Abstract
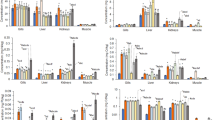
Toxicity to fish of multicomponent metal mixtures at maximum-permissible-concentrations (MPC: Cd—0.005, Cr—0.01, Cu—0.01, Ni—0.01, Pb—0.005 and Zn—0.1 mg/L) set for EU inland waters was evaluated using the whole-mixture approach. An extended follow-up study on the biological effects of multicomponent metal mixtures on three ecologically different fish species, i.e. Perca fluviatilis, Rutilus rutilus, and Salmo salar is reported. The aim of this study was to assess response patterns of biomarkers (erythrocytic nuclear abnormalities (ENAs), metal accumulation and metallothioneins) in tissues of fish species after 14-day treatment with multicomponent metal mixtures at MPC and metal mixtures with one of its components at reduced MPC (↓). After treatments with Cu↓ and Cr↓, the lowest amount of Ni was found in all tissues (except the liver) of all fish species tested. After Zn↓ and Pb↓ treatments, the amount of Ni in muscle of all the tested fish species significantly decreased. The highest amounts of Cr in gills and Pb in muscle were detected in all fish species after treatments with Ni↓ and Cd↓ mixtures, respectively. R. rutilus accumulated significantly larger amounts of metals than P. fluviatilis and S. salar. The data obtained show that tissues of the omnivorous R. rutilus exposed to metal mixtures accumulated higher amounts of Cr, Cu, Ni and Zn, while tissues of carnivorous S. salar and P. fluviatilis higher amounts of Cd and Pb. The analysis of ENAs revealed concentration-dependent responses, indicating Cu↓ and Cr↓ treatments as causes of higher geno- and cytotoxicity levels.
Highlights
-
Changes in MPC of single-metals in a mixture have an impact on biomarker responses.
-
The level of a single-metal in a mixture affects accumulation of other metals.
-
Roach mostly accumulates Cr, Cu, Ni and Zn, whereas salmon and perch—Cd and Pb.
-
Mixtures containing reduced MPC of Cr, Cu cause the greatest cytogenetic damage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atobatelea OE, Olutonaba GO (2015) Distribution of three non-essential trace metals (cadmium, mercury and lead) in the organs of fish from Aiba Reservoir, Iwo, Nigeria. Toxicol Rep 2:896–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2015.06.003
Authman MMN, Zaki MS, Khallaf EA, Abbas HH (2015) Use of fish as bio-indicator of the effects of heavy metals pollution. J Aquac. Res Dev 6:328–340. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9546.1000328
Ayangbenro AS, Babalola OO (2017) A new strategy for heavy metal polluted environments: a review of microbial biosorbents. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:94. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010094
Baršienė J, Lazutka J, Syvokienė J, Dedonytė V, Rybakovas A, Bagdonas E, Bjornstad A, Andersen OK (2004) Analysis of micronuclei in blue mussels and fish from the Baltic and the North Seas. Environ Toxicol 19(4):365–371. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20031
Baršienė J, Dedonytė V, Rybakovas A, Andreikenaitė L, Andersen OK (2006) Investigation of micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities in peripheral blood and kidney of marine fish treated with crude oil. Aquat Toxicol 78S:S99–S104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.02.022
Baršienė J, Butrimavičienė L, Grygiel W, Lang T, Michailovas A, Jackūnas T (2014) Environmental genotoxicity and cytotoxicity in flounder (Platichthys flesus), herring (Clupea harengus) and Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) from chemical munitions dumping zones in the southern Baltic Sea. Mar Environ Res 96:56–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2013.08.012
Birceanu O, Chowdhury MJ, Gillis P, McGeer J, Wood CM, Wilkie MP (2008) Modes of metal toxicity, and impaired branchial ionoregulation in rainbow trout exposed to mixtures of Pb and Cd in soft water. Aquat Toxicol 89:222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.07.007
Cavas T, Garanko NN, Arkhipchuk VV (2005) Induction of micronuclei and binuclei in blood, gill and liver cells of fishes subchronically exposed to cadmium chloride and copper sulphate. Food Chem Toxicol 43(4):569–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2004.12.014
Cedergreen N (2014) Quantifying synergy: a systematic review of mixture toxicity studies within environmental toxicology. PLoS ONE 9(5):e96580. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096580
Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 496 16 December 2008 on environmental quality standards in the field of water 497 policy, amending and subsequently repealing Council Directives 82/176/EEC, 498 83/513/EEC, 84/156/EEC, 84/491/EEC, 86/280/EEC and amending Directive 499 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Official Journal of the European Communities L 500 348, p 0084–0097
Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes
Dixit RD, Malaviya K, Pandiyan UB, Singh A, Sahu R, Shukla BP, Singh JP, Rai Sharma PK, Lade H (2015) Bioremediation of heavy metals from soil and aquatic environment: an overview of principles and criteria of fundamental processes. Sustainability 7:2189–2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7022189
Driessnack MK, Matthew AL, Raine JC, Niyogi S (2016) Interactive effects of chronic waterborne copper and cadmium exposure on tissue-specific metal accumulation and reproduction in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Comp Biochem Physiol C 179:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.10.009
Driessnack MK, Jamwal A, Niyogi S (2017) Effects of chronic exposure to waterborne copper and nickel in binary mixture on tissue-specific metal accumulation and reproduction in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Chemosphere 185:964–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.100
Duran S, Tunçsoy M, Yeşilbudak B, Ay Ö, Cicik B, Erdem C (2015) Metal accumulation in various tissues of Clarias gariepinus exposed to copper, zinc, cadmium and lead singly and in mixture. Fresen Environ Bull 24(12c):4738–4742
El-Sadaawy MM, El-Said GF, Sallam NA (2013) Bioavailability of heavy metals in freshwater Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus Linnaeus, 1758): potential risk to fishermen and consumers. J Environ Sci Health Part B 48:402–409. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2013.742719
Eroglu K, Atli G, Canli M (2005) Effects of metal (Cd, Cu, Zn) interactions on the profiles of metallothionein-like proteins in the nile fish Oreochromis niloticus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 75:390–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-005-0766-0
European Commission (2012) Communication from the commission to the council. The combination effects of chemicals mixtures. European Commission, Brussels. COM (2012) 252 final
Eyer P, Worek F, Kiderlen D, Sinko G, Stuglin A, Simeon-Rudolf V, Reiner E (2003) Molar absorption coefficients for the reduced Ellman reagent: reassessment. Anal Biochem 312:224–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2697(02)00506-7
Fenech M, Chang WP, Kirsch-Volders M, Holland N, Bonassi S, Zeiger E (2003) HUMN project: detailed description of the scoring criteria for the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay using isolated human lymphocyte cultures. Mutat Res 534:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-5718(02)00249-8
Gasulla J, Picco SJ, Carriquiriborde P, Dulout FN, Ronco AE, de Luca JC (2016) Genotoxic effects induced by Cd(+2), Cr(+6), Cu(+2) in the gill and liver of Odontesthes bonariensis (Piscies, Atherinopsidae). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96(5):591–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1774-y
Griffiths AM, Machado-Schiaffino G, Dillane E, Coughlan J, Horreo JL, Bowkett AE, Minting P et al (2010) Genetic stock identification of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) populations in the southern part of the European range. BMC Genet 11:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-11-31
Güner U, Muranlı FDG (2011) Micronucleus test, nuclear abnormalities and accumulation of Cu and Cd on Gambusia affinis (Baird & Girard, 1853). Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 11:615–622. https://doi.org/10.4194/1303-2712-v11_4_16
HELCOM (2012) Indicator based assessment of coastal fish community status in the Baltic Sea 2005–2009. Baltic Sea Environment Proceedings No. 131
Heys KA, Shore RF, Pereira MG, Jones KC, Martin FL (2016) Risk assessment of environmental mixture effects. RSC Adv 6:47844–47857. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA05406D
Horppila J, Ruuhijärvi J, Rask M, Karppinen C, Nyberg K, Olin M (2000) Seasonal changes in the food com position and relative abundance of perch and roach—a comparison between littoral and pelagial zones of a large lake. J Fish Biol 56:51–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2000.tb02086.x
ISO 10523 (2008) Water quality. Determination of pH. International Organization for Standardization
ISO 10304-1 (2007) Water quality. Determination of dissolved anions by liquid chromatography of ions. Determination of bromide, chloride, fluoride, nitrate, nitrite, phosphate and sulfate. International Organization for Standardization
ISO 15586 (2003) Water quality. Determination of trace elements using atomic absorption spectrometry with graphite furnace. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva
ISO 14911 (1998) Water quality. Determination of dissolved Li+, Na+, NH4+, K+, Mn2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+ using ion chromatography—method for water and waste water. International Organization for Standardization
ISO 9963-1 (1994) Water quality. Determination of alkalinity—part 1: determination of total and composite alkalinity. International Organization for Standardization
ISO 5814 (1990) Water quality. Determination of dissolved oxygen—electrotechnical probe method. SO, the International Organization for Standardization
ISO 6332 (1988) Water quality. Determination of iron—spectrometric method using 1.10-phenanthroline. ISO, the International Organization for Standardization
Jezierska B, Witeska M (2001) Metal toxicity to fish. Rev Fish Biol Fish 11(3):279. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020380730689
Jezierska B, Witeska M (2006) The metal uptake and accumulation in fish living in polluted waters. In: Twardowska, I et al. (eds) Soil and water pollution monitoring, protection and remediation. Springer, p 3–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-4728-2_6
Jia H, Ren H, Satoh S, Endo H, Hayashi T (2005) Comparison of pretreatment condition of cadmium in fish sample and diet by microwave digestion method for ICP-AES. J Tokyo Univ Mar Sci Technol 1:41–46
Kamunde C, MacPhail R (2011) Effect of humic acid during concurrent chronic waterborne exposure of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) to copper, cadmium and zinc. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74(3):259–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.10.007
Kargin F, Çoğun H (1999) Metal interaction during accumulation and elimination of zinc and cadmium in tissues of the freshwater fish tilapia nilotica. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 63:511–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001289901010
Komjarova I, Blust R (2009a) Multimetal interactions between Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn uptake from water in the zebrafish Danio rerio. Environ Sci Technol 43:7225–7229. https://doi.org/10.1021/es900587r
Komjarova I, Blust R (2009b) Effects of Na, Ca, and pH on the simultaneous uptake of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in the Zebrafish Danio rerio: a stable isotope experiment. Environ Sci Technol 43(20):7958–7963. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9016987
Land SN, Rocha RCC, Bordon IC, Saint’Pierre TD, Ziolli RL, Hauser-Davis RA (2018) Biliary and hepatic metallothionein, metals and trace elements in environmentally exposed neotropical cichlids Geophagus brasiliensis. J Trace Elem Med Biol 50:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2018.07.023
Lappalainen A, Rask M, Koponen H, Vesala S (2001) Relative abundance, diet and growth of perch (Perca fluviatilis) and roach (Rutilus rutilus) at Tvärminne, northern Baltic Sea, in 1975 and 1997: responses to eutrophication? Boreal Env Res 6:107–118
Liu Y, Vijver MG, Pan B, Peijnenburg WJGM (2017) Toxicity models of metal mixtures established on the basis of “additivity” and “interactions” Front Env Sci Eng 11:10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-017-0916-8
Lorenzoni M, Carosi A, Pedicillo G, Trusso A (2007) A comparative study on the feeding competition of the European perch Perca fluviatilis L. and the ruffe Gymnocephalus cernuus (L.) in Lake Piediluco (Umbria, Italy). Bull Francais Peche Pisciculture 387:35–57. https://doi.org/10.1051/kmae:2007016
McGeer JC, Nadella S, Alsop DH, Hollis L, Taylor LN, McDonald DG, Wood CM (2007) Influence of acclimation and cross-acclimation of metals on acute Cd toxicity and Cd uptake and distribution in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat Toxicol 84:190–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.03.023
Min EY, Ahn TY, Ju-Chan Kang (2016) Bioaccumulation, alterations of metallothionein, and antioxidant enzymes in the mullet Mugil cephalus exposed to hexavalent chromium. J Fish Aquat Sci 19:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41240-016-0020-1
Mokhtar MB, Aris AZ, Munusamy V, Praveena SM (2009) Assessment level of heavy metals in Penaeus monodon and Oreochromis spp in selected aquaculture ponds of high densities development area. Eur J Sci Res 30:348–360
Palaniappan PL, Karthikeyan S (2009) Bioaccumulation and depuration of chromium in the selected organs and whole body tissues of freshwater fish Cirrhinus mrigala individually and in a binary solution with nickel. J Environ Sci 21:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62256-1
Palermo FF, Risso WE, Simonato JD, Martinez CBR (2015) Bioaccumulation of nickel and its biochemical and genotoxic effects on juveniles of the neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 116:19–28
Peixoto NC, Roza T, Flores EMM, Pereira ME (2003) Effects of zinc and cadmium on HgCl2-δ-ALA-D inhibition and Hg levels in tissues of suckling rats. Toxicol Lett 146:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2003.08.006
Pelgrom SMGJ, Lamers LPMJ, Garritsen AM, Pels BM, Lock RAC, Balm PHM, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1994) Interactions between copper and cadmium during single and combined exposure in juvenile tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus: influence of deeding condition on whole body metal accumulation and the effect of the metals on tissue water and Ion content. Aquat Toxicol 30:117–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-445X(94)90009-4
Pelgrom SMGJ, Lock RAC, Balm PHM, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1995) Effects of combined waterborne Cd and Cu exposures on ionic composition and plasma Cortisol in tilapia, Oreochromis mossamicus. Comp Biochem Physiol 111:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/0742-8413(95)00041-L
Price MHH (2013) Sub-lethal metal toxicity effects on salmonids: a review. Report, Skeena Wild Conservation Trust, Smithers, BC. p 64
Rajeshkumar S, Li X (2018) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish species from the Meiliang Bay,Taihu Lake, China. Toxicol Rep 5:288–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.01.007
Ribeyre F, Amiardtriquet C, Boudou A, Amiard JC (1995) Experimental-study of interactions between five trace elements—Cu, Ag, Se, Zn, and Hg—toward their bioaccumulation by fish (Brachydanio rerio) from the direct route. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 32:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.1995.1078
Stankevičiūtė M, Sauliutė G, Svecevičius G, Kazlauskienė N, Baršienė J (2017) Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity response to environmentally relevant complex metal mixture (Zn, Cu, Ni, Cr, Pb, Cd) accumulated in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Part I: importance of exposure time and tissue dependence. Ecotoxicology 26(8):1051–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1833-0
Stankevičiūtė M, Sauliutė G, Makaras T, Markuckas A, Virbickas T, Baršienė J (2018a) Responses of biomarkers in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) following exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of complex metal mixture (Zn, Cu, Ni, Cr, Pb, Cd). Part II. Ecotoxicology 27(8):1069–1086. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1960-2
Stankevičiūtė M, Sauliutė G, Markuckas A, Virbickas T, Baršienė J (2018b) Erythrocytic nuclear abnormalities, DNA damage, bioconcentration factor and hematological changes induced by metal mixture at environmentally relevant concentrations in Rutilus rutilus. In: Proceedings of the 14th international conference on protection and restoration of the environment. Thessaloniki, Greece, p 785–794
Svecevičius G, Sauliutė G, Idzelis LR, Grigelevičiūtė J (2014) Accumulation of heavy metals in different body tissues of Atlantic Salmon, Salmo salar L., exposed to a model mixture (Cu, Zn, Ni, Cr, Pb, Cd) and singly to nickel, chromium, and lead. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92(4):440–445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1237-2
Valskienė R, Stankevičiūtė M, Butrimavičienė L, Greiciūnaitė J, Svecevičius G (2015) Induction of nuclear abnormalities in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after exposure to a model mixture of heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Ni, Cr, Cd, Pb) at maximum permissible concentration. In: Proceedings of the 18th conference for junior researchers “science—future of Lithuania”. Vilnius, Lithuania, p 100–105
Van Hoof F, Nauwelaers JP (1984) Distribution of nickel in the roach (Rutilus rutilus L.) after exposure to lethal and sublethal concentrations. Chemosphere 13:1053–1058. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(84)90064-X
Winter AR, Playle RC, Dixon DG, Borgmann Uwe, Wilkie MP (2012) Interactions of Pb and Cd mixtures in the presence or absence of natural organic matter with the fish gill. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 83:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.05.020
Yancheva V, Stoyanova S, Velcheva I, Petrova S, Georgieva E (2014) Metal bioaccumulation in common carp and rudd from the Topolnitsa reservoir, Bulgaria. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol 65:57–66. https://doi.org/10.2478/10004-1254-65-2014-2451
Zhang Y, Wang YJ, Yu RL, Zhang S, Wu ZB (2008) Effects of heavy metals Cd2+, Pb2+ and Zn2+ on DNA damage of loach Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. Front Biol China 3(1):50–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-008-0012-3
Zhu Y, Wang J, Bai Y, Zhang R (2004) Cadmium, chromium, and copper induce polychromatocyte micronuclei in carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 72(1):78–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-003-0243-6
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the research infrastructure Open Access Centre for Nature Research at the initiative of the Open R&D Lithuania network. This study was funded by the Research Council of Lithuania through the project ACTIS S-MIP-17-10. Metallothioneins determination was funded by the Research Council of Lithuania, Project No. MIP-108/2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. LT 61-13-005; SR-432.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sauliutė, G., Markuckas, A. & Stankevičiūtė, M. Response patterns of biomarkers in omnivorous and carnivorous fish species exposed to multicomponent metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn) mixture. Part III. Ecotoxicology 29, 258–274 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02170-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02170-y