Abstract
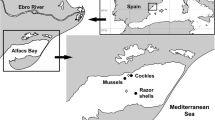
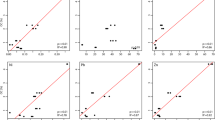
Common cockles (Cerastoderma edule, L. 1758, Bivalvia: Cardiidae) were subjected to a laboratory assay with sediments collected from distinct sites of the Sado Estuary (Portugal). Cockles were obtained from a mariculture site of the Sado Estuary and exposed through 28-day, semi-static, assays to sediments collected from three sites of the estuary. Sediments from these sites revealed different physico-chemical properties and levels of metals and organic contaminants, ranging from unimpacted (the reference site) to moderately impacted, when compared to available sediment quality guidelines. Cockles were surveyed for bioaccumulation of trace elements (Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd and Pb) and organic contaminants (PAHs, PCBs and DDTs). Two sets of potential biomarkers were employed to assess toxicity: whole-body metallothionein (MT) induction and digestive gland histopathology. The bioaccumulation factor and the biota-to-soil accumulation factor were estimated as ecological indices of exposure to metals and organic compounds. From the results it is inferred that C. edule responds to sediment-bound contamination and might, therefore, be suitable for biomonitoring. The species was found capable to regulate and eliminate both types of contaminants. Still, the sediment contamination levels do not account for all the variation in bioaccumulation and MT levels, which may result from the moderate metal concentrations found in sediments, the species’ intrinsic resistance to pollution and from yet unexplained xenobiotic interaction effects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiard J-C, Amiard-Triquet C, Barka S, Pellerin J, Rainbow PS (2006) Metallothioneins in aquatic invertebrates: their role in metal detoxification and their use as biomarkers. Aquat Toxicol 76:160–202
Baudrimont M, de Montaudouin X, Palvadeau A (2006) Impact of digenean parasite infection on metallothionein synthesis by the cockle (Cerastoderma edule): a multivariate field monitoring. Mar Pollut Bull 52:494–502
Bergayou H, Mouneyrac C, Pellerin J, Moukrim A (2009) Oxidative stress responses in bivalves (Scrobicularia plana, Cerastoderma edule) from the Oued Souss estuary (Morocco). Ecotox Environ Safe 72:765–769
Bigot A, Doyen P, Vasseur P, Rodius F (2009) Metallothionein coding sequence identification and seasonal mRNA expression of detoxification genes in the bivalve Corbicula fluminea. Ecotox Environ Safe 72:382–387
Buico A, Cassino C, Dondero F, Vergani L, Osella D (2008) Radical scavenging metallothionein isoforms: an ESR study. J Inorg Biochem 102:921–927
Caeiro S, Costa MH, Ramos TB, Fernandes F, Silveira N, Coimbra A, Medeiros G, Painho M (2005) Assessing heavy metal contamination in Sado Estuary sediment: an index analysis approach. Ecol Indic 5:151–169
Caetano M, Fonseca N, Cesário R, Vale C (2007) Mobility of Pb in salt marshes recorded by total content and stable isotopic signature. Sci Total Environ 380:84–92
Cajaraville MP, Bebianno MJ, Blasco J, Porte C, Sarasquete C, Viarengo A (2000) The use of biomarkers to assess the impact of pollution in coastal environments of the Iberian Peninsula: a practical approach. Sci Total Environ 247:295–311
Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (1999) Standard methods for examination of water & wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Baltimore
Cortesão C, Vale C (1995) Metals in sediments of the Sado Estuary, Portugal. Mar Pollut Bull 30:34–37
Costa PM, Repolho T, Caeiro S, Diniz ME, Moura I, Costa MH (2008) Modelling metallothionein induction in the liver of Sparus aurata exposed to metal-contaminated estuarine sediments. Ecotox Environ Safe 71:117–124
Costa PM, Santos HM, Peres I, Costa MH, Alves S, Capelo-Martinez JL, Diniz MS (2009) Toxicokinetics of waterborne trivalent arsenic in the freshwater bivalve Corbicula fluminea. Arch Environ Con Tox 57:338–347
De Kock WC, Kramer KJM (1994) Active biomonitoring (ABM) by translocation of bivalve molluscs. In: Kramer KJM (ed) Biomonitoring of coastal waters and estuaries. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 51–84
Del Valls TA, Forja JM, Gómez-Parra A (1998) The use of multivariate analysis to link sediment contamination and toxicity data to establish sediment quality guidelines: an example in the Gulf of Cádiz (Spain). Cienc Mar 24:127–154
Diniz M, Santos HM, Costa PM, Peres I, Costa MH, Capelo JL (2007) Metallothionein responses in the Asiatic clam (Corbicula fluminea) after exposure to trivalent arsenic. Biomarkers 12:589–598
Du Laing G, Rinklebe J, Vandecasteele B, Meers E, Tack FMG (2009) Trace metal behaviour in estuarine and riverine floodplain soils and sediments: a review. Sci Total Environ 407:3972–3985
Eggleton J, Thomas KV (2004) A review of factors affecting the release and bioavailability of contaminants during sediment disturbance events. Environ Int 30:973–980
Ferreira AM, Martins M, Vale C (2003) Influence of diffuse sources on levels and distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls in the Guadiana River estuary, Portugal. Mar Chem 89:175–184
Geret F, Serafim A, Bebianno MJ (2003) Antioxidant enzyme activities, metallothioneins and lipid peroxidation as biomarkers in Ruditapes decussatus. Ecotoxicology 12:417–426
Gold-Bouchot G, Simá-Alvarez R, Zapata-Pérez O, Guemez-Ricalde J (1995) Histopathological effects of petroleum hydrocarbons and heavy metals on the American oyster (Crassostrea virginica) from Tabasco, México. Mar Pollut Bull 31:4–12
Hédouin L, Pringault O, Metian M, Bustamante P, Warnau M (2007) Nickel bioaccumulation in bivalves from the New Caledonia lagoon: seawater and food exposure. Chemosphere 66:1449–1457
Huggett RJ, Kimerle RA, Mehrle PM, Bergman HL (eds) (1992) Biomarkers: biochemical, physiological, and histological markers of anthropogenic stress. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL
Jantunen APK, Tuikka A, Akkanen J, Kukkonen JVK (2008) Bioaccumulation of atrazine and chlorpyrifos to Lumbriculus variegatus from lake sediments. Ecotox Environ Safe 71:860–868
Jung K, Stelzenmüller V, Zauke G-P (2006) Spatial distribution of heavy metal concentrations and biomass indices in Cerastoderma edule Linnaeus (1758) from the German Wadden Sea: an integrated biomonitoring approach. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 338:81–95
Lee H (1992) Models, muddles, and mud: predicting bioaccumulation of sediment associated pollutants. In: Burton AG (ed) Sediment toxicity assessment. CRC, Boca Raton, FL, pp 267–293
Livingstone DR (2001) Contaminant-stimulated reactive oxygen species production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms. Mar Pollut Bull 42(8):656–666
Long ER, MacDonald DD (1998) Recommended uses of empirically derived, sediment quality guidelines for marine and estuarine ecosystems. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 4:1019–1039
Luoma S, Rainbow P (2005) Why is metal bioaccumulation so variable? Biodynamics as a unifying concept. Environ Sci Technol 39:1921–1931
MacDonald DD, Carr S, Calder F, Long E, Ingersoll C (1996) Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology 5:253–278
MacDonald DD, Carr RS, Eckenrod D, Greening H, Grabe S, Ingersoll CG, Janicki S, Janicki T, Lindskoog RA, Long ER, Pribble R, Sloane G, Smorong DE (2004) Development, evaluation, and application of sediment quality targets for assessing and managing contaminated sediments in Tampa Bay, Florida. Arch Environ Cont Tox 46:147–161
Machreki-Ajmi M, Ketata I, Ladhar-Chaabouni R, Hamza-Chaffai A (2008) The effect of in situ cadmium contamination on some biomarkers in Cerastoderma glaucum. Ecotoxicology 17:1–11
Marie V, Baudrimont M, Boudou A (2006) Cadmium and zinc bioaccumulation and metallothionein response in two freshwater bivalves (Corbicula fluminea and Dreissena polymorpha) transplanted along a polymetallic gradient. Chemosphere 65:609–617
Martins M, Ferreira AM, Vale C (2008) The influence of Sarcocornia fruticosa on retention of PAHs in salt marshes sediments (Sado estuary, Portugal). Chemosphere 71:1599–1606
Martoja R, Martoja M (1967) Initiation aux tecniques de l’histologie animal. Masson & Cie, Paris, p 345
Peakall DB, Shugart LR (eds) (1993) Biomarkers research and application in the assessment of environmental health. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg
Risso-de Faverney C, Lafaurie M, Girard J-P, Rahmani R (2000) Effects of heavy metals and 3-methylcholanthrene on expression and induction of CYP1A1 and metallothionein levels in trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatocyte cultures. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2239–2248
Serafim A, Bebianno MJ (2009) Metallothionein role in the kinetic model of copper accumulation and elimination in the clam Ruditapes decussates. Environ Res 109:390–399
Solé M, Kopecka-Pilarczyk J, Blasco J (2009) Pollution biomarkers in two estuarine invertebrates, Nereis diversicolor and Scrobicularia plana, from a Marsh ecosystem in SW Spain. Environ Int 35:523–531
Syasina IG, Vaschenko MA, Zhadan PM (1997) Morphological alterations in the digestive diverticula of Mizuhopecten yessoensis (Bivalvia: Pectinidae) from polluted areas of Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan. Mar Environ Res 44:85–98
Thorsson MH, Hedman JE, Bradshaw C, Gunnarsson JS, Gilek M (2008) Effects of settling organic matter on the bioaccumulation of cadmium and BDE-99 by Baltic Sea benthic invertebrates. Mar Environ Res 65:264–281
United States Environmental Protection Agency (1995) CRITFC exposure study. Water quality criteria and standards Newsletter. USEPA, Washington, DC
Zaldibar B, Cancio I, Soto M, Marigómez I (2007) Digestive cell turnover in digestive gland epithelium of slugs experimentally exposed to a mixture of cadmium and kerosene. Chemosphere 70:144–154
Zaldibar B, Cancio I, Soto M, Marigómez I (2008) Changes in cell-type composition in digestive gland of slugs and its influence in biomarkers following transplantation between a relatively unpolluted and a chronically metal-polluted site. Environ Pollut 156:367–379
Acknowledgments
The present research was approved by the Portuguese Science and Technology Foundation (FCT) and POCTI (Programa Operacional Ciência, Tecnologia e Inovação, research project ref. POCTI/AMB 57281/104) and financed by FEDER (European Fund for Regional Development). The authors would also like to thank APSS (Administração dos Portos de Setúbal e Sesimbra, SA) and RNES (Reserva Natural do Estuário do Sado) for the logistic support and Mr Manuel Ribeiro for the offer of the cockles.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lobo, J., Costa, P.M., Caeiro, S. et al. Evaluation of the potential of the common cockle (Cerastoderma edule L.) for the ecological risk assessment of estuarine sediments: bioaccumulation and biomarkers. Ecotoxicology 19, 1496–1512 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0535-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0535-7