Abstract
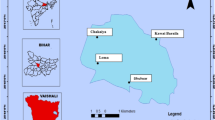
There is growing concern for the lake environment because polluted sediments may cause ecotoxicological effects. In the current study, persistent organochlorine compounds (OCPs), including hexachlorocyclohexanes (HCHs), dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethanes (DDTs) and cyclodienes, were analyzed in core sediments taken from Huoshaohei Lake, Xihulu Lake, Wanghua Lake and Keqin Lake, Heilongjiang Province, China. The total OCPs concentrations ranged from 0.92 to 7.09, 0.15 to 9.95, 0.19 to 1.84 and 0.06 to 3.52 ng/g, respectively. The most dominant pollutants were the HCHs, high proportions of γ-HCH isomer indicating the recent input of lindane. The ratios of α-HCH/γ-HCH of four lakes are all lower than that in technical HCH mixtures indicating that there was input of lindane in the past several years, and the mean ratios of (DDE+DDD)/DDTs are all <0.5, suggesting recent release of DDT compounds. Compared with the corresponding ecological environmental quality guidelines from Ingersoll and base on the model of risk based corrective action environmental health risk assessment, the sediments from the four lakes poses a lower potential hazard to human health and the environment but still should be taken into account.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
An Q, Dong YH, Wang H (2005) Residues and distribution character of organochlorine pesticides in soils in Nanjing area. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae 25:470–474
Barber JL, Sweetman AJ, Van Wijk D, Jones KC (2005) Hexachlorobenzene in the global environment: emissions, levels, distribution, trends and processes. Sci Total Environ 349:1–44
Bidlan R, Afsar M, Manonmani HK (2004) Bioremediation of HCH-contaminated soil: elimination of inhibitory effects of the insecticide on radish and green gram seed germination. Chemosphere 56:803–811
Chung MK, Hu R, Cheung KC, Wong MH (2007) Screening of PAHs and DDTs in sand and acrisols soil by a rapid solid-phase microalgal bioassay. Ecotoxicology 16:429–438
Covaci A, Gheorghe A, Voorspoels S, Maervoet J, Steen Redeker E, Blust R, Schepens P (2005) Polybrominated dipheny ethers, polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in sediment cores from the western Scheldt River (Belgium): analytical aspects and depth profiles. Environ Int 31:367–375
Davoren M, Ní Shúilleabháin S, O’ Halloran J, Hartl MGJ, Sheehan D, O’Brien NM, Van Pelt FNAM, Mothersill C (2005) A test battery approach for the ecotoxicological evaluation of estuarine sediments. Ecotoxicology 14:p741–p755
Doong RA, Peng CK, Sun YC, Liao PL (2002) Composition and distribution of organochlorine pesticide residues in surface sediments from the Wu-Shi River Estuary. Taiwan. Mar Pollut Bull 45:246–253
Fang M, Qi SH, Wu CX, Hu LS, Su QK (2006) High resolution sedimentary record of organochlorine pesticides in sediments core from Honghu Lake. Geol Sci Technol Infor 25:89–92 (in Chinese)
Fu S, Chu S, Xu X (2001) Organochlorine pesticide residue in soils from Tibet, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 66:171–177
George C (1995) Becking use of mechanistic information in risk assessment for toxic chemicals. Toxicol Lett 77:15–24
Glubala CP, Landers DH, Monetti M, Heitb M, Wadec T, Lasorsad B, Allen-Gile S (1995) The rates of accumulation and chronologies of atmospherically-derived pollutants in Arctic Alaska USA. Sci Total Environ 161–162:347–361
Hitch RK, Day HR (1992) Unusual persistence of DDT in some Western USA soils. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 48:259–264
Ingersoll CG, Haverland PS, Brunson EL (1996) Calculation and evaluation of sediment effect concentrations for the Amphipod Chironomus Riparius. J Great Lakes Res 22:602–623
Iwanowicz LR, Blazer VS, Hitt NP, McCormick SD, DeVault DS, Ottinger CA (2012) Histologic, immunologic and endocrine biomarkers indicate contaminant effects in fishes of the Ashtabula River. Ecotoxicology 21:165–182
Iwata H, Tanabe S, Ueda K, Tatsukawa R (1995) Persistent organochlorine residues in air, water, sediments, and soils from the lake Baikal region, Russia. Environ Sci Technol 29:792–801
Kumar M, Chaudhary P, Dwivedi M, Kumar R, Paul D, Jain RK, Garg SK, Kumar A (2005) Enhanced biodegradation of β- and δ-hexachlorocyclohexane in the presence of α- and γ-isomers in contaminated soils. Environ Sci Technol 39:4005–4011
Latimer JS, Quinn JG (1996) Historical trends and current inputs of hydrophobic organic compounds in urban estuary: the sedimentary record. Environ Sci Technol 30:623–633
Li MG (2001) Hydrographic and sediment analyses of Xinghua Bay. J Waterway Harbor 22:156–159
Long ER, Macdonald DD, Smith SL, Calder FD (1995) Incidence of adverse biological effects with ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. J Environ Manag 19:81–97
Lu GH, Yan ZH, Wang YH, Chen W (2011) Assessment of estrogenic contamination and biological effects in Lake Taihu. Ecotoxicology 20:974–981
Mark DM, Steve JG (1997) The relationship between land use and organochlorine compounds in streambed sediments and fish in the central Columbia Plateau, Washington and Idaho, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:1877–1887
Meter PCV, Callender E, Fuller C (1997) Historical trends in organochlorine compounds in river basin identified using sediment cores from reservoirs. Environ Sci Technol 31:2339–2344
Politov SV, Anokhin YuA, Surnina NN (2000) Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in the environment of the Baikal region. Aquat Ecosyst Health 3:235–238
Rawson CA, Lim RP, Tremblay LA, Warne MSJ, Ying GG, Laginestra E, Chapman JC (2010) Benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in remediated wetlands around Sydney, Australia. Ecotoxicology 19:1589–1600
Sahu SK, Patnaik KK, Bhuyan S, Sethunathan N (1993) Degradation of soil-applied isomers of hexachlorocyclohexane by a Pseudomonas sp. Soil Biol Biochem 25:387–391
Stronkhorst J, Schipper C, Brils J, Dubbeldam M, Postma J, Van de Hoevan N (2003) Using marine bioassays to classify the toxicity of Dutch harbour sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:1535–1547
Tanabe S, Iwata H, Tatsukawa R (1994) Global contamination by persistent organochlorine and their ecotoxicological impact on marine mammals. Sci Total Environ 154:163–177
US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA), Office of Solid Waste (2007) Technical background document for the supplemental report to Congress on remaining fossil fuel combustion wastes: groundwater pathway human health risk assessment [EB/OL]. Washington DC: US EPA
Voorspoels S, Covaci A, Maervoet J, De Meester I, Schepens P (2004) Distribution of PCBs/OCPs in benthic organisms and fish from the North Sea Continental Shelf and Scheldt Estuary. Mar Pollut Bull 49:393–404
Wang XP, Yao TD, Cong ZY, Yan XL, Kang SC, Zhang Y (2006) Gradient distribution of persistent organic contaminants along northern slope of central-Himalayas, China. Sci Total Environ 372:193–202
Xuan FH, Zang SY (2011) Evaluation of risk associated with organchlorine pesticide contaminated sediment of the Lake Lianhuan watershed. Ecotoxicology 20:1090–1098
Yao ZW, Jiang GB, Xu HZ (2002) Distribution of organochlorine pesticides in seawater of the Bering and Chukchi Sea. Environ Pollut 116:49–56
Zhang HY (2004) Countermeasure research on protection and development of ecological resource in Zhalong Wetland. Nat Ecol Cons 2:29–32 (in Chinese)
Zhang G, Andrew P, Alan H (2002) Sedimentary records of DDT and HCH in the Pearl River Delta, south China. Environ Sci Technol 36:3671–3677
Zhao ZH, Zhang L, Wu JL, Fan CX (2009) Distribution and bioaccumulation of organochlorine pesticides in surface sediments and benthic organisms from Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 77:1191–1198
Zhou JL, Maskaoui K, Qiu YW, Hong HS, Wang ZD (2001) Polychlorinated biphenyl congeners and organochlorine insecticides in the water column and sediments of Daya Bay, China. Environ Pollut 113:373–384
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the key National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41030743), the Science and Technology Innovative Programs Foundation of Higher Education of Heilongjiang Province of China (No. 2010td10), the key Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (No. ZD201308), and the Doctoral Innovation Foundation of Harbin Normal University (No. HSDBSCX2012-06). We also thank Dr. Richard S. Halbrook for proofreading our English.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hui, H., Zang, S. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides in sediments from four lakes of Heilongjiang Province, China. Ecotoxicology 23, 601–608 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1184-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1184-z