Abstract
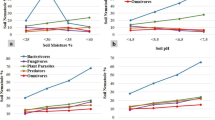
The effect of distance from a heavy metal pollution source on the soil nematode community was investigated on four sampling sites along an 4 km transect originating at the Kovohuty a.s. Krompachy (pollution source). The soil nematode communities were exposed to heavy metal influence directly and through soil properties changes. We quantified the relative effects of total and mobile fraction of metals (As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn) on soil ecosystem using the nematode community structure (trophic and c-p groups,) and ecological indices (Richness of genera, H′, MI2-5, etc.). Pollution effects on the community structure of soil free living nematodes was found to be the highest near the pollution source, with relatively low population density and domination of insensitive taxa. A decrease in heavy metals contents along the transect was linked with an increase in complexity of nematode community. The majority of used indices (MI2-5, SI, H′) negatively correlated (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01) with heavy metals content and were sensitive to soil ecosystem disturbance. Contamination by heavy metals has negatively affected the soil environment, which resulted in nematode community structure and ecological indices changes. Results showed that the free-living nematodes are useful tools for bioindication of contamination and could be used as an alternative to the common approaches based on chemical methods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ministry Decree No. 531/1994-540, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of Slovak Republic, (1994), http://enviroportal.sk/pdf/spravy_zp/svk99s_poda.pdf, Accessed 20 May 2011
Allen-Morley CR, Coleman DC (1989) Resilience of soil biota in various food webs to freezing perturbations. Ecology 70:1127–1141
Bakonyi G, Nagy P, Kádár I (2003) Long–term effects of heavy metals and microelements on nematode assemblage. Toxicol Lett 140–141:391–401. doi:10.1016/S0378-4274(03)00035-3
Banášová V, Lackovičová A (2004) The disturbance of grasslands in the vicinity of copper plant in the town of Krompachy (Slovenské Rudohorie Mts., NE Slovakia). Bull. Slov. Bot. Spoločn. 26:153–161
Benzarti S, Mohri S, Ono Y (2008) Plant response to heavy metal toxicity: comparative study between the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens (ecotype ganges) and nonaccumulator plants: lettuce, radish, and alfalfa. Environ Toxicol 23:607–616. doi:10.1002/tox.20405
Bodenkunde AG (1994) Bodenkudliche Kartieranleitung. Schweizerbartsche, Stuttgart
Bongers T (1990) The maturity index: an ecological measure of environmental disturbances based on nematode species composition. Oecologia 83:14–19
Bongers T, Bongers M (1998) Functional diversity of nematodes. Appl Soil Ecol 10:239–251
Bongers T, Ilieva-Makulec K, Ekschmitt K (2001) Acute sensitivity of nematode taxa to CuSO4 and relationships with feeding type and life-history classification. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1511–1516
Bremner JM (1996) Nitrogen-total. In: Sparks DL (ed) Methods of Soil Analysis. SSSA Inc., Madison, WI, pp 1085–1121
Carrillo-Gonzáles R, Šimunek J, Sauvé S, Adriano D (2006) Mechanisms and pathways of trace elements mobility in soils. Adv Agron 91:112–178
Chen G, Qin J, Shi D, Zhang Y, Ji W (2009) Diversity of soil nematodes in area polluted with heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Lanzhou, China. Environ Manage 44:163–172. doi:10.1007/s00267-008-9268-2
Connell JH (1978) Diversity in tropical forests and coral reefs. Science 199:1302–1310
de Goede RGM, Bongers T (1994) Nematode community structure in relation to soil and vegetation characteristics. Appl Soil Ecol 1:29–44
Edwards CA (2002) Assessing the effects of environmental pollutants on soil organisms, communities, processes and ecosystems. Eur J Soil Biol 38:225–231
Ettema CHH (1998) Soil nematode diversity: species coexistence and ecosystem function. J Nematol 30:159–169
Fargašová A (2009) Metal contamination in Slovakia. Available at: http://www.enviro-edu.sk/?page=environmentalne_problemy/znecistenie_kovmi_na_slovensku, Accessed 15 May 2011 (in Slovak)
Ferris H, Bongers T, de Goede RGM (2001) A framework for soil food web diagnostics: extension of the nematode faunal analysis concept. Appl Soil Ecol 18:13–29
Freckman DW, Baldwin JG (1990) Nematoda. In: Dindal DL (ed) Soil biology guide. Wiley, New York, pp 155–200
Georgieva SS, Mcgrath SP, Hooper DJ, Chambers BS (2002) Nematode communities under stress: the long–term effects of heavy metals in soil treated with sewage sludge. Appl Soil Ecol 20:27–42
Hančulák J, Bobro M, Fedorová E, Šestinová O, Brehuv J, Špadlon T, Slančo P (2007) Monitoring depozície ťažkých kovov z prašného spadu v oblasti pôsobenia železorudného banského závodu v Nižnej Slanej. Bioclimatology and natural hazards-international scientific conference, Poľana nad Detvou, September 17–20, 2007
Háněl L (2004) Colonization of chemical factory wastes by soil nematodes. Pedobiologia 48:373–381
Hronec O (1996) Exhaláty-pôda–vegetácia. Hronec, O. (Ed.). TOP s.r.o. Prešov and Slovak Agricultural and Food Chamber, Bratislava, p 326
Impellitteri CA, Allen HE, Yin Y, You SJ, Saxe JK (2001) Soil properties controlling metal partitioning. In: Selim HM, Sparks DL (eds) Heavy Metal Release in Soils, Lewis Publ, Boca Raton, pp 149–165
Jung MC (2008) Heavy metal concentrations in soils and factors affecting metal uptake by plants in the vicinity of a Korean Cu-W mine. Sensors 8:2413–2423
Kabata-Pendias A (2011) Trace elements in soils and plants, In: Kabata-Pendias A (ed), 4th edn, CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton.
Kawakami H, Yoshida K, Nishida Y, Kikuchi Y, Sato Y (2008) Antibacterial properties of metallic elements for alloying evaluated with application of JIS Z 2801:2000. ISIJ Int 48:1299–1304
Korthals GW, Alexiev AD, Lexmond TM, Kammenga JE, Bongers T (1996a) Long-term effects of copper and pH on the nematode community in an agroecosystem. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:979–985
Korthals GW, van de Ende A, van Megen H, Lexmond TM, Kammenga JE, Bongers T (1996b) Short-term effects of cadmium, copper, nickel and zinc on soil nematodes from different feeding and life-history strategy groups. Appl Soil Ecol 4:107–117
Korthals GW, Popovici J, Van Megen HHB (1998) Soil nematodes in heathland around a zinc-smelter near Budel, The Netherlands. In: De Goede RGM, Bongers T (eds) Nematode communities of northern temperate grassland ecosystems. Giessen, Germany, pp 155–158
Korthals GW, Bongers M, Fokkema A, Dueck TA, Lexmond TM (2000) Joint toxicity of copper and zinc to terrestrial nematode community in an acid sandy soil. Ecotoxicology 9:219–228
Li Q, Jiang Y, Liang WJ (2006) Effect of heavy metals on soil nematode communities in the vicinity of a metallurgical factory. J Environ Sci 18:323–328
Li Q, Zhong S, Li F, Lou Y, Liang W (2011) Nematode community structure as bioindicator of soil heavy metal pollution along an urban-rural gradient in southern Shenyang, China. Int J Environ Pollut 45:297–309. doi:10.1504/IJEP.2011.040276
Losos B, Gulička J, Lellák J, Pelikán J (1984) Animal ecology. Státní pedagogické nakladatelství Praha. (in Czech)
Nagy P (1999) Effect of an artificial metal pollution on nematode assemblage of a calcareous loamy chernozem soil. Plant Soil 212:35–43
Nagy P, Bakónyi G, Bongers T, Kádár I, Fábián M, Kiss I (2004) Effects of microelements on soil nematode assemblages seven years after contaminating an agricultural field. Sci Total Environ 320:131–143
Nahmani J, Hodson ME, Black S (2007) Effects of metals on life cycle parameters of the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to field-contaminated, metal-polluted soils. Environ Pollut 149:44–58. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.12.018
Navarro AF, Cegarra J, Roig A, Garcia D (1993) Relationships between organic matter and carbon contents of organic wastes. Bioresour Technol 44:203–207
Odum PE (1985) Trends expected in stressed ecosystems. Bioscience 35:419–422
Özdemir G, Limoncu MH, Yapar S (2010) The antibacterial effect of heavy metal and cetylpyridinium-exchanged montmorillonites. Appl Clay Sci 48:319–323. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2010.01.001
Park BY, Lee JK, Ro HM, Kim YH (2011) Effects of heavy metal contamination from an abandoned mine on nematode community structure as an indicator of soil ecosystem health. Appl Soil Ecol 51:17–24. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2011.08.006
Pen-Mouratov S, Shururov N, Steinberger Y (2008) Influence of industrial heavy metal pollution on soil free-living nematode population. Environ Pollut 152:172–183. doi:10.1016/j.evpol.2007.05.007
Pen-Mouratov S, Shukurov N, Steinberger Y (2010) Soil free-living nematodes as indicators of both industrial pollution and livestock activity in Central Asia. Ecol Ind 10:955–967. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2010.02.005
Peterson G, Allen CR, Holling CS (1998) Ecological resilience, biodiversity, and scale. Ecosystems 1:16–18
Sánchez-Moreno S, Navas A (2007) Nematode diversity and food web condition in heavy metal pollutes soils in river basin in Southern Spain. Eur J Soil Biol 43:166–179. doi:10.1016/j.ejsobi.2007.01.002
Sánchez-Moreno S, Camargo JA, Navas A (2006) Ecotoxicological assessment of the impact of residual heavy metals on soil nematodes in the Guadiamar river basin (Southern Spain). Environ Monit Assess 116:245–262. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-7398-7
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois, Urbana
Shao Y, Zhang W, Shen J, Zhou L, Xia H, Shu W, Ferris H, Fu S (2008) Nematodes as indicators of soil recovery in tailings of a lead/zinc mine. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2040–2046. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.04.014
Shukurov N, Pen-Mouratov S, Steinberger Y (2006) The influence of soil pollution on soil microbial biomass and nematode community structure in Navoiy Industrial Park, Uzbekistan. Environ Int 32:1–11. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2004.12.003
Skubała P, Zaleski T (2011) Heavy metal sensitivity and bioconcentration in oribatid mites (Acari, Oribatida). gradient study in meadow ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 414:364–372
Sochová I, Hofman J, Holoubek I (2006) Using nematodes in soil ecotoxicology. Environ Int 32:374–383. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2005.08.031
Sohlenius B (1980) Abundance, biomass and contribution to energy flow by soil nematodes in terrestrial ecosystems. Oikos 34:186–194
Southey JF (1986) Laboratory methods for work with plant and soil nematodes. In: Southey JF (ed) Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food Reference Book 402, H.M. Stationery Off., London.
Takáč P, Kozáková Ľ, Vaľková M, Zeleňák F (2008) Ťažké kovy v pôdach stredného Spiša. Acta Montan Slovaca 13:82–86
Valocká B, Sabová M (1997) Structure of soil nematode communities in some regions of Slovakia with different pollution levels. Biológia 52:609–613
van Bezooijen J (2006) Methods and techniques for nematology. Revised version 2006. Wageningen University (publisher), Wageningen
Wasilewska L (1997) Soil invertebrates as bioindicators, with special reference to soil-inhabiting nematodes. Russ J Nematol 5:113–126
Weiss B, Larink O (1991) Influence of sewage sludge and heavy metals on nematodes in arable soil. Biol Fertil Soils 12:5–9
Yeates GW (1994) Modification and qualification of the maturity index. Pedobiologia 38:97–101
Yeates GW, Bird AF (1994) Some observations on the influence of agricultural practices on the nematode faunae of some South Australian soils. Fundam Appl Nematol 17:133–145
Yeates GW, Bongers T (1999) Nematode diversity in agroecosystems. Agric Ecosyst Environ 74:113–135
Yeates GW, Bongers T, de Goede RGM, Freckman DW, Georgieva SS (1993) Feeding habits in nematode families and genera-an outline for soil ecologists. J Nematol 25:315–331
Zeng F, Ali S, Zhang H, Ouyang Y, Qiu B, Wu F, Zhang G (2011) The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environ Pollut 159:84–91
Zhang XK, Li Q, Wang SB, Jiang Y, Liang W (2006) Effect of zinc addition to soil on nematode community structure. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 76:589–594. doi:10.1007/s00128-006-0960-8
Zhang WD, Wang XF, Li Q, Jiang Y, Liang WJ (2007) Soil nematode responses to heavy metal stress. Helminthologia 44:87–91. doi:10.2478/s11687-007-0009-5
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the Slovak Research Development Agency (project LPP-0085-09) (0.6), VEGA (Grant No. 2/0136/10), (0.1) and project “Application Centre to protect humans, animals and plants against parasites” (Code ITMS: 26220220018) based on the support of the Operational Program “Research and Development funded from the European Regional Development Found (0.3). Special thanks are also due to RN Dr. Lívia Farkašová for her kind help with soil samples analysis and Dr. Nicola Sasanelli for valuable advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šalamún, P., Renčo, M., Kucanová, E. et al. Nematodes as bioindicators of soil degradation due to heavy metals. Ecotoxicology 21, 2319–2330 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0988-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0988-y