Abstract
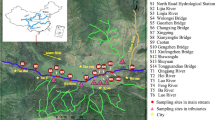
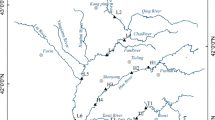
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) have received increasing attentions owing to their carcinogenicity, teratogenicity and environmental toxicity. The studies on the spatial variations, sources identification and potential ecological risk assessment of PAHs in the reservoir sediments after dam construction are becoming new hotpots. Sixteen PAHs contamination levels were investigated from 15 sample sections in the sediments of Manwan Reservoir in the middle of Lancang River, China. Total concentrations of 16 PAHs ranged from 14.4 to 137.7 ng g−1 dw with a mean concentration of 70.68 ng g−1 dw. The areas with residential settlement at large tributaries and near dam had higher PAHs concentrations. In the sight of classification of PAHs pollution levels, the sediments of Manwan Reservoir could be considered as low to moderate PAHs polluted levels. One-way analysis of variance for spatial analysis revealed that there were no significant differences (P < 0.05) for 16 PAHs at the reservoir head, centre and tail. Moreover, no significant differences (P < 0.05) were found for most individual PAH at the mainstream and tributaries except that BaP showed significant differences (P < 0.05) in the mainstream and tributaries. According to the diagnostic ratios, the possible pollution sources of PAHs in Manwan Reservoir might be mixed, primarily including the petroleum source and coal combustion. As compared with sediment quality guidelines, the observed concentrations of PAHs in all sample sections did not exceed the effects range low (ERL) and the threshold effect level (TEL) values, suggesting that there were little harmful biological toxic effects on the aquatic organisms in Manwan Reservoir. The study provided a comprehensive overview on the PAHs contaminations on the reservoir sediments in the middle Lancang River, which may have an important significances on the international river management.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araghi PE, Bastami KD, Rahmanpoor S (2014) Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surface sediments of Gorgan Bay, Caspian Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 89(1–2):494–498. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.12.001
Baumard P, Budzinski H, Garrigues P, Sorbe JC, Burgeot T, Bellocq J (1998) Concentrations of PAHs (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) in various marine organisms in relation to those in sediments and to trophic level. Mar Pollut Bull 36(12):951–960. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(98)00088-5
Beiras R, Fernández N, Bellas J, Besada V, González-Quijano A, Nunes T (2003) Integrative assessment of marine pollution in Galician estuaries using sediment chemistry, mussel bioaccumulation, and embryo-larval toxicity bioassays. Chemosphere 52(7):1209–1224
Bian FJ, Wang RY (1991) Characteristics and distribution of agro climatic resources in Yunnan torrid area. Trop Geogr 3:270–277 (in Chinese)
Bouloubassi I, Roussiez V, Lorre A (2012) Sources, dispersal pathways and mass budget of sedimentary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in the NW Mediterranean margin, Gulf of Lions. Mar Chem 142–144(11):18–28
Brian DR, Jeffrey VB, Jennifer P, David PB (1996) A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems. Conserv Biol 10(4):1163–1174. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1739.1996.10041163.x
Dong SK, Zhao C, Liu SL et al (2016) Speciation and pollution of heavy metals in sediment from middle Lancang-Mekong River influenced by dams [J]. Acta Sci Circumst 36(2):466–474
Doong RA, Lin YT (2004) Characterization and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminations in surface sediment and water from Gao-ping River. Taiwan Water Res 38(7):1733–1744. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2003.12.042
Esen F, Tasdemir Y, Vardar N (2008) Atmospheric concentrations of PAHs, their possible sources and gas-to-particle partitioning at a residential site of Bursa, Turkey. Atmos Res 88(3):243–255
Guevara SR, Arribére M, Bubach D, Vigliano P, Rizzo A, Alonso M, Sánchez R (2005) Silver contamination on abiotic and biotic compartments of Nahuel Huapi National Park Lakes, Patagonia Argentina. Sci Total Environ 336(1–3):119–134. doi:10.1016/jscitotenv200405020
Han F, Guo BD, Wang YY (2010) Distribution, sources and ecological risks assessment of PAHs in surface sediments in Liao River. Environ Prot Cycle Econ 12:62–66 (in Chinese)
Harrison RM, Smith DJT, Luhana L (1996) Source apportionment of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons collected from an urban location in Birmingham, U.K. Environ Sci Technol 30(3):825–832. doi:10.1021/es950252d
He DM, Zhao WJ, Chen LH (2004) Ecological change in the Manwan Reservoir area and its causes. Yunnan Univ Nat Sci 26(3):220–226 (in Chinese)
He DM, Wu C, Peng H, Yang Z, Ou X, Cui B (2005) A study of ecosystem changes in longitudinal range-gorge region and transbiundary eco-security in southwest China. Adv Earth Sci 20(3):338–344 (in Chinese)
Hu J, Aitken MD (2012) Desorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from field-contaminated soil to a two-dimensional hydrophobic surface before and after bioremediation. Chemosphere 89(5):542–547. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.046
Hu NJ, Shi XF, Huang P, Liu JH (2011) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea. China. Environ Earth Sci 63(1):121–133. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0675-3
Huang L, Chernyak SM, Batterman SA (2014) PAHs (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons), nitro-PAHs, and hopane and sterane biomarkers in sediments of southern Lake Michigan, USA. Sci Total Environ 487(1):173–186. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.03.131
Li LJ (1999) Water quality status assessment and causal analysis of Lancang River. Acta Geogr Sin 54:127–134. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.05.029
Li X, Shen Z, Wai OWH, Li YS (2001) Chemical forms of Pb, Zn and Cu in the sediment profiles of the Pearl River Estuary. Mar Pollut Bull 42(3):215–223. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00145-4
Li QZ, Li GX, Luo ZX, Zhang X, Yan CY (2009) Pollution characteritics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediment from Xiamen Bay. Environ Chem 6:869–875 (in Chinese)
Li YB, Liu ZT, Feng L, Zhou JL (2011) Ecological risk assessment of PAHs in the sediments from Taihu Lake. Environ Chem 30(10):1769–1774 (in Chinese)
Li WH, Tian YZ, Shi GL, Guo CS, Li X, Feng YC (2012) Concentrations and sources of PAHs in surface sediments of the Fenhe Reservoir and watershed, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 75(1):198–206. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.08.021
Liu Q, Liu SL, Zhao HD, Deng L, Wang C, Zhao QH, Dong SK (2013) Longitudinal variability of phosphorus fractions in sediments of a canyon reservoir due to cascade dam construction: a case study in Lancang River. China. PLoS One 8(12):1–9. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0083329
Machado KS, Figueira RC, Cocco LC, Froehner S, Fernandes CV, Ferreira PA (2014) Sedimentary record of PAHs in the Barigui River and its relation to the socioeconomic development of Curitiba, Brazil. Sci Total Environ 482–483(2):42–52. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.106
Mai BX, Qi SH, Zeng EY, Yang QS, Zhang G, Fu JM (2003) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the coastal region off Macao, China: assessment of input sources and transport pathways using compositional analysis. Environ Sci Technol 37(21):4855–4863. doi:10.1021/es034514k
Mehdinia A, Aghadadashi V, Fumani NS (2014) Origin, distribution and toxicological potential of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from the Bushehr coast, the Persian Gulf. Mar Pollut Bull 90(1–2):334–338. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.09.021
Ping LF, Luo YM, Zhang HB, Li QB, Wu LH (2007) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in thirty typical soil profiles in the Yangtze River Delta region, east China. Environ Pollut 147(2):489–515. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.05.027
Qiao M, Wang CX, Huang SB, Wang DH, Wang ZJ (2006) Composition, sources, and potential toxicological significance of PAHs in the surface sediments of the Meiliang Bay Taihu Lake China. Environ Int 32(1):28–33. doi:10.1016/jenvint200504005
Ren JL, Zhang J, Li DD, Cheng Y, Liu SM (2010) Behavior of dissolved inorganic arsenic in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Deep Sea Res II(57):1035–1046. doi:10.1016/jdsr2201002005
Santodonato J (1997) Review of the estrogenic and antiestrogenic activity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: relationship to carcinogenicity. Chemosphere 34(4):835–848. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(97)00012-X
Simpson CD, Mosi AA, Cullen WR, Reimer KJ (1996) Composition and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination in surficial marine sediments from Kitimat Harbor Canada. Sci Total Environ 181(3):265–278. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(95)05026-4
Song YX, Ji JF, Mao CP, Yang ZF, Yuan XY, Aokyo GA (2010) Heavy metal contamination in suspended solids of Changjiang River—environmental implications. Geoderma 159(3–4):286–295. doi:10.1016/jgeoderma201007020
Sun JH, Wang GL, Chai Y, Zhang G, Li J, Feng J (2009) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Henan Reach of the Yellow River Middle China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72(5):1614–1624. doi:10.1016/jecoenv200805010
Tobiszewski M, Namieśnik J (2012) PAH diagnostic ratios for the identification of pollution emission sources. Environ Pollut 162(1):110–119. doi:10.1016/jenvpol201110025
Unlu S, Alpar B, Ozturk K, Vardar D (2010) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the surficial sediments from Lake Iznik (Turkey): spatial distributions and sources. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85(6):573–580. doi:10.1007/s00128-010-0134-6
Van Metre PC, Mahler BJ, Furlong ET (2000) Urban sprawl leaves its PAH signature. Environ Sci Technol 32(19):4064–4070. doi:10.1021/es991007n
Wang P, Wang JL (2002) Basic climatic characteristics in the Manwan hydropower station reservoir area of lancang River, Yunnan Province, China. J Yunnan Norm Univ 6:57–61 (in Chinese)
Wang WT, Meng BJ, Lu XX, Liu Y, Tao S (2007) Extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides from soils: a comparison between Soxhlet extraction, microwave-assisted extraction and accelerated solvent extraction techniques. Anal Chim Acta 602(2):211–222. doi:10.1016/jaca200709023
Wang CP, Sun HW, Chang Y et al (2011) PAHs distribution in sediments associated with gas hydrate and oil seepage from the Gulf of Mexico. Mar Pollut Bull 62:2714–2723
Wang C, Liu SL, Zhao QH, Deng L, Dong SK (2012) Spatial variation and contamination assessment of heavy metals in sediments in the Manwan Reservoir Lancang River. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 82(4):32–39. doi:10.1016/jecoenv201205006
Wang XT, Miao Y, Zhang Y, Li YC, Wu MH, Yu G (2013) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban soils of the megacity Shanghai: occurrence, source apportionment and potential human health risk. Sci Total Environ 447(1):80–89. doi:10.1016/jscitotenv201212086
Yang D, Qi SH, Zhang Y, Xing XL, Liu HX, Qu CK, Liu J, Li F (2013) Levels, sources and potential risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in multimedia environment along the Jinjiang River mainstream to Quanzhou Bay China. Mar Pollut Bull 76(1–2):298–306. doi:10.1016/jmarpolbul201308016
Yin H, Tan Q, Chen Y, Lv GB, Hou XD (2011) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) pollution recorded in annual rings of gingko (Gingko biloba L): determination of PAHs by GC/MS after accelerated solvent extraction. Microchem J 97(2):138–143. doi:10.1016/jmicroc201008004
Yuan H, Li T, Ding X, Zhao G, Ye S (2014) Distribution, sources and potential toxicological significance of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface soils of the Yellow River Delta China. Mar Pollut Bull 83(1):258–264. doi:10.1016/jmarpolbul201403043
Yunker MB, Macdonald RW, Vingarzan R, Reginald HM, Goyette D, Sylvestre S (2002) PAHs in the Fraser River Basin: a critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and compositions. Org Geochem 33(4):489–515. doi:10.1016/S0146-6380(02)00002-5
Zhang L, Qin Y, Zheng B, Lin T, Li Y (2013) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediments of Xiangjiang River in south-central China: occurrence and sources. Environ Earth Sci 69(1):119–125. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-1939-x
Zhao QH, Liu SL, Deng L, Yang ZF, Dong SK, Wang C, Zhang ZL (2012) Spatio-temporal variation of heavy metals in fresh water after dam construction: a case study of the Manwan Reservoir, Lancang River. Environ Monit Assess 184(7):4253–4266. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2260-y
Zheng Y, Lin ZR, Li H, Ge Y, Zhang W, Ye YB, Wang XJ (2014) Assessing the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) pollution of urban stormwater runoff: a dynamic modeling approach. Sci Total Environ 481(2):554–563. doi:10.1016/jscitotenv201402097
Zuo Q, Duan YH, Yang Y, Wang XJ, Tao S (2007) Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface in Tianjin, China. Environ Pollut 147(2):303–310. doi:10.1016/jenvpol200605029
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41571173) and National Science and Technology Support Project (No. 2014BAK19B06-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Manwan Dam is managed by China Huaneng Group Corporation, a state-owned enterprise. The corporation gave us permission to conduct this sampling study, which did not involve any endangered or protected species. It was environmentally neutral and did not threaten the welfare of any species or that of the local population. Therefore, it was not related to ethical issues and no specific permissions were required for such activities. So there was no the potential conflicts of interest.
Human and animal rights
The study did not involve the human participants and animals
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, N., Liu, S., Yin, Y. et al. Spatial distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the reservoir sediments after impoundment of Manwan Dam in the middle of Lancang River, China. Ecotoxicology 25, 1072–1081 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1663-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1663-5