Abstract
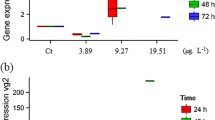
Sites along the Elizabeth River are contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from historical creosote production and other industrial processes. Previous studies have demonstrated that Atlantic killifish collected from sites throughout the Elizabeth River display resistance to the teratogenic effects of PAH-exposure in a manner commensurate with sediment PAH concentrations. The current study characterized various chemical pollutants in sediment and investigated the effects of aqueous sediment extracts from sites along the Elizabeth River to the cardiac development of Atlantic killifish embryos from fish collected from an uncontaminated reference site. Embryonic cardiac deformities were more prevalent after exposure to extracts from sites with high PAH loads. However, activation of cytochrome P4501A, a gene up-regulated by PAH-induction of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and measured using an in ovo EROD assay, did not consistently increase with PAH concentrations. This work further characterizes sediments in the Elizabeth River, as well as provides insight into the evolutionary pressures at each ER site.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong PB, Child JS (1965) Stages in the normal development of fundulus heteroclitus. Biol Bull 128:143–168
Barron MG, Heintz R, Rice SD (2004) Relative potency of PAHs and heterocycles as aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists in fish. Mar Environ Res 58:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2004.03.001
Billiard SM, Meyer JN, Wassenberg DM, Hodson PV, Di Giulio RT (2008) Nonadditive effects of PAHs on early vertebrate development: Mechanisms and implications for risk assessment. Toxicol Sci 105:5–23. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfm303
Billiard SM, Timme-Laragy AR, Wassenberg DM, Cockman C, Di Giulio RT (2006) The role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway in mediating synergistic developmental toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to zebrafish. Toxicol Sci 92:526–536. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfl011
Brown DR, Bailey JM, Oliveri AN, Levin ED, Di Giulio RT (2016) Developmental exposure to a complex PAH mixture causes persistent behavioral effects in naive Fundulus heteroclitus (killifish) but not in a population of PAH-adapted killifish. Neurotoxicol Teratol 53:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ntt.2015.10.007
Brown DR, Thompson J, Chernick M, Hinton DE, Di Giulio RT (2017). Later life swimming performance and persistent heart damage following subteratogenic PAH mixture exposure in the atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus). Environ Toxicol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3877
Brunström B, Broman D, Näf C (1991) Toxicity and EROD-inducing potency of 24 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in chick embryos. Arch Toxicol 65:485–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01977361
Buchman MF (1999). NOAA screening quick reference tables.
Burnett KG, Bain LJ, Baldwin WS, Callard GV, Cohen S, Di Giulio RT, Evans DH, Gómez-Chiarri M, Hahn ME, Hoover CA, Karchner SI, Katoh F, MacLatchy DL, Marshall WS, Meyer JN, Nacci DE, Oleksiak MF, Rees BB, Singer TD, Stegeman JJ, Towle DW, Van Veld PA, Vogelbein WK, Whitehead A, Winn RN, Crawford DL (2007) Fundulus as the premier teleost model in environmental biology: Opportunities for new insights using genomics. Comp Biochem Physiol—Part D Genomics Proteom 2:257–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbd.2007.09.001
Cerniglia CE (1992) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Biodegradation 3:351–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00129093
Clark BW, Cooper EM, Stapleton HM, Di Giulio RT (2013) Compound and mixture-specific differences in resistance to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and PCB-126 among Fundulus heteroclitus Subpopulations throughout the Elizabeth River Estuary (Virginia, USA). Environ Sci Technol 47:10556–10566
Clark BW, Matson CW, Jung D, Di Giulio RT (2010) AHR2 mediates cardiac teratogenesis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and PCB-126 in Atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus). Aquat Toxicol 99:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.05.004
Di Giulio RT, Clark BW (2015) The Elizabeth River Story: a case study in evolutionary toxicology. J Toxicol Environ Heal Part B 18:259–298. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2015.1074841
Di Giulio RT, Scanlon PF (1985) Heavy metals in aquatic plants, clams, and sediments from the chesapeake Bay, U.S.A.: implications for waterfowl. Sci Total Environ 41:259–274
Fang M, Getzinger GJ, Cooper EM, Clark BW, Garner LVT, Di Giulio RT, Ferguson PL, Stapleton HM (2014) Effect-directed analysis of Elizabeth River porewater: Developmental toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Toxicol Chem 33:2767–2774. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2738
Fouchécourt MO, Arnold M, Berny P, Videmann B, Rether B, Rivière JL (1999) Assessment of the bioavailability of PAHs in rats exposed to a polluted soil by natural routes: Induction of EROD activity and DNA adducts and PAH burden in both liver and lung. Environ Res 80:330–339. https://doi.org/10.1006/enrs.1998.3932
Heiri O, Lotter AF, Lemcke G (2000) Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: reproducibility and comparability of results. J Paleolimnol 25(1):101–110
Incardona JP, Carls MG, Teraoka H, Sloan CA, Collier TK, Scholz NL (2005) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-independent toxicity of weathered crude oil during fish development. Environ Health Perspect 113:1755–1762. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.8230
Jayasundara N, Fernando PW, Osterberg JS, Cammen KM, Schultz TF, Di Giulio RT (2017) Cost of tolerance: physiological consequences of evolved resistance to inhabit a polluted environment in teleost fish Fundulus heteroclitus. Environ Sci Technol acs.est.7b01913. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b01913
Jung D, Matson CW, Collins LB, Laban G, Stapleton HM, Bickham JW, Swenberg JA, Di Giulio RT (2011) Genotoxicity in Atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) from a PAH-contaminated Superfund site on the Elizabeth River, Virginia. Ecotoxicology 20:1890–1899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0727-9
Kanaly Ra, Harayama S (2000) Biodegradation of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria MINIREVIEW biodegradation of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria. J Bacteriol 182:2059–2067. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.182.8.2059-2067.2000.Updated
Long E, MacDonald D, Smith S (1995) Incidence of adverse bilogical effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Env Manag 19:81
Lotrich VA (1975) Summer home range and movements of fundulus heteroclitus (Pisces: Cyprinodontidae) in a Tidal Creek. Ecology 56:191–198
Matson CW, Clark BW, Jenny MJ, Fleming CR, Hahn ME, Di Giulio RT (2008) Development of the morpholino gene knockdown technique in Fundulus heteroclitus: A tool for studying molecular mechanisms in an established environmental model. Aquat Toxicol 87:289–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.02.010
Meyer JN, Volz DC, Freedman JH, Di Giulio RT (2005) Differential display of hepatic mRNA from killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) inhabiting a Superfund estuary. Aquat Toxicol 73:327–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.03.022
Mulvey M, Newman MC, Vogelbein W, Unger MA (2002) Genetic structure of Fundulus heteroclitus from PAH-contaminated and neighboring sites in the Elizabeth and York Rivers. Aquat Toxicol 61:195–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-445X(02)00055-3
Nacci DE, Champlin D, Jayaraman S (2010) Adaptation of the estuarine fish fundulus heteroclitus (Atlantic Killifish) to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Estuaries Coasts 33:853–864. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-009-9257-6
National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication (2010), 260–172, 39 pages
Nebert DW, Dalton TP, Okey AB, Gonzalez FJ (2004) Role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated induction of the CYP1 enzymes in environmental toxicity and cancer. J Biol Chem 279:23847–23850. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R400004200
Ownby DR, Newman MC, Mulvey M, Vogelbein WK, Unger MA, Arzayus LF (2002) Fish (Fundulus heteroclitus) populations with different exposure histories differ in tolerance of creosote-contaminated sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1897–1902. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620210917
Oziolor EM, Dubansky B, Burggren WW, Matson CW (2016) Cross-resistance in Gulf killifish (Fundulus grandis) populations resistant to dioxin-like compounds. Aquat Toxicol 175:222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.03.019
Reid NM, Proestou DA, Clark BW, Warren WC, Colbourne JK, Shaw JR, Karchner SI, Hahn ME, Nacci D, Oleksiak MF, Crawford DL, Whitehead A (2016) The genomic landscape of rapid repeated evolutionary adaptation to toxic pollution in wild fish. Science 354:1305–1308. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aah4993
Timme-Laragy AR, Cockman CJ, Matson CW, Di Giulio RT (2007) Synergistic induction of AHR regulated genes in developmental toxicity from co-exposure to two model PAHs in zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 85:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.09.005
US EPA (2007) Method 3051A (SW-846): Microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, and oils, Revision 1
Vogelbein WK, Fournie JW, Van Veld PA, Huggett RJ (1990) Hepatic neoplasms in the Mummichog Fundulus heteroclitus from a creosote-contaminated site. Cancer Res 50:5978–5986. https://doi.org/10.1177/019262339402200302
Wassenberg DM, Di Giulio RT (2004) Teratogenesis in Fundulus heteroclitus embryos exposed to a creosote-contaminated sediment extract and CYP1A inhibitors. Mar Environ Res 58:163–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2004.03.012
Wessel N, Santos R, Menard D, Le Menach K, Buchet V, Lebayon N, Loizeau V, Burgeot T, Budzinski H, Akcha F (2010) Relationship between PAH biotransformation as measured by biliary metabolites and EROD activity, and genotoxicity in juveniles of sole (Solea solea). Mar Environ Res 69:S71–S73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2010.03.004
Whyte J, Jung R, Schmitt C, Tillitt DE (2000) Ethoxyresorufin- O-deethylase (EROD) Activity in Fish as a Biomarker of Chemical Exposure. Crit Rev Toxicol 30:347–570. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408440091159239
Wills LP, Jung D, Koehrn K, Zhu S, Willett KL, Hinton DE, di Giulio RT (2010) Comparative chronic liver toxicity of benzo[a]pyrene in two populations of the atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) with different exposure histories. Environ Health Perspect 118:1376–1381. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901799
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Michael Unger and George Vadas of Virginia Institute of Marine Sciences (VIMS) for their support in collecting sediment from the Republic field site. We authors also thank Marc Gutterman (USACE) for allowing us access to the Atlantic Wood Industries site and for assisting with sediment collection.
Funding
This work was funded by the NIEHS-sponsored Duke University Superfund Research Center (P42ES010356).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Mention of trade names or commercial products does not constitute endorsement or recommendation for use. All applicable institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volkoff, S.J., Osterberg, J.S., Jayasundara, N. et al. Embryonic Fundulus heteroclitus responses to sediment extracts from differentially contaminated sites in the Elizabeth River, VA. Ecotoxicology 28, 1126–1135 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-019-02116-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-019-02116-z