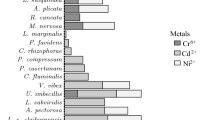
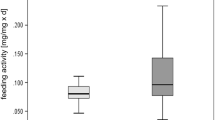
Abstract
Amphipods play an important role in many aquatic ecosystems and are commonly used in ecotoxicology and ecosystem health assessment. Several alien gammarids have been introduced in many regions of the world during the last decades. In this study, we investigated if differences in cadmium sensitivity occurred between (1) different species belonging to the family Gammaridae and (2) different populations of the same species originating from a polluted or a non-polluted site. The acute cadmium toxicity to two indigenous (Gammarus pulex and Gammarus fossarum) and four alien (Dikerogammarus villosus, Echinogammarus berilloni, Gammarus roeseli and Gammarus tigrinus) gammarids occurring in Belgium was tested. Significant differences (P < 0.05) in median lethal concentrations (LC50) were found between the different species, with 72 h-LC50s ranging from 6.3 to 268 μg/l and 96 h-LC50s from 4.7 to 88.9 μg/l. No clear trend in Cd sensitivity was found when comparing indigenous and alien gammarids. D. villosus, an alien invasive species, was the most sensitive to Cd toxicity and E. berilloni, another alien species, the least sensitive. In addition, larger Gammarid species were more sensitive to Cd toxicity than smaller ones. No significant differences were found between populations of the same species originating from metal polluted sites or non-polluted sites. Overall, our results showed that considerable differences in Cd sensitivity exist between gammarid species, which should be taken into consideration in environmental risk assessment and water quality standard setting. Finally, our data suggest that alien gammarids would not have an advantage over indigenous gammarids in Cd contaminated environments.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allendorf FW, Lundquist LL (2003) Introduction: population biology, evolution and control of invasive species. Conserv Biol 17(24):30
Alonso A, Camargo JA (2006) Toxicity of nitrite to three species of freshwater invertebrates. Environ Toxicol 21:90–94
Alonso A, De Lange HJ, Peeters ETHM (2010) Contrasting sensitivities to toxicants of the freshwater amphipods Gammarus pulex and G. fossarum. Ecotoxicology 19:133–140
Annabi A, Messaoudi I, Kerkeni A, Said K (2009) Comparative study of the sensitivity to cadmium of two populations of Gambusia affinis from two different sites. Environ Monit Assess 155:459–465
Barata C, Baird DJ, Soares AMVM (2002) Determining genetic variability in the distribution of sensitivities of toxic stress among and within field populations of Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 36:3045–3049
Boets P, Lock K, Goethals PLM (2010) Combining data-driven methods and lab studies to analyse the ecology of Dikerogammarus villosus. Ecol Inf 5:133–139
Boets P, Lock K, Goethals PLM (2011a) Alterations in the gammarid (Amphipoda) fauna in brackish polder waters of Flanders (Belgium). J Crus Biol 31:270–277
Boets P, Lock K, Goethals PLM (2011b) Using long-term monitoring to investigate the changes in species composition in the harbour of Ghent (Belgium). Hydrobiologia 663:155–166
Bollache L, Devin S, Wattier R, Chovet M, Beisel JN, Moreteau JC, Rigaud T (2004) Rapid range extension of the Ponto-Caspian amphipod Dikerogammarus villosus in France: potential consequences. Arch Hydrobiol 160:57–66
Bossuyt BTA, Janssen CR (2005) Copper toxicity to different field-collected cladoceran species: intra- and inter-species sensitivity. Environ Poll 136:145–154
Chaumot A, Gos P, Garric J, Geffard O (2009) Additive vs non-additive genetic components in lethal cadmium tolerance of Gammarus (Crustacea): novel light on the assessment of the potential for adaptation to contamination. Aquat Toxicol 94:294–299
Clements WH (1999) Metal tolerance and predator–prey interactions in benthic macroinvertebrate stream communities. Ecol Appl 9:1073–1084
Conover WJ (1980) Practical non-parametric statistics. Wiley, New York
Dick JTA, Platvoet D (1996) Intraguild predation and species exclusions in amphipods: the interaction of behaviour, physiology and environment. Freshw Biol 36:375–383
Dlugosch KM, Parker IM (2008) Founding events in species invasions: genetic variation, adaptive evolution, and the role of multiple introductions. Mol Ecol 17:431–449
Elliot JM (2005) Day–night changes in the spatial distribution and habitat preferences of freshwater shrimps, Gammarus pulex, in a stony stream. Freshw Biol 50:552–566
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2002) Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms, 5th edn. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Wahington, DC
European Chemicals Bureau (2007) European Union risk assessment on cadmium metal/cadmium oxide. ECB, Ispra
Felten V, Charmantier G, Mons R, Geffard A, Rouselle P, Coquery M, Garric J, Geffard O (2008) Physiological and behavioural responses of Gammarus pulex (Crustacea: Amphipoda) exposed to cadmium. Aquat Toxicol 86:413–425
Gabriels W, Lock K, de Pauw N, Goethals PLM (2010) Multimetric Macroinvertebrate Index Flanders (MMIF) for biological assessment of rivers and lakes in Flanders (Belgium). Limnologica 40:199–207
Gonzalo C, Camargo JA, Masiero L, Casellato S (2010) Fluoride toxicity and bioaccumulation in the invasive amphipod Dikerogammarus villosus (Sowinsky, 1894): a laboratory study. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85:472–475
Grabowski M, Bacela K, Konopacka A (2007) How to be an invasive gammarid (Amphipoda: Gammaroidea)—comparison of life history traits. Hydrobiologia 590:75–84
Grosell M, Nielsen C, Bianchini A (2002) Sodium turnover rate determines sensitivity to acute copper and silver exposure in freshwater animals. Comp Biochem Physiol C 133:287–303
Hamilton MA, Russo RC, Thurston RV (1977) Trimmed Spearman-Karber method for estimating median lethal concentrations in toxicity bioassays. Environ Sci Technol 11:714–719
Hering D, Borja A, Carstensen J, Carvalho L, Elliott M, Feld CK, Heiskanen AS, Johnson RK, Moe J, Pont D, Solheim AL, van de Bund W (2010) The European Water Framework Directive at the age of 10: a critical review of the achievements with recommendations for the future. Sci Total Environ 408:4007–4019
Howell R (1985) Effect of Zinc on cadmium toxicity to the Amphipod Gammarus pulex. Hydrobiologia 123:245–249
Jazdzewski K (1980) Range extensions of some gammaridean species in European inland waters caused by human activity. Crustaceana Suppl 6:84–107
Josens G, Bij de Vaate A, Usseglio-Polatera P, Cammaerts R, Cherot F, Grisez F, Verboonen P, Vanden Bossche JP (2005) Native and exotic Amphipoda and other Peracarida in the River Meuse: new assemblages emerge from a fast changing fauna. Hydrobiologia 542:203–220
Karaman G, Pinkster S (1977) Freshwater Gammarus species from Europe, North Africa and adjacent regions of Asia (Crustacea, Amphipoda). I. Gammarus pulex group and related species. Bijdr Dierk 47:1–97
Klerks PL, Weis SJ (1987) Genetic adaptation to heavy metals in aquatic organisms: a review. Environ Pollut 45:173–205
Kunz PY, Kienle C, Gerhardt A (2010) Gammarus spp. in aquatic ecotoxicology and water quality assessment: toward integrated multilevel tests. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 205:1–76
Lock K, Janssens F, Janssen CR (2003) Effects of metal contamination on the activity and diversity of springtails in an ancient Pb-Zn mining area at Plombières, Belgium. Eur J Soil Biol 39:25–29
Maazouzi C, Masson G, Izquierdo MS, Pihan JC (2008) Chronic copper exposure and fatty acid composition of the amphipod Dikerogammarus villosus: results from a field study. Environ Pollut 156:221–226
MacNeil C, Dick JTA, Elwood RW (1997) The trophic ecology of freshwater Gammarus spp. (Crustacea: Amphipoda): concepts and perspectives concerning the functional feeding group concept. Biol Revisions 72:349–364
MacNeil C, Elwood RW, Dick JTA (2000) Factors influencing the importance of Gammarus spp. (Crustacea: Amphipoda) in riverine salmonid diets. Arch Hydrobiol 149:87–107
MacNeil C, Platvoet D, Dick JTA, Fielding NJ, Constable A, Hall N, Aldrige D, Renals T, Diamond M (2010) The Ponto-Caspian ‘killer shrimp’, Dikerogammarus villosus (Sowinsky, 1894), invades the British Isles. Aquat Invasions 5:441–445
Martin TR, Holdich DM (1986) The acute lethal toxicity of heavy metals to peracarid crustaceans (with particular reference to freshwater asellids and gammarids). Water Res 20:1137–1147
Martinez M, DelRamo J, Torreblanca A, Pastor A, DiazMayans J (1996) Cadmium toxicity, accumulation and metallothionein induction in Echinogammarus echinosetosus. J Environ Sci Health A 31:1605–1617
McCahon CP, Pascoe D (1988a) Use of Gammarus pulex (L.) in safety evaluation tests: culture and selection of a sensitive life stage. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 15:245–252
McCahon CP, Pascoe D (1988b) Cadmium toxicity to the freshwater amphipod Gammarus pulex (L.) during the moult cycle. Freshw Biol 19:197–203
McCahon CP, Pascoe D (1988c) Increased sensitivity to cadmium of the freshwater amphipod Gammarus pulex (L.) during the reproductive period. Aquat Toxicol 13:183–194
Messiaen M, Lock K, Gabriels W, Vercauteren T, Wouters K, Boets P, Goethals PLM (2010) Alien macrocrustaceans in freshwater ecosystems in the eastern part of Flanders (Belgium). Belgian J Zool 140:30–39
MIRA Environment report (2010) www.environmentflanders.be
Muller JC, Schramm S, Seitz A (2002) Genetic and morphological differentiation of Dikerogammarus invaders and their invasion history in Central Europe. Freshw Biol 47:2039–2048
Muyssen BTA, Janssen CR, Bossuyt BTA (2002) Tolerance and acclimation to zinc of field-collected Daphnia magna populations. Aquat Toxicol 56:69–79
Nowak C, Jost D, Vogt C, Oetken M, Schwenk K, Oehlman J (2007) Consequences of inbreeding and reduced genetic variation on tolerance to cadmium stress in the midge Chironomus riparius. Aquat Toxicol 85:278–285
Peeters ETHM, Gardeniers JJP (1998) Logistic regression as a tool for defining habitat requirements of two common gammarids. Freshw Biol 39:605–615
Pestana JLT, Re A, Nogueira AJA, Soares AMVM (2007) Effects of Cadmium and Zinc on the feeding behaviour of two freshwater crustaceans: Atyaephyra desmarestii (Decapoda) and Echinogammarus meridionalis (Amphipoda). Chemosphere 8:1556–1562
Roast SD, Widdows J, Jones MB (2001) Effects of salinity and chemical speciation on cadmium accumulation and toxicity to two mysid species. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1078–1084
Simberloff D, Parker IM, Windle PN (2005) Introduced species policy, management, and future research needs. Front Ecol Environ 3:12–20
Sornom P, Felten V, Médoc V, Sroda S, Rousselle P, Beisel J-N (2010) Effect of gender on physiological and behavioural responses of Gammarus roeseli (Crustacea Amphipoda) to salinity and temperature. Environ Poll 158:1288–1295
Sroda S, Cossu-Leguille C (2011) Effects of sublethal copper exposure on two gammarid species: which is the best competitor? Ecotoxicology 20:264–273
StatSoft Inc (2004) STATISTICA (data analysis software system), version 7. www.statsoft.com
Statzner B, Bonada N, Dolédec S (2008) Biological attributes discriminating invasive from native European stream macroinvertebrates. Biol Invasions 10:517–530
Stuhlbacher A, Maltby L (1992) Cadmium resistance in Gammarus pulex (L.). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 22:319–324
Tan QG, Wang WX (2011) Acute Toxicity of Cadmium in Daphnia magna under different calcium and pH conditions: importance of influx rate. Environ Sci Technol 45:1970–1976
Templeton AR (2006) Population genetics and microevolutionary theory. Wiley, New York
United States Geological Survey (USGS) (2006) Cadmium risks to freshwater life: derivation and validation of low-effect criteria values using laboratory and field studies. Scientific investigations report 2006-5245
van der Velde G, Rajagopal S, Kelleher B, Muskó I, Bij de Vaate A (2000) Ecological impact of crustacean invaders: general considerations and examples from the River Rhine. In: von Vaupel Klein JK, Scram FR (eds) The biodiversity crisis and crustacea: proceedings of the fourth international crustacean congress. AA Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 35–46
VMM Flemish Environment Agency (2010) Geoloket water quality. http://www.vmm.be/geoview/
Ward TJ, Robinson WE (2005) Evolution of cadmium resistance in Daphnia magna. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2341–2349
Wheeler MW, Park RM, Bailer AJ (2006) Comparing median lethal concentration values using confidence interval overlap or ratio tests. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:1441–1444
Williams KA, Green WJ, Pascoe D (1985) Studies on the acute toxicity of pollutants to freshwater macroinvertebrates. 1. Cadmium. Arch Hydrobiol 102:461–471
Wouters K (2002) On the distribution of alien non-marine and estuarine macro-crustaceans in Belgium. RBINS 72:119–129
Wright DA, Frain JW (1981) The effect of calcium on cadmium toxicity in the Freshwater Amphipod, Gammarus pulex (L.). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 10:321–328
Acknowledgments
Koen Lock was supported by a post-doctoral fellowship from the Fund for Scientific Research (FWO-Vlaanderen, Belgium). This study was also funded by BOF09/24J/092.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boets, P., Lock, K., Goethals, P.L.M. et al. A comparison of the short-term toxicity of cadmium to indigenous and alien gammarid species. Ecotoxicology 21, 1135–1144 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0868-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0868-5