Abstract
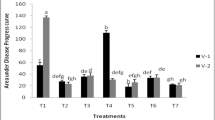
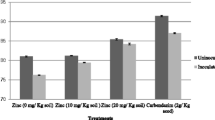
The use of irrigation water containing cyanobacterial toxins may generate a negative impact in both yield and quality of agricultural crops causing significant economic losses. We evaluated the effects of microcystins (MC) on the growth, nodulation process and nitrogen uptake of a Faba bean cultivar (Vicia faba L., Fabaceae), particularly the effect of MC on rhizobia-V. faba symbiosis. Three rhizobial strains (RhOF4, RhOF6 and RhOF21), isolated from nodules of local V. faba were tested. The exposure of rhizobia to MC showed that the toxins had a negative effect on the rhizobial growth especially at the highest concentrations of 50 and 100 μg/l. The germination of faba bean seeds was also affected by cyanotoxins. We registered germination rates of 75 and 68.75% at the toxin levels of 50 and 100 μg/l as compared to the control (100%). The obtained results also showed there was a negative effect of MC on plants shoot, root (dry weight) and total number of nodules per plant. Cyanotoxins exposure induced a significant effect on nitrogen assimilation by faba bean seedlings inoculated with selected rhizobial strains RhOF6 and RhOF21, while the effect was not significant on beans seedling inoculated with RhOF4. This behavior of tolerant rhizobia-legumes symbioses may constitute a very important pathway to increase soil fertility and quality and can represent a friendly biotechnological way to remediate cyanotoxins contamination in agriculture.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelly C, Krouma A, Drevon JJ (2005) Nitrogen fixation and yield of Chickpea in saline Mediterranean zones. Grain legumes 42:16–17
Asada K (1992) Ascorbate peroxidise: a hydrogen peroxide scavenging enzyme in plants. Physiol Plant 85:235–241
Chen J, Song L, Dai J, Gan N, Liu Z (2004) Effects of microcystins on the growth and the activity of superoxide dismutase and peroxidase of Rape (Brassica napus L.) and Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Toxicon 43:393–400
Cordovilla MP, Ligero F, Lluch C (1994) The effect of salinity on N fixation and assimilation in Vicia faba. J Exp Bot 45:1483–1488
Crush JR, Briggs LR, Sprosen JM, Nichols SN (2008) Effect of irrigation with lake water containing microcystins on microcystin content and growth of ryegrass, clover, rape, and lettuce. Environ Toxicol 23:246–252
Delgado MJ, Ligero F, Lluch C (1993) Effects of salt stress on growth and N2 fixation by pea, faba bean, common bean, and soybean plants. Soil Biol Biochem 26:371–376
Dixon RA, Al-Nazawi M, Alderson G (2004) Permeabilising effects of sub-inhibitory concentrations of microcystin on the growth of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 230:167–170
Dulormne M, Musseau O, Muller F, Toribio A, Bâ A (2010) Effects of NaCl on growth, water status, N2 fixation, and ion distribution in Pterocarpus officinalis seedlings. Plant Soil 327:23–34
El Khalloufi F, Oufdou K, Lahrouni M, El Ghazali I, Saqrane S, Vasconcelos V, Oudra B (2011) Allelopatic effects of cyanobacteria extracts containing microcystins on Medicago sativa-rhizobia symbiosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:431–438
Garg N, Singla R (2004) Growth, photosynthesis, nodule nitrogen and carbon fixation in the chickpea cultivars under salt stress. Braz J Plant Physiol 16:137–146
Haider S, Naithani V, Viswanathan PN, Kakkar P (2003) Cyanobacterial toxins: a growing environmental concern. Chemosphere 52:1–21
Hunt S, Layzell DB (1993) Gas exchange of legume nodules and the regulation of nitrogenase activity. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Mol Biol 44:483–511
Khan HR, Paull JG, Siddique KHM, Stoddard FL (2010) Faba bean breeding for drought-affected environments: a physiological and agronomic perspective. Field Crops Res 115:279–286
Ko′s P, Gorzo G, Suranyi G, Borbely G (1995) Simple and efficient method for isolation and measurement of cyanobacterial hepatotoxins by plant tests (Sinapis alba L.). Anal Biochem 225:49–53
Krouma A (2009) Physiological and nutritional response of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) to salinity. Turk J Agric 33:503–512
Kurki-Helasmo K, Meriluoto J (1998) Microcystin uptake inhibits growth and protein phosphatase activity in Mustard (Sinapis alba L.) seedlings. Toxicon 36:1921–1926
McElhiney J, Lawton LA, Leifert C (2001) Investigations into the inhibitory effects of microcystins on plant growth, and the toxicity of plant tissues following exposure. Toxicon 39:1411–1420
Oudra B, Loudiki M, Sbiyyaa B, Martins R, Vasconcelos V, Namikoshi M (2001) Isolation, characterization and quantification of microcystins (heptapeptides hepatotoxins) in Microcystis aeruginosa dominated bloom of Lalla Takerkoust lake reservoir (Morocco). Toxicon 39:1375–1381
Oudra B, Loudiki M, Sbiyyaa B, Sabour B, Amorim A, Martins R, Vasconcelos V (2002) Detection and variation of microcystin contents of Microcystis blooms in eutrophic Lalla Takerkoust Lake (Morocco). Lakes Reservoirs Res Manag 7:35–44
Peuthert A, Chakrabarti S, Pflugmacher S (2007) Uptake of microcystins-LR and–LF (cyanobacterial toxins) in seedlings of several important agricultural plant species and the correlation with cellular damage (lipid peroxidation). Environ Toxicol 22:436–442
Pflugmacher S (2002) Possible allelopathic effects of cyanotoxins, with reference to microcystin-LR, in aquatic ecosystems. Environ Toxicol 17:407–413
Pflugmacher S, Jung K, Lundvall L, Neumann S, Peuthert A (2006) Effects of cyanobacterial toxins and cyanobacterial cell-free crude extract on germination of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and induction of oxidative stress. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2381–2387
Polle A (2001) Dissecting the superoxide dismutase-ascorbate-glutathionepathway in chloroplasts by metabolic modelling. Computer simulations as a step towards flux analysis. Plant Physiol 126:445–462
Sadiki M, Rabih K (2001) Selection of chickpea (Cicer arietinum) for yield and symbiotic nitrogen fixation ability under salt stress. Agronomy 21:659–666
Saqrane S, Oudra B (2009) CyanoHAB occurrence and water irrigation cyanotoxin contamination: ecological impacts and potential health risks. Toxins 1:113–122
Saqrane S, El ghazali I, Ouahid Y, El hassani M, El Hadrami I, Oudra B, Bouarab L, Del Campo FF, Vasconnelos V (2007) Phytotoxic effects of cyanobacteria extract on the aquatic plant Lemna gibba: microcystin accumulation, detoxication and oxidative stress induction. Aquat Toxicol 83:284–294
Saqrane S, El Ghazali I, Oudra B, Bouarab L, Vasconcelos V (2008) Effects of cyanobacteria producing microcystins on seed germination and seedling growth of several agricultural plants. J Environ Sci Health B 43:443–451
Saqrane S, Ouahid Y, El Ghazali I, Oudra B, Bouarab L, del Campo FF (2009) Physiological changes in Triticum durum, Zea mays, Pisum sativum and Lens esculenta Cultivars, caused by irrigation with water contaminated with microcystins: a laboratory experimental approach. Toxicon 53:786–796
Sheokand S, Dhandi S (1995) Studies on nodule functioning and hydrogen peroxide scavenging enzymes under salt stress in chickpea nodules. Plant Physiol 33:561–566
Singleton PW (1983) Asplit-root growth system for evaluating the effect of salinity on the components of the soybean Rhizobium japonicum symbiosis. Crop Sci 23:259–262
Sivonen K, Jones G (1999) Cyanobacterial toxins. In: Toxic cyanobacteria in water: a guide to public health significance, monitoring, management. In: Chorus I, Bertram J (eds) The world health organization. ISBN 0–419–23930–8. E & FN Spon, London, pp 41–111
Tejera NA, Soussi M, Lluch C (2006) Physiological and nutritional indicators of tolerance to salinity in chickpea plants growing under symbiotic conditions. Environ Exp Bot 58:17–24
Valdor R, Aboal M (2007) Effects of living cyanobacteria, cyanobacterial extracts and pure microcystins on growth and ultrastructure of microalgae and bacteria. Toxicon 49:769–779
Vassilakaki M, Pflugmacher S (2007) Oxidative stress response of Synechocystis sp. (PCC 6803) due to exposure to microcystin-LR and cell-free cyanobacterial crude extract containing microcystin-LR. J Appl Phycol 20:219–225
Velagaleti RR, Marsh S (1989) Influence of host cultivars and Bradyrhizobium strain on the growth and symbiotic performance of soybean under salt stress. Plant Soil 119:133–138
Vincent JM (1970) The cultivation, isolation and maintenance of rhizobia. In: Vincent JM (ed) A manual for the practical study of root-nodule. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 1–13
Zahran HH (1991) Conditions for successful Rhizobium legume symbiosis in saline environments. Biol Fertil Soils 12:73–80
Zahran HH (2001) Rhizobia from wild legumes: diversity, taxonomy, ecology, nitrogen fixation and biotechnology. J Biotechnol 91:143–153
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the International Foundation for Sciences (ifs project No F/2826-3F). This work is also carried out within the framework of the cooperation Morocco–Portuguese collaboration (convention of cooperation CNRST-Morocco/GRICES or FCT-Portugal; Prof. Brahim Oudra/Prof. V. M. Vasconcelos) and the Morocco–Spanish collaboration (AECID projects n°A/018163/08 and n°A/025374/09; Prof. Khalid Oufdou/Prof. Alvaro Peix). Authors thank F. F. Del Campo and Y. Ouahid from the UAM-Spain for help and HPLC technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lahrouni, M., Oufdou, K., Faghire, M. et al. Cyanobacterial extracts containing microcystins affect the growth, nodulation process and nitrogen uptake of faba bean (Vicia faba L., Fabaceae). Ecotoxicology 21, 681–687 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0826-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0826-7