Abstract
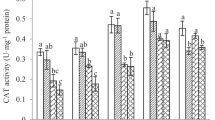
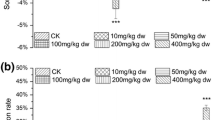
Triclosan (TCS) is released into the terrestrial environment via the application of sewage sludge and reclaimed water to agricultural land. More attention has been paid to its effect on non-target soil organisms. In the present study, chronic toxic effects of TCS on earthworms at a wide range of concentrations were investigated. The reproduction, DNA damage, and expression levels of heat shock protein (Hsp70) gene of earthworms were studied as toxicity endpoints. The results showed that the reproduction of earthworms were significantly reduced (p < 0.05) after exposure to the concentrations ranges from 50 to 300 mg kg−1, with a half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) of 142.11 mg kg−1. DNA damage, detected by the comet assay, was observed and there was a clear significant (R2 = 0.941) relationship between TCS concentrations and DNA damage, with the EC50 value of 8.85 mg kg−1. The expression levels of Hsp70 gene of earthworms were found to be up-regulated under the experimental conditions. The expression level of hsp70 gene increased, up to about 2.28 folds that in the control at 50 mg kg−1. The EC50 value based on the Hsp70 biomarker was 1.79 mg kg−1. Thus, among the three toxicity endpoints, the Hsp70 gene was more sensitive to TCS in soil.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amorim MJB, Oliveira E, Soares AMVM, Scott-Fordsmand JJ (2010) Predicted no effect concentration (PNEC) for triclosan to terrestrial species (invertebrates and plants). Environ Int 36:338–343
Binelli A, Cogni D, Parolini M, Riva C, Provini A (2009) In vivo experiments for the evaluation of genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of triclosan in zebra mussel hemocytes. Aquat Toxicol 91:238–244
Bolognesi C, Buschini A, Branchi E, Carboni P, Furlini M, Martino A, Monteverde M, Poli P, Rossi C (2004) Comet and micronucleus assays in zebra mussel cells for genotoxicity assessment of surface drinking water treated with three different disinfectants. Sci Total Environ 333:127–136
Booth L, O’Halloran K (2001) A comparison of biomarker responses in the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa to the organophosphorus insecticides diazinon and chlorpyrifos. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2494–2502
Brulle F, Mitta G, Cocquerelle C, Vieau D, Lemiere S, Lepretre A, Vandenbulcke F (2006) Cloning and real-time PCR testing of 14 potential biomarkers in Eisenia fetida following cadmium exposure. Environ Sci Technol 40:2844–2850
Canesi L, Ciacci C, Lorusso LC, Betti M, Gallo G, Pojana G, Marcomini A (2007) Effects of triclosan on Mytilus galloprovincialis hemocyte function and digestive gland enzyme activities: possible modes of action on non target organisms. Comp Biochem Physiol C 145:464–472
Ciniglia C, Cascone C, Giudice RL, Pinto G, Pollio A (2005) Application of methods for assessing the geno- and cytotoxicity of triclosan to C. ehrenbergii. J Hazard Mater 122:227–232
Crofton KM, Paul KB, DeVito MJ, Hedge JM (2007) Short-term in vivo exposure to the water contaminant triclosan: evidence for disruption of thyroxine. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 24:194–197
Delorenzo ME, Keller JM, Arthur CD, Finnegan MC, Harper HE, Winder VL, Zdankiewicz DL (2008) Toxicity of the antimicrobial compound triclosan and formation of the metabolite methyl-triclosan in estuarine systems. Environ Toxicol 23:224–232
Dhawan A, Bajpayee M, Parmar D (2009) Comet assay: a reliable tool for the assessment of DNA damage in different models. Cell Biol Toxicol 25:5–32
Evrard E, Devaux A, Bony S, Burgeot T, Riso R, Budzinski H, Le Du M, Quiniou L, Laroche J (2010) Responses of the European flounder Platichthys flesus to the chemical stress in estuaries: load of contaminants, gene expression, cellular impact and growth rate. Biomarkers 15:111–137
Eyambe GS, Goven AJ, Fitzpatrick LC, Venables BJ, Cooper EL (1991) A non-invasive technique for sequential collection of earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) leukocytes during subchronic immunotoxicity studies. Lab Anim 25:61–67
Fridovich I (1983) Superoxide radical: an endogenous toxicant. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 23:239–257
Guilherme S, Santos MA, Barroso C (2012) Differential genotoxicity of Roundup (R) formulation and its constituents in blood cells of fish (Anguilla anguilla): considerations on chemical interactions and DNA damaging mechanisms. Ecotoxicology 21:1381–1390
Heidler J, Halden RU (2007) Mass balance assessment of triclosan removal during conventional sewage treatment. Chemosphere 66:362–369
Ishibashi H, Matsumura N, Hirano M, Matsuoka M, Shiratsuchi H, Ishibashi Y, Takao Y, Arizono K (2004) Effects of triclosan on the early life stages and reproduction of medaka Oryzias latipes and induction of hepatic vitellogenin. Aquat Toxicol 67:167–179
James MO, Li WJ, Summerlot DP, Rowland-Faux L, Wood CE (2009) Triclosan is a potent inhibitor of estradiol and estrone sulfonation in sheep placenta. Environ Int 36:942–949
Kinney CA, Furlong ET, Zaugg SD, Burkhardt MR, Werner SL, Cahill JD, Jorgensen GR (2006) Survey of organic wastewater contaminants in biosolids destined for land application. Environ Sci Technol 40:7207–7215
Kinney CA, Furlong ET, Kolpin DW, Burkhardt MR, Zaugg SD, Werner SL, Bossio JP, Benotti MJ (2008) Bioaccumulation of pharmaceuticals and other anthropogenic waste indicators in earthworms from agricultural soil amended with biosolid or swine manure. Environ Sci Technol 42:1863–1870
Końca K, Lankoff A, Banasik A, Lisowska H, Kuszewski T, Góźdź S, Koza Z, Wojcik A (2003) A cross-platform public domain PC image-analysis program for the comet assay. Mutat Res 543:15–20
Lin DS, Zhou QX, Xie XJ, Liu Y (2010) Potential biochemical and genetic toxicity of triclosan as an emerging pollutant on earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 81:1328–1333
Lin DS, Xie XJ, Zhou QX, Liu Y (2012) Biochemical and genotoxic effect of triclosan on earthworms (Eisenia fetida) using contact and soil tests. Environ Toxicol 27:385–392
Liu F, Ying GG, Yang LH, Zhou QX (2009) Terrestrial ecotoxicological effects of the antimicrobial agent triclosan. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:86–92
Liu Y, Zhou QX, Xie XJ, Lin DS, Dong LX (2010) Oxidative stress and DNA damage in the earthworm Eisenia fetida induced by toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene. Ecotoxicology 19:1551–1559
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Lozano N, Rice CP, Ramirez M, Torrents A (2010) Fate of triclosan in agricultural soils after biosolid applications. Chemosphere 78:760–766
Matozzo V, Devoti AC, Marin MG (2012) Immunotoxic effects of triclosan in the clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Ecotoxicology 21:66–74
Nadeau D, Corneau S, Plante I (2001) Evaluation for Hsp70 as a biomarker of effect of pollutants on the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris. Cell Stress Chaperon 6:153–163
Reiss R, Lewis G, Griffin J (2009) An ecological risk assessment for triclosan in the terrestrial environment. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1546–1556
Rzeuski R, Chlubek D, Machoy Z (1998) Interactions between fluoride and biological free radical reactions. Fluoride 31:43–45
Schnug L, Jakob L, Hartnik T (2013) The toxicity of a ternary biocide mixture to two consecutive earthworm (Eisenia fetida) generations. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:937–947
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Weber L, Carvalho L, Sa N, Silva V, Beraldini N, Souza V, Conceicao M (2013) Genotoxic effects of the water-soluble fraction of heavy oil in the brackish/freshwater amphipod Quadrivisio aff. lutzi (Gammaridea) as assessed using the comet assay. Ecotoxicology 22:642–655
Wu CX, Spongberg AL, Witter JD, Fang M, Czajkowski KP (2010) Uptake of pharmaceutical and personal care products by soybean plants from soils applied with biosolids and irrigated with contaminated water. Environ Sci Technol 44:6157–6161
Xue YG, Gu XY, Wang XR, Sun C, Xu XH, Sun J, Zhang BG (2009) The hydroxyl radical generation and oxidative stress for the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to tetrabromobisphenol A. Ecotoxicology 18:693–699
Ying GG, Yu ZY, Kookana RS (2007) Biological degradation of triclocarban and triclosan in a soil under aerobic and anaerobic conditions and comparison with environmental fate modeling. Environ Pollut 150:300–305
Zhou QX, Kong FX, Zhu L (2004) Ecotoxicology (in Chinese). Science Press, Beijing
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China as a key project (Grant No. 21037002) and as a general project (Grant No. 20977053).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, D., Li, Y., Zhou, Q. et al. Effect of triclosan on reproduction, DNA damage and heat shock protein gene expression of the earthworm Eisenia fetida . Ecotoxicology 23, 1826–1832 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1320-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1320-9