memory functions in mice and rats, and the possible mechanisms involved. J Food Sci 76(6):T125–T129. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02267.x
Giguère V, Yang N, Segui P, Evans RM (1988) Identification of a new class of steroid hormone receptors. Nature 331(6151):91–94. https://doi.org/10.1038/331091a0
Grze IM (2010) Ants and heavy metal pollution-a review. Eur J Soil Biol 46(6):350–355
Gupta R, Ranjan S, Yadav A et al. (2019) Toxic effects of food colorants erythrosine and tartrazine on zebrafish embryo development. Curr Res Nutr Food Sci 7(3):876–885. https://doi.org/10.12944/CRNFSJ.7.3.26
Hartmann B, Reichert H, Walldorf U (2001) Interaction of gap genes in the Drosophila head: tailless regulates expression of empty spiracles in early embryonic patterning and brain development. Mech Dev 109(2):161–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0925-4773(01)00519-6
Hong H, Yang L, Stallcup MR (1999) Hormone-independent transcriptional activation and coactivator binding by novel orphan nuclear receptor ERR3. J Biol Chem 274(32):22618–22626. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.32.22618
Husain A, Sawaya W, Al-Omair A et al. (2006) Estimates of dietary exposure of children to artificial food colours in Kuwait. Food Addit Contam A 23(3):245–251
Imran M, Shaharoona B, Crowley DE et al. (2015) The stability of textile azo dyes in soil and their impact on microbial phospholipid fatty acid profiles. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 120:163–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.06.004
Inoue Y, Mito T, Miyawaki K et al. (2002) Correlation of expression patterns of homothorax, dachshund, and Distal-less with the proximodistal segmentation of the cricket leg bud. Mech Dev 113(2):141–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0925-4773(02)00017-5
Jiang LL, Li K, Yan DL et al. (2020) Toxicity assessment of 4 azo dyes in zebrafish embryos. Int J Toxicol 39(2):115–123. https://doi.org/10.1177/1091581819898396
Khan IS, Ali MN, Hamid R, Ganie SA (2020) Genotoxic effect of two commonly used food dyes metanil yellow and carmoisine using Allium cepa L. as indicator. Toxicol Rep 15(7):370–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.02.009
Kiziltan T, Baran A, Kankaynar M et al. (2022) Effects of the food colorant carmoisine on zebrafish embryos at a wide range of concentrations. Arch Toxicol 96(4):1089–1099. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03240-2
Kovalenko EV, Mazina MY, Krasnov AN, Vorobyeva NE (2019) The Drosophila nuclear receptors EcR and ERR jointly regulate the expression of genes involved in carbohydrate metabolism. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 112:103184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2019.103184
Kurant E, Pai CY, Sharf R et al. (1998) Dorsotonals/homothorax, the Drosophila homologue of meis1, interacts with extradenticle in patterning of the embryonic PNS. Development 125(6):1037–1048. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.125.6.1037
Kus E, Eroglu HE (2015) Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of Sunset Yellow and Brilliant Blue, colorant food additives, on human blood lymphocytes. Pak J Pharm Sci 28(1):227–230
Li D, Sihamala O, Bhulaidok S, Shen L (2009) Changes in the organic compounds following sun drying of edible black ant (Polyrhachis vicina Roger). Acta Alimentaria 38(4):493–501. https://doi.org/10.1556/066.2021.00077
Li DM, Zhong M, Su QB et al. (2020) Active fraction of Polyrhachis vicina Rogers (AFPR) suppressed breast cancer growth and progression via regulating EGR1/lncRNA-NKILA/NF-κB axis. Biomed Pharmacother 123:109616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109616
Li J, Zhao L, Qi S et al. (2021) Sublethal effects of Isoclast™ Active (50% sulfoxaflor water dispersible granules) on larval and adult worker honey bees (Apis mellifera L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 220:112379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112379
Liu XM, Xi GS, Zhang ZY, Li K, He H (2011) Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of a Tailless homolog in the ant Polyrhachis vicina (hymenoptera: formicidae). Sociobiolo 58(3):667–679
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt Method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth20011262
Long W, Wu J, Shen G et al. (2020) Estrogen-related receptor participates in regulating glycolysis and influences embryonic development in silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Mol Biol 29(2):160–169. https://doi.org/10.1111/imb.12619
Lopes CS, Casares F (2010) Hth maintains the pool of eye progenitors and its downregulation by Dpp and Hh couples retinal fate acquisition with cell cycle exit. Dev Biol 339(1):78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.12.020
Luo J, Sladek R, Carrier J et al. (2003) Reduced fat mass in mice lacking orphan nuclear receptor estrogen-related receptor alpha. Mol Cell Biol 23(22):7947–7956. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.23.22.7947-7956.2003
Lynch JA, Olesnicky EC, Desplan C (2006) Regulation and function of tailless in the long germ wasp Nasonia vitripennis. Dev Genes Evol 216(7):493–498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-006-0076-5
Markandeya MD, Shukla SP (2022) Hazardous consequences of textile mill effluents on soil and their remediation approaches. Clean Eng Technol 7:100434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2022.100434
Mehedi N, Ainad-Tabe S, Mokrane N et al. (2009) Reproductive toxicology of tartrazine (FD and C yellow No. 5) in swiss albino mice. Am J Pharmacol Toxicol 4(4):130–135. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajptsp.2009.130.135
Moczek AP, Rose DJ (2009) Differential recruitment of limb patterning genes during development and diversification of beetle horns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(22):8992–8997. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0809668106
Montaser MM, Alkafafy ME (2013) Effects of synthetic food color (carmoisine) on expression of some fuel metabolism genes in liver of male albino rats. Life Sci J 10(2):2191–2198
Mota Filho TMM, Camargo RS, Zanuncio JC et al. (2021) Contamination routes and mortality of the leaf-cutting ant Atta sexdens (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) by the insecticides fipronil and sulfluramid through social interactions. Pest Manag Sci 77(10):4411–4417. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6475
Mpountoukas P, Pantazaki A, Kostareli E et al. (2010) Cytogenetic evaluation and DNA interaction studies of the food colorants amaranth, erythrosine and tartrazine. Food Chem Toxicol 48(10):2934–2944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.07.030
Newsome AG, Culver CA, Van Breemen RB (2014) Nature’s palette: the search for natural blue colorants. J Agric Food Chem 62(68):6498–6511. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf501419q
Olas B, Białecki J, Urbańska K, Bryś M (2021) The effects of natural and synthetic blue dyes on human health: a review of current knowledge and therapeutic perspectives. Adv Nutr 12(6):2301–2311. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmab081
Ouyang XH, Xi GS, Bu CP et al. (2009) Molecular cloning and expression of an estrogen receptor-related receptor gene in the ant polyrhachis vicina (hymenoptera: formicidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 102(2):295–302. https://doi.org/10.1603/008.102.0211
Pai CY, Kuo TS, Jaw TJ et al. (1998) The homothorax homeoprotein activates the nuclear localization of another homeoprotein, extradenticle, and suppresses eye development in Drosophila. Gene Dev 12(3):435–446. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.12.3.435
Park WR, Lim DJ, Sang H et al. (2021) Aphid estrogen-related receptor controls glycolytic gene expression and fecundity. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 130:103529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2021.103529
Peksa V, Jahn M, Štolcová L et al. (2015) Quantitative SERS analysis of azorubine (E 122) in sweet drinks. Anal Chem 87(5):2840–2844. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac504254k
Prpic NM, Tautz D (2003) The expression of the proximodistal axis patterning genes Distal-less and dachshund in the appendages of Glomeris marginata (Myriapoda: Diplopoda) suggests a special role of these genes in patterning the head appendages. Dev Biol 260(1):97–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-1606(03)00217-3
Qu B, Zhou J, Xiang X et al. (2008) Adsorption behavior of azo dye C. I. acid red 14 in aqueous solution on surface soils. J Environ Sci 20(6):704–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(08)62116-6
Raposa B, Pónusz R, Gerencsér G et al. (2016) Food additives: Sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate, azorubine, and tartrazine modify the expression of NFκB, GADD45α, and MAPK8 genes. Physiol Int 103(3):334–343. https://doi.org/10.1556/2060.103.2016.3.6
Rastogi N (2011) Provisioning services from ants: food and pharmaceuticals. Asian Myrmecol 3(1):103–120
Ratcliffe NA, Mello CB, Garcia ES, Butt TM, Azambuja P (2011) Insect natural products and processes: new treatments for human disease. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 41(10):747–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2011.05.007
Refat NA, Ibrahim ZS, Moustafa GG et al. (2008) The induction of cytochrome P450 1A1 by sudan dyes. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 22(2):77–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.20220
Rehman K, Shahzad T, Sahar A et al. (2018) Effect of Reactive Black 5 azo dye on soil processes related to C and N cycling. PeerJ 6:e4802. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4802
Reza MSA, Hasan MM, Kamruzzaman M et al. (2019) Study of a common azo food dye in mice model: toxicity reports and its relation to carcinogenicity. Food Sci Nutr 7(2):667–677. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.906
Rieckhof GE, Casares F, Ryoo HD, Abu-Shaar M, Mann RS (1997) Nuclear translocation of extradenticle requires homothorax, which encodes an extradenticle-related homeodomain protein. Cell 91(2):171–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80400-6
Rodrigues PS, Rios AO, Cladera-Olivera F (2021) Estimation of theoretical intake of synthetic food colours Azorubine, Erythrosine, Indigotine, and Ponceau 4R by the Brazilian population. Food Sci Tech 42. https://doi.org/10.1590/fst.17821
Ronco M, Uda T, Mito T et al. (2008) Antenna and all gnathal appendages are similarly transformed by homothorax knock-down in the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. Dev Biol 313(1):80–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.09.059
Shen B, Liu HC, Ou WB et al. (2015) Toxicity induced by Basic Violet 14, Direct Red 28 and Acid Red 26 in zebrafish larvae. J Appl Toxicol 35(12):1473–1480. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3134
Shen G, Wu J, Lin Y et al. (2021) Estrogen-related receptor influences the hemolymph glucose content by regulating midgut trehalase gene expression in the last instar larvae of Bombyx mori. Int J Mol Sci 22(9):4343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094343
Shen LR, Li D, Feng FQ, Ren YC (2006) Nutritional composition of polyrhachis vicina roger (edible chinese black ant). Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 28(S1):107–114
Simonnet F, Moczek AP (2011) Conservation and diversification of gene function during mouthpart development in Onthophagus beetles. Evol Dev 13(3):280–289. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-142X.2011.00479.x
Smith FW, Angelini DR, Jockusch EL (2014a) A functional genetic analysis in flour beetles (Tenebrionidae) reveals an antennal identity specification mechanism active during metamorphosis in Holometabola. Mech Develop 132:13–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mod.2014.02.002
Smith FW, Jockusch EL (2014b) Hox genes require homothorax and extradenticle for body wall identity specification but not for appendage identity specification during metamorphosis of Tribolium castaneum. Dev Biol 395(1):182–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.08.017
Snehalatha M, Ravikumar C, Hubert JI, Sekar N, Jayakumar VS (2009) Spectroscopic analysis and DFT calculations of a food additive carmoisine. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 72(3):654–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2008.11.017
Sun-Waterhouse D, Waterhouse GIN, You L et al. (2016) Transforming insect biomass into consumer wellness foods: a review. Food Res Int 89(Pt1):129–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2016.10.001
Tang JJ, Fang P, Xia HL et al. (2015) Constituents from the edible chinese black ants (polyrhachis dives) showing protective effect on rat mesangial cells and anti-inflammatory activity. Food Res Int 67:163–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.11.022
Tennessen JM, Baker KD, Lam G, Evans J, Thummel CS (2011) The Drosophila estrogen-related receptor directs a metabolic switch that supports developmental growth. Cell Metab 13(2):139–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.01.005
Truman JW, Riddiford LM (1999) The origins of insect metamorphosis. Nature 401(6752):447–452. https://doi.org/10.1038/46737
USFDA (2017) Summary of color additives for use in the United States in foods, drugs, cosmetics, and medical devices. USFDA
Uysal H, Genç S, Ayar A (2017) Toxic effects of chronic feeding with food azo dyes on Drosophila melanogaster Oregon R. Scientia Iranica 24(6):3081–3086. https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2017.4523
Wang YN, Xi GS, Yang DL (2016) Life cycle and larval instar differentiation of Polyrhachis vicina Roger. J Northwest Agric Forest Univ 44(3):167–172
Weiner AK, Ramirez A, Zintel T et al. (2014) Bisphenol A affects larval growth and advances the onset of metamorphosis in Drosophila melanogaster. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 101:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.12.008
Wernet MF, Labhart T, Baumann F et al. (2003) Homothorax switches function of Drosophila photoreceptors from color to polarized light sensors. Cell 115(3):267–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00848-1
Wilson MJ, Dearden PK (2009) Tailless patterning functions are conserved in the honeybee even in the absence of Torso signaling. Dev Biol 335(1):276–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.09.002
Wu J (2010) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of the homothorax gene in Polyrhachis vicina Roger (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Master Thesis, Shaanxi Normal University, China.
Wu J, Cohen SM (1999) Proximodistal axis formation in the Drosophila leg: subdivision into proximal and distal domains by Homothorax and Distal-less. Development 126(1):109–117. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.126.1.109
Wu J, Shen G, Liu D et al. (2022) The response of the estrogen-related receptor to 20-hydroxyecdysone in Bombyx mori: insight into the function of estrogen-related receptor in insect 20-hydroxyecdysone signaling pathway. Front Physiol 12:785637. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.785637
Zhang CX, Tang XD, Cheng JA (2010) The utilization and industrialization of insect resources in china. Entomol Res 38(s1):S38–S47. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-5967.2008.00173.x
Zheng C, Zeng L, Xu Y (2016) Effect of sweeteners on the survival and behaviour of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Pest Manag Sci 72(5):990–996. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.4079
Zhou Q (2001) Chemical pollution and transport of organic dyes in water-soil-crop systems of the Chinese coast. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 66(6):784–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001280077
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZL: data curation, formal analysis, methodology, resources, software, visualization, writing original draft, writing review and editing. JZ: formal analysis, investigation, software. SY: formal analysis, resources, methodology. GX: funding acquisition, methodology, project administration, writing review and editing.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 31571276 and 31171195).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent to publish
This research did not involve human subjects, so clinical trial registration is not applicable. All the authors are in agreement with the publishment.
Ethics approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Zhang, J., Yin, S. et al. Toxicity effect of the edible pigment carmoisine on Polyrhachis vicina Roger (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Ecotoxicology 31, 1009–1022 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-022-02563-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-022-02563-1