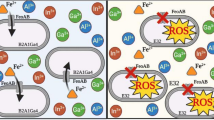
Abstract
The sulfate reducing bacterium Desulfovibrio alaskensis strain G20 can grow in lactate sulfate medium with up to 4 mM uranyl acetate. In order to identify the genes that are required for the growth of strain G20 at toxic levels of uranium(VI) (U(VI)), 5,760 transposon insertion mutants were screened for U(VI) resistance defects, and 24 of them showed loss of U(VI) resistance in lactate sulfate medium with 2 mM uranyl acetate. In the 24 mutants, 23 genes were disrupted by transposon insertions, and one transposon is located in a non-coding region. In the ten mutants that were completely inhibited by 2 mM uranyl acetate, the disrupted genes are involved in DNA repair, rRNA methylation, regulation of expression and RNA polymerase renaturation. The remaining 14 mutants showed partial inhibition of growth by 2 mM U(VI), in which the disrupted genes participate in DNA repair, regulation of transcription, membrane transport, etc. In addition, none except one of these 24 mutants showed loss in its ability to reduce U(VI) to U(IV) in the washed cell test. These results altogether suggest that U(VI) toxicity mainly involves damage to nucleic acids and proteins.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RT, Vrionis HA, Ortiz-Bernad I, Resch CT, Long PE, Dayvault R, Karp K, Marutzky S, Metzler DR, Peacock A (2003) Stimulating the in situ activity of Geobacter species to remove uranium from the groundwater of a uranium-contaminated aquifer. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(10):5884–5891
Baca TE, Florkowski T (2000) The environmental challenges of nuclear disarmament, vol 29. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Boschi Muller S, Azza S, Branlant G (2001) E. coli methionine sulfoxide reductase with a truncated N terminus or C terminus, or both, retains the ability to reduce methionine sulfoxide. Protein Sci 10(11):2272–2279
Botsford JL, Harman JG (1992) Cyclic AMP in prokaryotes. Microbiol Rev 56(1):100–122
Cheung K, Gu J-D (2007) Mechanism of hexavalent chromium detoxification by microorganisms and bioremediation application potential: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 59(1):8–15
Cologgi DL, Lampa-Pastirk S, Speers AM, Kelly SD, Reguera G (2011) Extracellular reduction of uranium via Geobacter conductive pili as a protective cellular mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(37):15248–15252
Coutellec MA, Barata C (2013) Special issue on long-term ecotoxicological effects: an introduction. Ecotoxicology 22(5):763–766. doi:10.1007/s10646-013-1092-7
Dallinger R, Hockner M (2013) Evolutionary concepts in ecotoxicology: tracing the genetic background of differential cadmium sensitivities in invertebrate lineages. Ecotoxicology 22(5):767–778. doi:10.1007/s10646-013-1071-z
Drotschmann K, Fritz H-J, Aronshtam A, Marinus MG (1998) The Escherichia coli MutL protein stimulates binding of Vsr and MutS to heteroduplex DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 26(4):948–953
Dutilleul M, Lemaire L, Réale D, Lecomte C, Galas S, Bonzom J-M (2013) Rapid phenotypic changes in caenorhabditis elegans under uranium exposure. Ecotoxicology 22(5):862–868. doi:10.1007/s10646-013-1090-9
Garten CT Jr (1978) A review of parameter values used to assess the transport of plutonium, uranium, and thorium in terrestrial food chains. Environ Res 17(3):437–452
Grissa I, Bouchon P, Pourcel C, Vergnaud G (2008) On-line resources for bacterial micro-evolution studies using MLVA or CRISPR typing. Biochimie 90(4):660–668
Groh JL, Luo Q, Ballard JD, Krumholz LR (2005) A method adapting microarray technology for signature-tagged mutagenesis of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans G20 and Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 in anaerobic sediment survival experiments. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(11):7064–7074
Groudev S, Georgiev P, Spasova I, Komnitsas K (2001) Bioremediation of a soil contaminated with radioactive elements. Hydrometallurgy 59(2):311–318
Gu JD, Wang Y (2012) Environmental feedback: lessons from pollution problems in China. Ecotoxicology 21(6):1583–1584. doi:10.1007/s10646-012-0954-8
Holdway D (1992) Uranium mining in relation to toxicological impacts on inland waters. Ecotoxicology 1(2):75–88. doi:10.1007/BF00831889
Ion S (2007) Nuclear energy: current situation and prospects to 2020. Phil Trans R Soc A 365(1853):935–944
Li X, Krumholz LR (2007) Regulation of arsenate resistance in Desulfovibrio desulfuricans G20 by an arsRBCC operon and an arsC gene. J Bacteriol 189(10):3705–3711
Li X, Krumholz LR (2009) Thioredoxin is involved in U(VI) and Cr(VI) reduction in Desulfovibrio desulfuricans G20. J Bacteriol 191(15):4924–4933
Lovley DR (2001) Anaerobes to the rescue. Science 293(5534):1444–1446
Lovley DR, Phillips E (1992) Reduction of uranium by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(3):850–856
Lovley DR, Phillips EJ, Gorby YA, Landa ER (1991) Microbial reduction of uranium. Nature 350(6317):413–416
Lovley DR, Widman PK, Woodward JC, Phillips E (1993) Reduction of uranium by cytochrome c3 of Desulfovibrio vulgaris. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(11):3572–3576
Luo Q, Groh JL, Ballard JD, Krumholz LR (2007) Identification of genes that confer sediment fitness to Desulfovibrio desulfuricans G20. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(19):6305–6312
Marqués AM, Roca X, Simon-Pujol MD, Fuste MC, Congregado F (1991) Uranium accumulation by Pseudomonas sp. EPS-5028. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35(3):406–410
Maxwell W, Metzler R, Spoerl E (1971) Uranyl nitrate inhibition of transport systems in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol 105(3):1205
N’Guessan AL, Vrionis HA, Resch CT, Long PE, Lovley DR (2008) Sustained removal of uranium from contaminated groundwater following stimulation of dissimilatory metal reduction. Environ Sci Technol 42(8):2999–3004
Neves O, Abreu MM (2009) Are uranium-contaminated soil and irrigation water a risk for human vegetables consumers? A study case with Solanum tuberosum L., Phaseolus vulgaris L. and Lactuca sativa L. Ecotoxicology 18(8):1130–1136. doi:10.1007/s10646-009-0376-4
Ordal GW (1985) Bacterial chemotaxis: biochemistry of behavior in a single cell. Crit Rev Microbiol 12(2):95–130
Pajor AM, Kahn E, Gangula R (2000) Role of cationic amino acids in the Na+/dicarboxylate co-transporter NaDC-1. Biochem J 350(Pt 3):677
Payne RB, Gentry DM, Rapp-Giles BJ, Casalot L, Wall JD (2002) Uranium reduction by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans strain G20 and a cytochrome c3 mutant. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(6):3129–3132
Payne RB, Casalot L, Rivere T, Terry JH, Larsen L, Giles BJ, Wall JD (2004) Interaction between uranium and the cytochrome c3 of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans strain G20. Arch Microbiol 181(6):398–406
Pietzsch K, Babel W (2003) A sulfate-reducing bacterium that can detoxify U(VI) and obtain energy via nitrate reduction. J Basic Microbiol 43(4):348–361
Priest N (2001) Toxicity of depleted uranium. Lancet 357(9252):244–246
Pyle G, Swanson S, Lehmkuhl D (2001) Toxicity of uranium mine-receiving waters to caged fathead minnows, Pimephales promelas. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 48(2):202–214
Sani RK, Peyton BM, Dohnalkova A, Amonette JE (2005) Reoxidation of reduced uranium with iron(III) (hydr)oxides under sulfate-reducing conditions. Environ Sci Technol 39(7):2059–2066
Sani RK, Peyton BM, Dohnalkova A (2006) Toxic effects of uranium on Desulfovibrio desulfuricans G20. Environ Toxicol Chem 25(5):1231–1238
Sorek R, Kunin V, Hugenholtz P (2008) CRISPR—a widespread system that provides acquired resistance against phages in bacteria and archaea. Nat Rev Microbiol 6(3):181–186
Tao X, Li Y, Huang H, Chen Y, Liu P, Li X (2013) Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough prefers lactate over hydrogen as electron donor. Ann Microbiol 63(2):1–7. doi:10.1007/s13213-013-0675-0
Thun MJ, Baker DB, Steenland K, Smith AB, Halperin W, Berl T (1985) Renal toxicity in uranium mill workers. Scand J Work Environ Health 11(2):83–90
Van Nostrand JD, Wu WM, Wu L, Deng Y, Carley J, Carroll S, He Z, Gu B, Luo J, Criddle CS (2009) GeoChip-based analysis of functional microbial communities during the reoxidation of a bioreduced uranium-contaminated aquifer. Environ Microbiol 11(10):2611–2626
Wade R, DiChristina TJ (2000) Isolation of U(VI) reduction-deficient mutants of Shewanella putrefaciens. FEMS Microbiol Lett 184(2):143–148
Wall JD, Krumholz LR (2006) Uranium reduction. Annu Rev Microbiol 60:149–166
Xu M, Wu W-M, Wu L, He Z, Van Nostrand JD, Deng Y, Luo J, Carley J, Ginder-Vogel M, Gentry TJ (2010) Responses of microbial community functional structures to pilot-scale uranium in situ bioremediation. ISME J 4(8):1060–1070
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Funding from the Environmental Remediation Science Program (ERSP) of the Office of Biological and Environmental Research of the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science to L. Krumholz and NSFC 31200085 to X. Li and 31100888 to P. Liu.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiangkai Li and He Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhang, H., Ma, Y. et al. Genes required for alleviation of uranium toxicity in sulfate reducing bacterium Desulfovibio alaskensis G20. Ecotoxicology 23, 726–733 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1201-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1201-2