Abstract
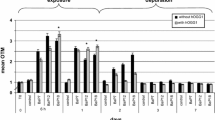
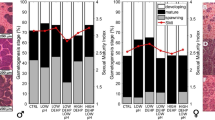
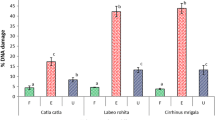
The Comet assay is finding increasing application as a biomarker assay for the genotoxic potential of contaminants in field transplantation experiments involving mussels. Especially in estuaries, habitats that are of particular concern, environmental variables, such as salinity, can vary significantly. Although hinted at in the literature, there is a lack of clarification as to whether changes in salinity or emersion-induced hypoxia have the potential to alter background DNA damage in mussels, thus masking the extent of potential genotoxic effects following exposure to environmental contaminants. The present study exposed Mytilus edulis in the laboratory to static salinities (25, 50, 75, and 100 %) for 72 h. Mussels were also subjected to simulated tidal cycles, including periods of emersion, for 72 h. None of these treatments resulted in a significant change in the level of DNA damage expressed as % tail DNA. These experiments demonstrate that salinity, within the limits of the concentrations tested, and temporary emersion are not confounding factors for Comet assay data derived from M. edulis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Absolom DR (1986) Basic methods for the study of phagocytosis. Methods Enzymol 132:95–182
Akcha F, Tanguy A, Leday G, Pelluhet L, Budzinski H, Chiffoleau JF (2004) Measurement of DNA single-strand breaks in gill and hemolymph cells of mussels, Mytilus sp., collected on the French Atlantic Coast. Mar Environ Res 58:753–756
Baussant T, Bechmann RK, Taban IC, Larsen BK, Tandberg AH, Bjornstad A, Torgrimsen S, Naevdal A, Oysaed KB, Jonsson G, Sanni S (2009) Enzymatic and cellular responses in relation to body burden of PAHs in bivalve molluscs: a case study with chronic levels of North Sea and Barents Sea dispersed oil. Mar Pollut Bull 58:1796–1807
Bellas J, Ekelund R, Halldorsson HP, Berggren M, Granmo A (2007) Monitoring of organic compounds and trace metals during a dredging episode in the Gota Alv Estuary (SW Sweden) using caged mussels. Water Air Soil Pollut 181:265–279
Boisson F, Hartl MGJ, Fowler SW, Amiard-Triquet C (1998) Influence of chronic exposure to silver and mercury in the field on the bioaccumulation potential of the bivalve Macoma balthica. Mar Environ Res 45:325–340
Coughlan BM, Hartl MGJ, O’Reilly SJ, Sheehan D, Morthersill C, van Pelt FNAM, O’Halloran J, O’Brien NM (2002) Detecting genotoxicity using the Comet assay following chronic exposure of Manila clam Tapes semidecussatus to polluted estuarine sediments. Mar Pollut Bull 44:1359–1365
Coughlan BM, Moroney GM, van Pelt FNAM, O’Brien NM, Davenport J, O’Halloran J (2009) The effects of salinity on the Manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) using the neutral red retention assay with adapted physiological saline solutions. Mar Pollut Bull 58:1680–1684
de Zwaan A (1977) Anaerobic energy metabolism on bivalve molluscs. Annu Rev Oceanogr Mar Biol 15:103–187
de Zwaan A, Zandee DI (1972) The utilization of glycogen and accumulation of some intermediates during anaerobiosis in Mytilus edulis L. Comp Biochem Physiol 43B:47–54
Frenzilli G, Nigro M, Lyons BP (2009) The Comet assay for the evaluation of genotoxic impact in aquatic environments. Mutat Res-Rev Mutat Res 681:80–92
Hamer B, Jakcic Z, Pavicic-Hamer D, Peric L, Medakovic D, Ivankovic D, Pavicic J, Zilberberg C, Schroder HC, Muller WEG, Smodlaka N, Batel R (2008) Effect of hypoosmotic stress by low salinity acclimation of Mediterranean mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis on biological parameters used for pollution assessment. Aquat Toxicol 89:137–151
Hartl MGJ, Coughlan BM, Sheehan D, van Pelt FNAM, Mothersill C, Heffron JJA, O’Reilly SJ, O’Halloran J, O’Brien NM (2004) Implications of seasonal priming and reproductive activity on the interpretation of Comet assay data derived from the clam, Tapes semidecussatus Reeves 1864, exposed to contaminated sediments. Mar Environ Res 57:295–310
Hartl MGJ, Kilemade M, Sheehan D, O’Halloran J, O’Brien NM, van Pelt FNAM (2007) Hepatic biomarkers of sediment-associated pollution in juvenile turbot, Scophthalmus maximus L. Mar Environ Res 64:191–208
Hartl MGJ, Grigson S, Sinet E (2010) Maintenance of bivalve haemocytes for the purpose of delayed DNA strand break assessment using the Comet assay. Environ Mol Mutagen 51:64–68
Hines A, Oladiran GS, Bignell JP, Stentiford GD, Viant MR (2007) Direct sampling of organisms from the field and knowledge of their phenotype: key recommendations for environmental metabolomics. Environ Sci Technol 41:3375–3381
Ho KT, Gielazyn ML, Pelletier MC, Burgess RM, Cantwell MC, Perron MM, Serbst JR, Johnson RL (2009) Do toxicity identification and evaluation laboratory-based methods reflect causes of field impairment? Environ Sci Technol 43:6857–6863
Jaksic Z, Batel R, Bihari N, Micic M, Zahn RK (2005) Adriatic coast as a microcosm for global genotoxic marine contamination—A long-term field study. Mar Pollut Bull 50:1314–1327
Jha AN (2008) Ecotoxicological applications and significance of the comet assay. Mutagenesis 23:207–221
Jha AN, Dogra Y, Turner A, Millward GE (2005) Impact of low doses of tritium on the marine mussel, Mytilus edulis: genotoxic effects and tissue-specific bioconcentration. Mutat Res-Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 586:47–57
Kilemade MF, Hartl MGJ, Sheehan D, Mothersill C, van Pelt F, O’Halloran J, O’Brien NM (2004) Genotoxicity of field-collected inter-tidal sediments from Cork Harbor, Ireland, to juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) as measured by the Comet assay. Environ Mol Mutagen 44:56–64
Klobucar GIV, Stambuk A, Hylland K, Pavlica M (2008) Detection of DNA damage in haemocytes of Mytilus galloprovincialis in the coastal ecosystems of Kastela and Trogir bays, Croatia. Sci Total Environ 405:330–337
Large AT, Shaw JP, Peters LD, McIntosh AD, Webster L, Mally A, Chipman JK (2002) Different levels of mussel (Mytilus edulis) DNA strand breaks following chronic field and acute laboratory exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Mar Environ Res 54:493–497
Liepelt A, Karbe L, Westendorf J (1995) Induction of dna strand breaks in rainbow trout oncorhynchus mykiss under hypoxic and hyperoxic conditions. Aquat Toxicol 33:177–181
Lovell DP, Omori T (2008) Statistical issues in the use of the comet assay. Mutagenesis 23:171–183
Mamaca E, Bechmann RK, Torgrimsen S, Aas E, Bjørnstad A, Baussant T, Le Floch S (2005) The neutral red lysosomal retention assay and Comet assay on haemolymph cells from mussels (Mytilus edulis) and fish (Symphodus melops) exposed to styrene. Aquat Toxicol 75:191–201
Møller P, Loft S, Lundby C, Olen NV (2001) Acute hypoxia and hypoxic exercise induce DNA strand breaks and oxidative DNA damage in humans. FASEB J 15:1181–1186
Mustafa SA, Al-Subiai SN, Davies SJ, Jha AN (2011) Hypoxia-induced oxidative DNA damage links with higher level biological effects including specific growth rate in common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Ecotoxicology 20:1455–1466
Nigro M, Falleni A, Del Barga I, Scarcelli V, Lucchesi P, Regoli F, Frenzilli G (2006) Cellular biomarkers for monitoring estuarine environments: transplanted versus native mussels. Aquat Toxicol 77:339–347
Pisanelli B, Benedetti M, Fattorini D, Regoli F (2009) Seasonal and inter-annual variability of DNA integrity in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis: a possible role for natural fluctuations of trace metal concentrations and oxidative biomarkers. Chemosphere 77:1551–1557
Rank J (1999) Use of the comet assay on the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis, from coastal waters in Denmark. Neoplasma 46:9–10
Rank J, Jensen M (2003) Comet assay on gill cells and hemocytes from the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 54:323–329
Rank J, Jensen K, Jespersen PH (2005) Monitoring DNA damage in indigenous blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) sampled from coastal sites in Denmark. Mutat Res-Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 585:33–42
Rank J, Lehtonen KK, Strand J, Laursen M (2007) DNA damage, acetylcholinesterase activity and lysosomal stability in native and transplanted mussels (Mytilus edulis) in areas close to coastal chemical dumping sites in Denmark. Aquat Toxicol 84:50–61
Regoli F, Frenzilli G, Bocchetti R, Annarumma F, Scarcelli V, Fattorini D, Nigro M (2004) Time-course variations of oxyradical metabolism, DNA integrity and lysosomal stability in mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis, during a field translocation experiment. Aquat Toxicol 68:167–178
Richardson BJ, Siu SYM, Lam PKS, Martin M, Caldwell CW (2008) The use of selected genotoxicity assays in green-lipped mussels (Perna viridis): a validation study in Hong Kong coastal waters. Mar Pollut Bull 57:479–492
Rojas E, Lopez MC, Valverde M (1999) Single cell gel electrophoresis assay: methodology and applications. J Chromatogr B722:225–254
Sparks T (2000) Statistics in ecotoxicology ecological & environmental toxicology series. Wiley, Chichester, p 320
Taban IC, Bechmann RK, Torgrimsen S, Baussant T, Sanni S (2004) Detection of DNA damage in mussels and sea urchins exposed to crude oil using comet assay. Mar Environ Res 58:701–705
Tran D, Moody AJ, Fisher AS, Foulkes ME, Jha AN (2007) Protective effects of selenium on mercury-induced DNA damage in mussel haemocytes. Aquat Toxicol 84:11–18
Widdows J (1978) Combined effects of body size, food concentration and season on the physiology of Mytillus edulis. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 58:109–124
Widdows J, Bayne BL, Livingstone DR (1979) Physiological and biochemical responses of bivalve molluscs to exposure to air. Comp Biochem Physiol 62A:301–308
Woods JA, O'Leary KA, McCarthy RP, O'Brien NM (1999) Preservation of comet assay slides: comparison with fresh slides. Mutation Research-Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis 429:181–187
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the laboratory, aquarium and field work support provided by Mrs Margaret Stobie, Mr. Hugh Barras and Mr. Sean McMenamy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R., Hartl, M.G.J. Fluctuating estuarine conditions are not confounding factors for the Comet assay assessment of DNA damage in the mussel Mytilus edulis . Ecotoxicology 21, 1998–2003 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0934-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0934-z