Abstract
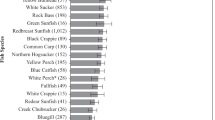
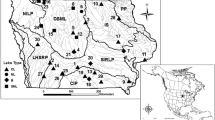
We collected 849 fish of 16 species from New York portions of Lake Erie, Lake Ontario and the intervening Niagara River and its tributary Cayuga Creek, and analyzed fillets from individual fish for total mercury. Concentrations ranged from 0.029 to 1.090 ppm wet weight, with 92% below the EPA tissue residue criterion of 0.3 ppm, and thus not posing an undue risk from human consumption. We compared these 2010–2017 results to historical data spanning 40 years to assess temporal changes. The temporal pattern was generally consistent among water bodies and species: Mercury concentrations differed little between the most recent collections and fish taken from 1999–2008 and 1988–1996, while concentrations in all three of these periods were generally lower than in 1970. Smallmouth Bass from Lake Ontario were an exception with a continued decline, likely due to diet change following the introduction of exotic prey. Overall, though, fish tissue mercury concentrations from these large water bodies, which integrate regional influences, appear to have changed little in the last quarter century. We also report a consistent spatial pattern for multiple species having lower mercury concentrations in Lake Erie than in Lake Ontario over the period of record.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson H, McCann P, Stahl J, Alexander L, Hornshaw T, Day R, Bohr J, Groetsch K, Forti A, Shaskus M, Frey R, Barron T, Schrank C, Steenport D (2007) A protocol for mercury-based fish consumption advice. Great Lakes Consortium for Fish Consumption Advisories. https://www.health.state.mn.us/communities/environment/fish/docs/consortium/mercuryprot.pdf
Barkay T, Wagner‐Döbler I (2005) Microbial transformations of mercury: Potentials, challenges, and achievements in controlling mercury toxicity in the environment. Adv Appl Microbiol 57:1–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2164(05)57001-1
Bentzen E, Mackay D, Hickie BE, Lean DRS (1999) Temporal trends of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in Lake Ontario fish and invertebrates. Environ Rev 7:203–223. https://doi.org/10.1139/a99-013
Bhavsar SP, Awad E, Fletcher R, Hayton A, Somers KM, Kolic T, MacPherson K, Reiner EJ (2008) Temporal trends and spatial distribution of dioxins and furans in lake trout or lake whitefish from the Canadian Great Lakes. Chemosphere 73:S158–S165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.05.100
Bhavsar SP, Gewurtz SB, McGoldrick DJ, Keir MJ, Backus SM (2010) Changes in mercury levels in Great Lakes fish between 1970s and 2007. Environ Sci Technol 44:3273–3279. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903874x
Bhavsar SP, Jackson DA, Hayton A, Reiner EJ, Chen T, Bodnar J (2007) Are PCB levels in fish from the Canadian Great Lakes still declining? J Gt Lakes Res 33:592–605. https://doi.org/10.3394/0380-1330(2007)33[592:APLIFF]2.0.CO;2
Bloom NS (1992) On the chemical form of mercury in edible fish and marine invertebrate tissue. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 49:1010–1017. https://doi.org/10.1139/f92-113
Borgmann U, Whittle DM (1991) Contaminant concentration trends in Lake Ontario lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush): 1977 to 1988. J Gt Lakes Res 17:368–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0380-1330(91)71373-7
Breteler RJ, Bowen VT, Schneider DL, Henderson R (1984) Sedimentological reconstruction of the recent pattern of mercury pollution in the Niagara River. Environ Sci Technol 18:404–409. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00124a003
Carlson DL, De Vault DS, Swackhamer DL (2010) On the rate of decline of persistent organic contaminants in lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush) from the Great Lakes, 1970−2003. Environ Sci Technol 44:2004–2010. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903191u
Chang F, Pagano JJ, Crimmins BS, Milligan MS, Xia X, Hopke PK, Holsen TM (2012) Temporal trends of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in Great Lakes fish, 1999–2009. Sci Total Environ 439:284–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.09.019
Chen CY, Driscoll CT (2018) Integrating mercury research and policy in a changing world. Ambio 47:111–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-017-1010-y
Connerton MJ, Legard CD (2019) Eastern basin of Lake Ontario warmwater fisheries assessment, 1976–2018. In: 2018 Annual Report of the Bureau of Fisheries Lake Ontario Unit and St. Lawrence River Unit to the Great Lakes Fishery Commission’s Lake Ontario Committee. New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, Albany, NY
Crane DP, Farrell JM, Einhouse DW, Lantry JR, Markham JL (2015) Trends in body condition of native piscivores following invasion of Lakes Erie and Ontario by the round goby. Freshw Biol 60:111–124. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12473
Crimmins BS, Pagano JJ, Xia X, Hopke PK, Milligan MS, Holsen TM (2012) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs): Turning the corner in Great Lakes trout 1980–2009. Environ Sci Technol 46:9890–9897. https://doi.org/10.1021/es302415z
Cross FA, Evans DW, Barber RT (2015) Decadal declines of mercury in adult bluefish (1972–2011) from the mid-Atlantic coast of the U.S.A. Environ Sci Technol 49:9064–9072. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01953
Dang F, Wang W-X (2012) Why mercury concentration increases with fish size? Biokinetic explanation. Environ Pollut 163:192–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.12.026
De Vault DS, Hesselberg R, Rodgers PW, Feist TJ (1996) Contaminant trends in lake trout and walleye from the Laurentian Great Lakes. J Gt Lakes Res 22:884–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0380-1330(96)71009-2
Depew DC, Basu N, Burgess NM, Campbell LM, Evers DC, Grasman KA, Scheuhammer AM (2012) Derivation of screening benchmarks for dietary methylmercury exposure for the common loon (Gavia immer): Rationale for use in ecological risk assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:2399–2407. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.1971
Dietz R, Outridge PM, Hobson KA (2009) Anthropogenic contributions to mercury levels in present-day Arctic animals—a review. Sci Total Environ 407:6120–6131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.08.036
Drevnick PE, Engstrom DR, Driscoll CT, Swain EB, Balogh SJ, Kamman NC, Long DT, Muir DGC, Parsons MJ, Rolfhus KR, Rossmann R (2012) Spatial and temporal patterns of mercury accumulation in lacustrine sediments across the Laurentian Great Lakes region. Environ Pollut 161:252–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.05.025
Driscoll CT, Mason RP, Chan HM, Jacob DJ, Pirrone N (2013) Mercury as a global pollutant: Sources, pathways, and effects. Environ Sci Technol 47:4967–4983. https://doi.org/10.1021/es305071v
Eagles-Smith CA, Wiener JG, Eckley CS, Willacker JJ, Evers DC, Marvin-DiPasquale M, Obrist D, Fleck JA, Aiken GR, Lepak JM, Jackson AK, Webster JP, Stewart AR, Davis JA, Alpers CN, Ackerman JT (2016) Mercury in western North America: A synthesis of environmental contamination, fluxes, bioaccumulation, and risk to fish and wildlife. Sci Total Environ 568:1213–1226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.094
Fitzgerald WF, Engstrom DR, Mason RP, Nater EA (1998) The case for atmospheric mercury contamination in remote areas. Environ Sci Technol 32:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/es970284w
Gandhi N, Drouillard KG, Arhonditsis GB, Gewurtz SB, Bhavsar S (2017) Are fish consumption advisories for the Great Lakes adequately protective against chemical mixtures? Environ Health Perspect 125:586–593. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP104
Gandhi N, Tang RWK, Bhavsar SP, Arhonditsis GB (2014) Fish mercury levels appear to be increasing lately: A report from 40 years of monitoring in the province of Ontario, Canada. Environ Sci Technol 48:5404–5414. https://doi.org/10.1021/es403651x
Gandhi N, Tang RWK, Bhavsar SP, Reiner EJ, Morse D, Arhonditsis GB, Drouillard K, Chen T (2015) Is mirex still a contaminant of concern for the North American Great Lakes? J Gt Lakes Res 41:1114–1122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2015.09.015
Gewurtz SB, Bhavsar SP, Fletcher R (2011) Influence of fish size and sex on mercury/PCB concentration: Importance for fish consumption advisories. Environ Int 37:425–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2010.11.005
Gewurtz SB, Lega R, Crozier PW, Whittle DM, Fayez L, Reiner EJ, Helm PA, Marvin CH, Tomy GT (2009) Factors influencing trends of polychlorinated naphthalenes and other dioxin-like compounds in lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush) from Lake Ontario, North America (1979–2004). Environ Toxicol Chem 28:921–930. https://doi.org/10.1897/08-307.1
Harris RC, Rudd JWM, Amyot M, Babiarz CL, Beaty KG, Blanchfield PJ, Bodaly RA, Branfireun BA, Gilmour CC, Graydon JA, Heyes A, Hintelmann H, Hurley JP, Kelly CA, Krabbenhoft DP, Lindberg SE, Mason RP, Paterson MJ, Podemski CL, Robinson A, Sandilands KA, Southworth GR, Louis VLS, Tate MT (2007) Whole-ecosystem study shows rapid fish-mercury response to changes in mercury deposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:16586–16591. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0704186104
Hartig JH, Zarull MA, Ciborowski JJ, H Gannon JE, Wilke E, Norwood G, Vincent AN (2009) Long-term ecosystem monitoring and assessment of the Detroit River and western Lake Erie. Environ Monit Assess 158:87–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0567-0
Hickey JP, Batterman SA, Chernyak SM (2006) Trends of chlorinated organic contaminants in Great Lakes trout and walleye from 1970 to 1998. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50:97–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-1007-6
Horn EG, Sloan RJ, Skinner LC (1986) Insights from contaminated fish in New York. In: Transactions of the 51st North American Wildlife and Natural Resources Conference. Reno, NV, pp 384–391. Wildlife Management Institute, Washington, DC
Hsu-Kim H, Kucharzyk KH, Zhang T, Deshusses MA (2013) Mechanisms regulating mercury bioavailability for methylating microorganisms in the aquatic environment: A critical review. Environ Sci Technol 47:2441–2456. https://doi.org/10.1021/es304370g
Huestis SY, Servos MR, Whittle DM, Dixon DG (1996) Temporal and age-related trends in levels of polychlorinated biphenyl congeners and organochlorine contaminants in Lake Ontario lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush). J Gt Lakes Res 22:310–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0380-1330(96)70958-9
Hutcheson MS, Smith CM, Rose J, Batdorf C, Pancorbo O, West CR, Strube J, Francis C (2014) Temporal and spatial trends in freshwater fish tissue mercury concentrations associated with mercury emissions reductions. Environ Sci Technol 48:2193–2202. https://doi.org/10.1021/es404302m
IJC (International Joint Commission) (1988) Revised Great Lakes water quality agreement of 1978. International Joint Commission. https://ijc.org/sites/default/files/GLWQA_e.pdf
Jackson TA (2013) Mass-dependent and mass-independent variations in the isotope composition of mercury in a sediment core from Lake Ontario as related to pollution history and biogeochemical processes. Chem Geol 355:88–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.07.007
Johnson BM, Lepak JM, Wolff BA (2015) Effects of prey assemblage on mercury bioaccumulation in a piscivorous sport fish. Sci Total Environ 506–507:330–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.10.101
Karjalainen AK, Hallikainen A, Hirvonen T, Kiviranta H, Knip M, Kronberg-Kippilä C, Leino O, Simell O, Sinkko H, Tuomisto JT, Veijola R, Venäläinen E-R, Virtanen SM (2013) Estimated intake levels for Finnish children of methylmercury from fish. Food Chem Toxicol 54:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.02.074
Kojadinovic J, Potier M, Le Corre M, Cosson RP, Bustamante P (2006) Mercury content in commercial pelagic fish and its risk assessment in the Western Indian Ocean. Sci Total Environ 366:688–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.02.006
Lane O, Adams EM, Pau N, O’Brien KM, Regan K, Farina M, Schneider Moran T, Zarudsky J (2020) Long-term monitoring of mercury in adult saltmarsh sparrows breeding in Maine, Massachusetts and New York, USA 2000–2017. Ecotoxicology, in press
Lantry JR (2014) Eastern basin of Lake Ontario warmwater fisheries assessment, 1976-2013. Section 4 in: 2013 Annual Report of the Bureau of Fisheries Lake Ontario Unit and St. Lawrence River Unit to the Great Lakes Fishery Commission’s Lake Ontario Committee. New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, Albany, NY
Lantry JR, Eckert TH (2015) 2014 Lake Ontario fishing boat survey. In: 2014 Annual Report of the Bureau of Fisheries Lake Ontario Unit and St. Lawrence River Unit to the Great Lakes Fishery Commission’s Lake Ontario Committee. New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, Albany, NY
Lepak RF, Janssen SE, Yin R, Krabbenhoft DP, Ogorek JM, DeWild JF, Tate MT, Holsen TM, Hurley JP (2018) Factors affecting mercury stable isotopic distribution in piscivorous fish of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Environ Sci Technol 52:2768–2776. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b06120
Lepak RF, Yin R, Krabbenhoft DP, Ogorek JM, DeWild JF, Holsen TM, Hurley JP (2015) Use of stable isotope signatures to determine mercury sources in the Great Lakes. Environ Sci Technol Lett 2:335–341. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.5b00277
Li X, Richter W, Skinner LC (2014) Xenobiotics in fish from Lake Erie, the Niagara River, Cayuga Creek and Lake Ontario, New York York State Department of Environmental Conservation, Albany, NY. https://www.dec.ny.gov/docs/fish_marine_pdf/xenobiofish2014.pdf
Liang P, Qin Y-Y, Zhang C, Zhang J, Cao Y, Wu S-C, Wong CKC, Wong MH (2013) Plasma mercury levels in Hong Kong residents: In relation to fish consumption. Sci Total Environ 463–464:1225–1229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.04.049
Ma M, Du H, Wang D (2019) Mercury methylation by anaerobic microorganisms: A review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 49:1893–1936. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1594517
Marvin C, Painter S, Rossmann R (2004) Spatial and temporal patterns in mercury contamination in sediments of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Environ Res 95:351–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2003.09.007
Millard GD, Driscoll C, Montesdeoca M, Yang Y, Taylor M, Boucher S, Shaw A, Richter W, Paul E, Parker C, Yokota K (2020) Patterns and trends of fish mercury in New York State. Ecotoxicology, this issue
NRTC (Niagara River Toxics Committee) (1984) Report of the Niagara River Toxics Committee. New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, Environment Canada, Ontario Ministry of the Environment, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
NYSDEC (New York State Department of Environmental Conservation) (2017) How to properly fillet a fish for contaminant analysis. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HYMgXRCGSi4&feature=youtu.be. Accessed 7 Oct 2019
NYSDOH (New York State Department of Health) (1981) Love Canal: A special report to the governor and legislature. New York State Department of Health, Albany, NY
NYSDOH (New York State Department of Health) (2019a) Advice on eating fish. https://www.health.ny.gov/environmental/outdoors/fish/health_advisories/background.htm#derivation. Accessed 16 Sep 2019
NYSDOH (New York State Department of Health) (2019b) Health Advice on Eating Sportfish and Game. New York State Department of Health, Albany, NY
Pacyna EG, Pacyna JM, Steenhuisen F, Wilson S (2006) Global anthropogenic mercury emission inventory for 2000. Atmos Environ 40:4048–4063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.03.041
Perry PC, Loukmas JJ, Fisher WL, Sullivan PJ, Jackson JR (2014) Characterizing the status of black bass populations in New York. New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, Albany, NY
Pirrone N, Cinnirella S, Feng X, Finkelman RB, Friedli HR, Leaner J, Mason R, Mukherjee AB, Stracher GB, Streets DG, Telmer K (2010) Global mercury emissions to the atmosphere from anthropogenic and natural sources. Atmos Chem Phys 10:5951–5964. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-5951-2010
R Development Core Team (2011) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria
Razavi NR, Halfman JD, Cushman SF, Massey T, Beutner R, Foust J, Gilman B, Cleckner LB (2020) Mercury concentrations in fish and invertebrates of the Finger Lakes in central New York. Ecotoxicology, this issue
Riva-Murray K, Razavi NR, Richter W, Burns DA, Cleckner LB, Burton M, George SD, Freehafer D (2020) Mercury in fish from New York’s streams and rivers: Spatial patterns, temporal trends, and environmental drivers. Ecotoxicology, this issue
Robinson JM (2015) Open lake sport fishing survey. In: Lake Erie 2014 annual report. New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, Albany, NY
Shimshack JP, Ward MB (2010) Mercury advisories and household health trade-offs. J Health Econ 29:674–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhealeco.2010.05.001
Simoneau M, Lucotte M, Garceau S, Laliberté D (2005) Fish growth rates modulate mercury concentrations in walleye (Sander vitreus) from eastern Canadian lakes. Environ Res 98:73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2004.08.002
Smith RM, O’Keefe PW, Aldous KM, Hilker DR, O’Brien JE (1983) 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in sediment samples from Love Canal storm sewers and creeks. Environ Sci Technol 17:6–10. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00107a004
Sonesten L (2003) Fish mercury levels in lakes—adjusting for Hg and fish-size covariation. Environ Pollut 125:255–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(03)00051-4
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1991) Method 245.6: Determination of mercury in tissues by cold vapor atomic absorption spectroscopy. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, OH
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1997) Mercury study report to Congress. Volume I: Executive summary. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Washington, DC
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2001) Water quality criterion for the protection of human health: Methylmercury. Office of Science and Technology, Office of Water, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2007) Method 7473: Mercury in solids and solutions by thermal decomposition, amalgamation and atomic absorption spectrophotometry. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2019) Detroit River-Western Lake Erie Basin indicator project; Indicator: Mercury in Lake St. Clair walleye. http://www.epa.gov/med/grosseile_site/indicators/hg-walleye.html. Accessed 27 Sep 2019
Walters LJ, Kovacik TL, Herdendorf CE (1974) Mercury occurrence in sediment cores from western Lake Erie. Ohio J Sci 74:1–19
Ward DM, Nislow KH, Chen CY, Folt CL (2010) Rapid, efficient growth reduces mercury concentrations in stream-dwelling Atlantic salmon. Trans Am Fish Soc 139:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1577/T09-032.1
Weis IM (2004) Mercury concentrations in fish from Canadian Great Lakes areas of concern: An analysis of data from the Canadian Department of Environment database. Environ Res 95:341–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2004.01.013
Wentz DA, Chasar LC, Lutz MA, Krabbenhoft DP (2014) Mercury in the nation’s streams—levels, trends, and implications. U.S. Geological Survey Circular, Reston, Virginia. https://doi.org/10.3133/cir1395
Wiedinmyer C, Yokelson RJ, Gullett BK (2014) Global emissions of trace gases, particulate matter, and hazardous air pollutants from open burning of domestic waste. Environ Sci Technol 48:9523–9530. https://doi.org/10.1021/es502250z
Wiener JG, Evers DC, Gay DA, Morrison HA, Williams KA (2012) Mercury contamination in the Laurentian Great Lakes region: introduction and overview. Environ Pollut 161:243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.08.051
Wiener JG, Krabbenhoft DP, Heinz GH, Scheuhammer AM (2002) Ecotoxicology of mercury. In: Hoffman DJ, Rattner B, Burton GA, Cairns J (eds) Handbook of ecotoxicology, 2nd edition. Lewis Publishers, Baca Raton, p 409–463
Zananski TJ, Holsen TM, Hopke PK, Crimmins BS (2011) Mercury temporal trends in top predator fish of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Ecotoxicology 20:1568–1576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0751-9
Zhou C, Cohen MD, Crimmins BA, Zhou H, Johnson TA, Hopke PK, Holsen TM (2017) Mercury temporal trends in top predator fish of the Laurentian Great Lakes from 2004 to 2015: Are concentrations still decreasing? Environ Sci Technol 51:7386–7394. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00982
Acknowledgements
We thank the United States Environmental Protection Agency for providing Great Lakes Restoration Initiative funding (grant number GL-97229201) to make this study possible. We also thank New York State Department of Environmental Conservation regional staff and Great Lakes units for fish collections, and the Analytical Services Unit for sample preparation and chemical analyses. Xiangrong Li helped with statistics and graphics, and Matthew Porter assisted with technical aspects of manuscript preparation. We thank Jesse Becker for helpful discussions. Deb Ferguson and Emilie Wacogne of the NYSDEC Research Library gave invaluable assistance in obtaining published papers.
Funding
This study was funded by US Environmental Protection Agency grant GL-97229201.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richter, W., Skinner, L.C. Mercury in the fish of New Yorkʼs Great Lakes: A quarter century of near stability. Ecotoxicology 29, 1721–1738 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-019-02130-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-019-02130-1