Abstract
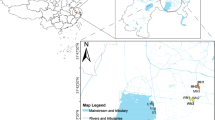
Bacteria play an important role in groundwater chemistry. The groundwater resource in the Pearl River Delta (PRD) is responsible for 50 million people’s water requirement. High amount of ammonium, arsenic and methane had been reported in groundwater of the PRD, which was considered as the result of intensive bacterial metabolism in the multilayer aquifer-aquitard system. To investigate bacterial community in this system and its relation with groundwater chemistry, sediment and groundwater samples were taken from representative locations in the PRD at different lithological units. Bacterial 16S rRNA gene clone libraries were constructed for microbial identifications and community structures in different strata. Canonical correlation analysis between bacterial linages and environment variables (Cl−, PO4 3−, SO4 2−, NH4 +) showed that community structures were significantly modified by geological conditions. Higher bacterial diversity was observed in samples from the Holocene aquitard M1 and aquifer T1, while in the older aquitard M2 and basal aquifer T2, bacterial diversity was much lower. Chloroflexi, γ-proteobacteria and δ-proteobacteria were the dominant phyla in the aquitard sediment. β-proteobacteria was the dominant phylum in sediment which was strongly influenced by fresh water. The results of this study demonstrated that bacterial community contains information of geological events such as sea transgression and deltaic evolution, and microbes in the aquitards have great potential in dominating groundwater quality in aquifers.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano T, Yoshinaga I, Okada K, Yamagishi T, Ueda S, Obuchi A, Sako Y, Suwa Y (2007) Detection of anammox activity and diversity of anammox bacteria-related 16S rRNA genes in coastal marine sediment in japan. Microbes Environ 22(3):232–242
Balkwill DL, Murphy EM, Fair DM, Ringelberg DB, White DC (1998) Microbial communities in high and low recharge environments: implications for microbial transport in the vadose zone. Microbial Ecol 35(2):156–171. doi:10.1007/s002489900070
Bothe H, Ferguson SJ, Newton WE (2007) Biology of the nitrogen cycle, 1st edn. Elsevier, Boston
Bowman JP, McCuaig RD (2003) Biodiversity, community structural shifts, and biogeography of prokaryotes within Antarctic continental shelf sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(5):2463–2483. doi:10.1128/Aem.69.5.2463-2483.2003
Braak Ct, Smilauer P (2002) CANOCO reference manual and user’s guide to Canoco for Windows: software for canonical community ordination (version 4.5). Microcomputer Power, Ithaca
Brock TD, Gustafson J (1976) Ferric iron reduction by sulfur- and iron-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 32(4):567–571
Castignetti D, Hollocher TC (1984) Heterotrophic nitrification among denitrifiers. Appl Environ Microbiol 47(4):620–623
Chapelle FH, Lovley DR (1992) Competitive exclusion of sulfate reduction by Fe (lll)-reducing bacteria: a mechanism for producing discrete zones of high-iron ground water. Gr Water 30(1):29–36
Chapelle FH, McMahon PB (1991) Geochemistry of dissolved inorganic carbon in a Coastal Plain aquifer. 1. Sulfate from confining beds as an oxidant in microbial CO2 production. J Hydrol 127(1):85–108
Chen FR, Zhang L, Yang YQ, Zhang DR (2008) Chemical and isotopic alteration of organic matter during early diagenesis: Evidence from the coastal area off-shore the Pearl River estuary, south China. J Marine Syst 74(1–2):372–380. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2008.02.004
Clark KW, Stephens JHG (1981) Proceedings of the 8th North American rhizobium conference: held Aug 3–7, 1981, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg
Collins MD, Wallbanks S, Lane DJ, Shah J, Nietupski R, Smida J, Dorsch M, Stackebrandt E (1991) Phylogenetic analysis of the genus listeria based on reverse-transcriptase sequencing of 16 s Ribosomal-Rna. Int J Syst Bacteriol 41(2):240–246
Cottrell MT, Waidner LA, Yu LY, Kirchman DL (2005) Bacterial diversity of metagenomic and PCR libraries from the Delaware River. Environ Microbiol 7(12):1883–1895. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00762.x
Crump BC, Armbrust EV, Baross JA (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of particle-attached and free-living bacterial communities in the Columbia river, its estuary, and the adjacent coastal ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(7):3192–3204
Dolédec S, Chessel D (1994) Co-inertia analysis: an alternative method for studying species–environment relationships. Freshwater Biol 31(3):277–294
Dubilier N, Mülders C, Ferdelman T, de Beer D, Pernthaler A, Klein M, Wagner M, Erséus C, Thiermann F, Krieger J (2001) Endosymbiotic sulphate-reducing and sulphide-oxidizing bacteria in an oligochaete worm. Nature 411(6835):298–302
Edwards M, Webb J (2009) The importance of unsaturated zone biogeochemical processes in determining groundwater composition, southeastern Australia. Hydrogeol J 17(6):1359–1374. doi:10.1007/s10040-009-0449-8
Fan X, Cui B, Zhang K, Zhang Z, Zhao H (2012) Construction of river channel-wetland networks for controlling water pollution in the Pearl River Delta, China. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 40(10):1027–1035
Feng BW, Li XR, Wang JH, Hu ZY, Meng H, Xiang LY, Quan ZX (2009) Bacterial diversity of water and sediment in the Changjiang estuary and coastal area of the East China Sea. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70(2):236–248. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2009.00772.x
Freitag TE, Chang L, Prosser JI (2006) Changes in the community structure and activity of betaproteobacterial ammonia-oxidizing sediment bacteria along a freshwater–marine gradient. Environ Microbiol 8(4):684–696
Gault A, Islam F, Polya D, Charnock J, Boothman C, Chatterjee D, Lloyd J (2005) Microcosm depth profiles of arsenic release in a shallow aquifer. West Bengal. Mineralogical Magazine 69(5):855–863
GHT (1981) Regional Hydrogeological Survey Report. Guangzhou, Guangdong Hydrogeological Team
Glockner FO, Zaichikov E, Belkova N, Denissova L, Pernthaler J, Pernthaler A, Amann R (2000) Comparative 16S rRNA analysis of lake bacterioplankton reveals globally distributed phylogenetic clusters including an abundant group of actinobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(11):5053
Goldscheider N, Hunkeler D, Rossi P (2006) Review: Microbial biocenoses in pristine aquifers and an assessment of investigative methods. Hydrogeol J 14(6):926–941. doi:10.1007/s10040-005-0009-9
Gumaelius L, Magnusson G, Pettersson B, Dalhammar G (2001) Comamonas denitrificans sp. nov., an efficient denitrifying bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51(3):999
Harrison BK, Zhang H, Berelson W, Orphan VJ (2009) Variations in archaeal and bacterial diversity associated with the sulfate-methane transition zone in continental margin sediments (Santa Barbara Basin, California). Appl Environ Microbiol 75(6):1487
Harvey JW, McCormick PV (2009) Groundwater’s significance to changing hydrology, water chemistry, and biological communities of a floodplain ecosystem, Everglades, South Florida USA. Hydrogeol J 17(1):185–201. doi:10.1007/s10040-008-0379-x
Heck KL, Vanbelle G, Simberloff D (1975) Explicit calculation of rarefaction diversity measurement and determination of sufficient sample size. Ecology 56(6):1459–1461
Inagaki F, Suzuki M, Nealson KH, Horikoshi K, D’Hondt SL, Jorgensen BB, Party OLSS (2003) Subseafloor microbial diversity in the Peru Margin (ODP Leg. 201). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67(18):A171–A171
Jetten MSM, Wagner M, Fuerst J, van Loosdrecht M, Kuenen G, Strous M (2001) Microbiology and application of the anaerobic ammonium oxidation (′anammox′) process. Curr Opin Biotechnol 12(3):283–288
Jetten M, Sliekers O, Kuypers M, Dalsgaard T, Niftrik L, Cirpus I, Pas-Schoonen K, Lavik G, Thamdrup B, Paslier DL (2003) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation by marine and freshwater planctomycete-like bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63(2):107–114
Jiao JJ, Wang Y, Cherry JA, Wang XS, Zhi BF, Du HY, Wen DG (2010) Abnormally high ammonium of natural origin in a coastal aquifer-aquitard system in the Pearl River Delta. China. Environ Sci Technol 44(19):7470–7475. doi:10.1021/Es1021697
Jørgensen BB, Boetius A (2007) Feast and famine—microbial life in the deep-sea bed. Nat Rev Microbiol 5(10):770–781
Lehman RM, O’Connell SP, Banta A, Fredrickson JK, Reysenbach AL, Kieft TL, Colwell FS (2004) Microbiological comparison of core and groundwater samples collected from a fractured basalt aquifer with that of dialysis chambers incubated in situ. Geomicrobiol J 21(3):169–182. doi:10.1080/01490450490275848
Leloup J, Fossing H, Kohls K, Holmkvist L, Borowski C, Jorgensen BB (2009) Sulfate-reducing bacteria in marine sediment (Aarhus Bay, Denmark): abundance and diversity related to geochemical zonation. Environ Microbiol 11(5):1278–1291. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01855.x
Li PR, Qiao PN (1982) The Model of Evolution of the Pearl River Delta During Last 6,000 Years. J Sedim Res 3(1):33–41
Ma D, Hu Y, Wang J, Ye S, Li A (2006) Effects of antibacterials use in aquaculture on biogeochemical processes in marine sediment. Sci Total Environ 367(1):273–277
McMahon PB (2001) Aquifer/aquitard interfaces: mixing zones that enhance biogeochemical reactions. Hydrogeol J 9(1):34–43. doi:10.1007/s100400000109
Qi S, Leipe T, Rueckert P, Di Z, Harff J (2010) Geochemical sources, deposition and enrichment of heavy metals in short sediment cores from the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. J Marine Syst 82:S28–S42
Santoro AE (2010) Microbial nitrogen cycling at the saltwater-freshwater interface. Hydrogeol J 18(1):187–202. doi:10.1007/s10040-009-0526-z
Schloss PD, Handelsman J (2005) Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(3):1501–1506. doi:10.1128/Aem.71.3.1501-1506.2005
Schramm A, de Beer D, Wagner M, Amann R (1998) Identification and activities in situ of Nitrosospira and Nitrospira spp. as dominant populations in a nitrifying fluidized bed reactor. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(9):3480–3485
Sievert SM, Scott KM, Klotz MG, Chain PS, Hauser LJ, Hemp J, Hügler M, Land M, Lapidus A, Larimer FW (2008) Genome of the epsilonproteobacterial chemolithoautotroph Sulfurimonas denitrificans. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(4):1145–1156
Silverman MP (1967) Mechanism of bacterial pyrite oxidation. J Bacteriol 94(4):1046–1051
Tabrez Khan S, Hiraishi A (2002) Diaphorobacter nitroreducens gen. nov., sp. nov., a poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)-degrading denitrifying bacterium isolated from activated sludge. J General Appl Microbiol 48(6):299–308
Takai K, Campbell BJ, Cary SC, Suzuki M, Oida H, Nunoura T, Hirayama H, Nakagawa S, Suzuki Y, Inagaki F (2005) Enzymatic and genetic characterization of carbon and energy metabolisms by deep-sea hydrothermal chemolithoautotrophic isolates of Epsilonproteobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(11):7310–7320
Tamaki H, Sekiguchi Y, Hanada S, Nakamura K, Nomura N, Matsumura M, Kamagata Y (2005) Comparative analysis of bacterial diversity in freshwater sediment of a shallow eutrophic lake by molecular and improved cultivation-based techniques. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(4):2162–2169
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Clustal-w—improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22(22):4673–4680
Toffin L, Webster G, Weightman AJ, Fry JC, Prieur D (2004) Molecular monitoring of culturable bacteria from deep-sea sediment of the Nankai Trough, Leg 190 Ocean Drilling Program. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48(3):357–367
Walker J, Colwell R, Petrakis L (1975) Evaluation of petroleum-degrading potential of bacteria from water and sediment. Appl Microbiol 30(6):1036–1039
Wang Y, Jiao JJ, Cherry JA (2012) Occurrence and geochemical behavior of arsenic in a coastal aquifer-aquitard system of the Pearl River Delta, China. Sci Total Environ 427:286–297. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.04.006
Wang X-S, Jiao JJ, Wang Y, Cherry JA, Kuang X, Liu K, Lee C, Gong Z (2013) Accumulation and transport of ammonium in aquitards in the Pearl River Delta (China) in the last 10,000 years: conceptual and numerical models. Hydrogeol J 21(5):961–967
Webster G, Sass H, Cragg BA, Gorra R, Knab NJ, Green CJ, Mathes F, Fry JC, Weightman AJ, Parkes RJ (2011) Enrichment and cultivation of prokaryotes associated with the sulphate–methane transition zone of diffusion-controlled sediments of Aarhus Bay, Denmark, under heterotrophic conditions. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 77(2):248–263. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01109.x
Whitman WB, Parte AC (2009) Systematic bacteriology. Springer Verlag, New York
Wright ES, Yilmaz LS, Noguera DR (2012) DECIPHER, a search-based approach to chimera identification for 16S rRNA sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(3):717–725
Wu C, Ren J, Bao Y, Lei Y, Shi H (2007) A long-term morphological modeling study on the evolution of the Pearl River Delta, network system, and estuarine bays since 6000 yr BP. Geol S Am S 426:199–214
Yeates C, Gillings M, Davison A, Altavilla N, Veal D (1998) Methods for microbial DNA extraction from soil for PCR amplification. Biolog Proc Online 1(1):40–47
Yim WWS, Hilgers A, Huang G, Radtke U (2008) Stratigraphy and optically stimulated luminescence dating of subaerially exposed Quaternary deposits from two shallow bays in Hong Kong, China. Quatern Int 183:23–39. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2007.07.004
Yu FL, Zong YQ, Lloyd JM, Huang GQ, Leng MJ, Kendrick C, Lamb AL, Yim WWS (2010) Bulk organic delta C-13 and C/N as indicators for sediment sources in the Pearl River delta and estuary, southern China. Estuar Coast Shelf S 87(4):618–630. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2010.02.018
Zhao J-L, Ying G-G, Liu Y-S, Chen F, Yang J-F, Wang L (2010) Occurrence and risks of triclosan and triclocarban in the Pearl River system, South China: from source to the receiving environment. J Hazard Mater 179(1):215–222
Ziegler S, Ackermann S, Majzlan J, Gescher J (2009) Matrix composition and community structure analysis of a novel bacterial pyrite leaching community. Environ Microbiol 11(9):2329–2338. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01959.x
Zong Y, Huang G, Switzer AD, Yu F, Yim WWS (2009a) An evolutionary model for the Holocene formation of the Pearl River delta. China. Holocene 19(1):129–142. doi:10.1177/0959683608098957
Zong Y, Yim WWS, Yu F, Huang G (2009b) Late Quaternary environmental changes in the Pearl River mouth region, China. Quatern Int 206:35–45. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2008.10.012
Zong Y, Huang K, Yu F, Zheng Z, Switzer A, Huang G, Wang N, Tang M (2012) The role of sea-level rise, monsoonal discharge and the palaeo-landscape in the early Holocene evolution of the Pearl River delta, southern China. Quaternary Science Reviews, Pearl River delta
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the General Research Fund of the Research Grants Council, the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China (HKU 702612P and HKU 703010P) and Sustainable Water Environment” Strategic Research Sub-Theme in the University of Hong Kong. Dr. Kuang Xingxing and Luo Xin are thanked for their help in field sampling; Dr. Li Meng and Jessie Lai are thanked for their help in lab facility arrangement.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, K., Jiao, J.J. & Gu, JD. Investigation on bacterial community and diversity in the multilayer aquifer-aquitard system of the Pearl River Delta, China. Ecotoxicology 23, 2041–2052 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1311-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1311-x