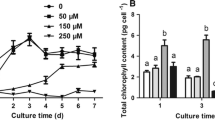
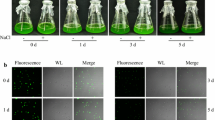
Abstract
Investigation of mercury toxicology in green algae is of great importance from ecological point of view, because mercury has become a major contaminant in recent years. In higher plants, accumulation of mercury modifies many aspects of cellular functions. However, the process that mercury exerts detrimental effects on green algae is largely unknown. In this study, we performed an experiment focusing on the biological responses of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, a unicellular model organism, to Hg2+-induced toxicity. C. reinhardtii was exposed to 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 μM Hg in media. Concentrations of Hg were negatively correlated with the cell growth. Treatment with Hg induced accumulation of reactive oxygen species and peroxidative products. Endogenous proline levels increased in Hg-exposed algae. Hg exposure activated superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and ascorbate peroxidase (APX). To get insights into the molecular response, a RT-PCR-based assay was performed to analyze the transcript abundance of Mn-SOD, CAT and APX. Our analysis revealed that expression of the genes was up-regulated by Hg exposure, with a pattern similar to the enzyme activities. Additional investigation was undertaken on the effect of Hg on the transcript amount of ∆1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase, a key enzyme of proline biosynthesis and on that of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), an enzyme regulating heavy metal tolerance. Expressions of both P5CS and HO-1 were up-regulated by Hg. These data indicate that Hg-induced oxidative stress was responsible for the disturbance of the growth and antioxidant defensive systems in C. reinhardtii.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Alia MP, Matysik J (2001) Effect of proline on the production of singlet oxygen. Amino Acids 21:191–203
Alscher RG, Erturk N, Heath LS (2002) Role of superoxide dismutases (SODs) in controlling oxidative stress in plants. J Exp Bot 53:1331–1341
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplast: polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Tear ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Beauchamp CH, Fridovixh I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287
Boening DW (2000) Ecological effects, transport and fate of mercury: a general review. Chemosphere 40:1335–1351
Cargnelutti D, Tabaldi LA, Spanevello RM, Jucoski GO, Battisti V, Redin M, Linares CEB, Dressler VL, Flores MM, Nicoloso FT, Morsch VM, Schetinger MRC (2006) Mercury toxicity induces oxidative stress in growing cucumber seedlings. Chemosphere 65:999–1006
Chen J, Shiyab S, Han FX, Monts DL, Waggoner CA, Yang ZM, Su Y (2009a) Bioaccumulation and physiological effects of mercury in Pteris vittata and Nephrolepis exaltata. Ecotoxicology 18:110–121
Chen J, Yang ZM, Su Y, Han FX, Monts DL (2009b) Phytoremediation of heavy metal/metalloid-contaminated soils. In: Steinberg RV (ed) Contaminated soils: environmental impact, disposal and treatment. Nova Science Publishers, Inc., NY
Cho UH, Park JO (2000) Mercury-induced oxidative stress in tomato seedlings. Plant Sci 156:1–9
Clemens S (2006) Toxic metal accumulation, responses to exposure and mechanisms of tolerance in plants. Biochimie 88:1707–1719
Cuyers A, Vangronsveld J, Clijsters H (2000) Biphasic effect of copper on the ascorbate-glutathione pathway in primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris seedlings during the early stages of metal assimilation. Physiol Plant 110:512–517
del Río LA, Sandalio LM, Corpas FJ, Palma JM, Barroso JB (2006) Reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species in peroxisomes, production, scavenging, and role in cell signaling. Plant Physiol 141:330–335
Dennis IF, Clair TA, Driscoll CT, Kamman N, Chalmers A, Shanley J, Norton SA, Kahl S (2005) Distribution patterns of mercury in lakes and rivers of northeastern North America. Ecotoxicology 14:113–123
Domínguez-Solís JR, López-Martín MC, Ager FJ, Ynsa MD, Romero LC, Gotor C (2004) Increased cysteine availability is essential for cadmium tolerance and accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Biotechnol J 2:469–476
Evers DC, Savoy LJ, DeSorbo CR, Yates DE, Hanson W, Taylor KM, Siegel LS, Cooley JC Jr, Bank MS, Major A, Munney K, Mower BF, Vogel HS, Schoch N, Pokras M, Goodale MW, Fair J (2008) Adverse effects from environmental mercury loads on breeding common loons. Ecotoxicology 17:69–81
Godbold DL (1991) Mercury-induced root damage in spruce seedlings. Water Air Soil Pollut 56:823–831
Han FX, Banin A, Su Y, Monts DL, Plodinec MJ, Kingery WL, Triplett GB (2002) Industrial age anthropogenic inputs of heavy metals into the pedosphere. Naturwissenschaften 89:497–504
Han FX, Su Y, Monts DL, Waggoner AC, Plodinec JM (2006) Binding, distribution, and plant uptake of mercury in a soil from Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. Sci Total Environ 368:753–768
Hu S, Lau KWK, Wu M (2001) Cadmium sequestration in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Sci 161:987–996
Huang SQ, Peng J, Qiu CX, Yang ZM (2009) Heavy metal-regulated new microRNAs from rice. J Inorg Biochem 103:282–287
Huang SQ, Xiang AL, Che LL, Chen S, Li H, Song JB, Yang ZM (2010) A set of miRNAs from Brassica napus in response to sulfate-deficiency and cadmium stress. Plant Biotechnol J. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00517.x
Hylander LD (2001) Globla mercury pollution and its expected decrease after a mercury trade ban. Water Air Soil Pollut 125:331–344
Israr M, Sahi S, Datta R, Sarkar D (2006) Bioaccumulation and physiological effects of mercury in Sesbania drummondii. Chemosphere 65:591–598
Keyse SM, Tyrrell RM (1989) Heme oxygenase is the major 32-kDa stress protein induced in human skin fibroblasts by UV radiation, hydrogen peroxide and sodium arsenate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:99–103
Khedr AH, Abbas MA, Wahid AA, Quick WP, Abogadallah GM (2003) Proline induces the expression of salt-stress responsive proteins and may improve the adaptation of Pancratium maritimum L. to salt-stress. J Exp Bot 54:2553–2562
Lee Y, Bak G, Choi Y, Chuang WI, Cho HT (2008) Roles of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in root hair growth. Plant Physiol 147:624–635
Mehta SK, Gaur JP (1999) Heavy-metal-induced proline accumulation and its role in ameliorating metal toxicity in Chlorella vulgaris. New Phytol 143:253–259
Miller G, Stein H, Honing A, Kapulnik Y, Zilberstein A (2005) Responsive modes of Medicago sativa proline dehydrogenase genes during salt and recovery dictate free proline accumulation. Planta 222:70–79
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:490–498
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Nocito FF, Lancilli C, Crema B, Fourcoy P, Davidian JC, Sacchi GA (2006) Heavy metal stress and sulfate uptake in maize roots. Plant Physiol 141:1138–1148
Noriega GO, Balestrasse KB, Batlle AMC, Tomaro ML (2004) Heme oxygenase exerts a protective role against oxidative stress in soybean leaves. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 323:1003–1008
Palma JM, Sandalio LM, Corpas FJ, Romero-Puertas MC, McCarthy I, del Río LA (2002) Plant proteases, protein degradation and oxidative stress: role of peroxisomes. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:521–530
Patra M, Sharma A (2000) Mercury toxicity in plants. Bot Rev 66:379–422
Pedersen AL, Feldner HC, Rosendahl L (1996) Effect of proline on nitrogenase activity in symbiosomes from root nodules of soybean (Glycine max L.) subjected to drought stress. J Exp Bot 47:1533–1539
Peterson SA, Van Sickle J (2007) Mercury concentration in fish from streams and rivers throughout the western United States. Environ Sci Technol 41:58–65
Puckette MC, Hua Weng, Mahalingam R (2007) Physiological and biochemical responses to acute ozone-induced oxidative stress in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:70–79
Shah K, Dubey RS (1998) Effect of cadmium on proline accumulation and ribonuclease activity in rice seedlings: role of proline as a possible enzyme protectant. Biol Plant 40:121–130
Shibahara S, Muller RM, Taguchi H (1987) Transcriptional control of rat heme oxygenase by heat shock. J Biol Chem 262:12889–12892
Siripornadulsil S, Traina S, Verma DPS, Sayre RT (2002) Molecular mechanisms of proline-mediated tolerance to toxic heavy metals in transgenic microalgae. Plant Cell 14:2837–2847
Solomon A, Beer S, Waisel Y, Jones GP, Paleg LG (1994) Effect of NaCl on the carboxylating activity of Rubisco from Tamaxis jordanis in presence and absence of proline-related compatible solutes. Physiol Plant 90:198–204
Song NH, Yin XL, Chen GF, Yang H (2007) Biological responses of wheat (Triticum aestivum) plants to the herbicide chlorotoluron in soils. Chemosphere 69:1779–1787
Srisook K, Jung NH, Kim BR, Cha SH, Kim HS, Cha YN (2005) Heme oxygenase-1-mediated partial cytoprotective effect by NO on cadmium-induced cytotoxicity in C6 rat glioma cells. Toxicol In Vitro 19:31–39
Sudo E, Itouga M, Yoshida-Hatanaka K, Ono Y, Sakakibara H (2008) Gene expression and sensitivity in response to copper stress in rice leaves. J Exp Bot 59:3465–3474
Sun XM, Bo Lu, Xu LL, Wang SQ, Mehta SK, Yang ZM (2007) Coordinated expression of sulfate transporters and its relation with sulfur metabolites in Brassica napus exposed to cadmium. Bot Stud 48:43–54
Wang Y, Greger M (2004) Clonal differences in mercury tolerance, accumulation and distribution in willow. J Environ Qual 33:1779–1785
Wang SH, Yang ZM, Lu B, Li SQ, Lu YP (2004) Copper-induced stress and antioxidative responses in roots of Brassica juncea L. Bot Bull Acad Sin 45:203–212
Zhang LP, Mehta SK, Liu ZP, Yang ZM (2008) Copper-induced proline synthesis is associated with nitric oxide generation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell Physiol 49:411–419
Zhou ZS, Huang SQ, Guo K, Mehta SK, Zhang PC, Yang ZM (2007) Metabolic adaptations to mercury-induced oxidative stress in roots of Medicago sativa L. J Inorg Biochem 101:1–9
Zhou ZS, Wang SJ, Yang ZM (2008) Biological detection and analysis of mercury toxicity to alfalfa (Medicago sativa) plants. Chemosphere 70:1500–1509
Zhou ZS, Guo K, Elbaz AA, Yang ZM (2009) Salicylic acid alleviates mercury toxicity by preventing oxidative stress in roots of Medicago sativa. Environ Exp Bot 65:27–34
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20877041) and National Foundation for Fostering Talents of Basic Science (J0730647).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elbaz, A., Wei, Y.Y., Meng, Q. et al. Mercury-induced oxidative stress and impact on antioxidant enzymes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii . Ecotoxicology 19, 1285–1293 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0514-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0514-z