Abstract
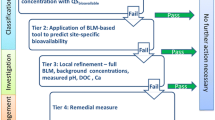
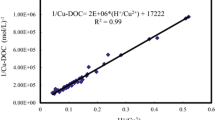
Farming of tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus is an important aquacultural activity in Taiwan. Due to the elevated arsenic (As) concentration in pond water, it is important to assess the bioavailability and toxicity of As to tilapia for protection of aquatic life and human health. In the present study, we developed a biotic ligand model (BLM)-based toxicodynamic approach to dynamically predict both acute and chronic effective concentrations of As to tilapia in two tilapia farms located at Pudai and Chiangchun counties in southwestern Taiwan. Parameters revealed in the mechanistic model were obtained by fitting this model to the toxicokinetic and toxicodynamic data from our previous laboratory experiments. Based on our extended BLM concepts, the site-specific water effect ratios and ambient water quality criteria can be determined with known water chemistry. The proposed methodology was capable of bridging the gap between laboratory toxicity bioassays and field investigations. With respect to risk assessments, our research may also provide an useful means of generating and adjusting the site-specific ambient water quality criteria.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bielmyer GK, Grosell M, Paquin PR, Mathews R, Wu KB, Santore RC, Brix KV (2007) Validation study of the acute biotic ligand model for silver. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:2241–2246. doi:10.1897/06-634R.1
Bury NR, Grosell M, Grover AK, Wood CM (1999) ATP-dependent silver transport across the basolateral membrane of rainbow trout gills. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 159:1–8. doi:10.1006/taap.1999.8706
Chen CJ, Hsueh YM, Tseng MP, Lin YC, Hsu LI, Chou WL, Chiou HY, Wang IH, Chou YL, Tseng CH, Liou SH (2001) Individual susceptibility to arseniasis. In: Chappell WR, Abernathy CO, Calderon RL (eds) Arsenic exposure and health effects IV. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 135–143
Chen CJ, Hsu LI, Wang CH, Shih WL, Hsu YH, Tseng MP, Lin YC, Chou WL, Chen CY, Wang LH, Cheng YC, Chen CL, Chen SY, Wang YH, Hsueh YM, Chiou HY, Wu MM (2005) Biomarkers of exposure, effect, and susceptibility of arsenic-induced health hazards in Taiwan. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 206:198–206. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2004.10.023
De Schamphelaere KA, Janssen CR (2002) A biotic ligand model predicting acute copper toxicity for Daphnia magna: the effect of calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, and pH. Environ Sci Technol 36:48–54. doi:10.1021/es000253s
Di Toro DM, Allen HE, Bergman HL, Meyer JS, Paquin PR, Santore RC (2001) Biotic ligand model of the acute toxicity of metals. 1. Technical basis. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2383–2396. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2001)020<2383:BLMOTA>2.0.CO;2
Ferguson JF, Gavis J (1972) A review of the arsenic cycle in natural waters. Water Res 6:1259–1274. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(72)90052-8
Liao CM, Ling MP (2003) Assessment of human health risks for arsenic bioaccumulation in tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) and large-scale mullet (Liza macrolepis) from blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 45:264–272. doi:10.1007/s00244-003-0107-4
Liao CM, Chen BC, Singh S, Lin MC, Liu CW, Han BC (2003) Acute toxicity and bioaccumulation of arsenic in tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) from a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Environ Toxicol 18:252–259. doi:10.1002/tox.10122
Liao CM, Tsai JW, Ling MP, Liang HM, Chou YH, Yang PT (2004) Organ-specific toxicokinetics and dose-response of arsenic in tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 47:502–510. doi:10.1007/s00244-004-3105-2
Liao CM, Jou LJ, Lin CM, Chiang KC, Yeh CH, Chou BYH (2007) Predicting acute copper toxicity to valve closure behavior in the freshwater clam Corbucula fluminea supports the biotic ligand model. Environ Toxicol 22:295–307. doi:10.1002/tox.20263
Morgan TP, Wood CM (2004) A relationship between gill silver accumulation and acute silver toxicity in the freshwater rainbow trout: support for the acute silver biotic ligand model. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1261–1267. doi:10.1897/03-181
Natale OE, Gómez CE, Leis MV (2007) Application of the biotic ligand model for regulatory purposes to selected rivers in Argentina with extreme water-quality characteristics. Integr Environ Assess Manag 3:517–528. doi:10.1897/IEAM_2006-058.1
Niyogi S, Wood CM (2004) Biotic ligand model, a flexible tool for developing site-specific water quality guidelines for metals. Environ Sci Technol 38:6177–6190. doi:10.1021/es0496524
Paquin PR, Santore RC, Wu KB, Kavvadas CD, Di Toro DM (2000) The biotic ligand model: a model of the acute toxicity of metals to aquatic life. Environ Sci Policy 3:S175–S182. doi:10.1016/S1462-9011(00)00047-2
Paquin PR, Zoltay V, Winfield RP, Wu KB, Mathew R, Santore RC, Di Toro DM (2002) Extension of the biotic ligand model of acute toxicity to a physiologically-based model of the survival time of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed to silver. Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 133:305–343. doi:10.1016/S1532-0456(02)00105-9
Pelgrom SMGJ, Lock RAC, Balm PHM, Bonga SEW (1997) Calcium fluxes in juvenile tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus, exposed to sublethal waterborne Cd, Cu or mixtures of these metals. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:770–774. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1997)016<0770:CFIJTO>2.3.CO;2
Playle RC (1998) Modelling metal interaction at fish gills. Sci Total Environ 219:147–163. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(98)00232-0
Santore RC, Di Toro DM, Paquin PR, Allen HE, Meyer JS (2001) Biotic ligand model of the acute toxicity of metals 2 application to acute copper toxicity in freshwater fish and Daphnia. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2397–2402. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2001)020<2397:BLMOTA>2.0.CO;2
Schwartz ML, Vigneault B (2007) Development and validation of a chronic copper biotic ligand model for Ceriodaphnia dubia. Aquat Toxicol 84:247–254. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.01.011
Szebedinszky C, McGeer JC, McDonald DG, Wood CM (2001) Effect of chronic Cd exposure via the diet or water on internal organ-specific distribution and subsequent gill Cd uptake kinetics in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ Toxicol Chem 20:597–607. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2001)020<0597:EOCCEV>2.0.CO;2
Tao S, Liu C, Dawson R, Long A, Xu F (2000) Uptake of cadmium adsorbed on particulates by gills of goldfish (Carassius auratus). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 47:306–313. doi:10.1006/eesa.2000.1990
Tsai JW, Liao CM (2006) Mode of action and growth toxicity of arsenic to tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus can be determined bioenergetically. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50:144–152. doi:10.1007/s00244-005-1054-z
US EPA (2000) Technical progress report of the implementation plan for probabilistic ecological assessments: aquatic systems. Meeting scheduled for April 6–7. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Vahter M (2002) Mechanisms of arsenic biotransformation. Toxicol 181–182:211–217. doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(02)00285-8
Wong CKC, Wong MH (2000) Morphological and biochemical changes in the gills of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) to ambient cadmium exposure. Aquat Toxicol 48:517–527. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(99)00060-0
Yost LJ, Tao SH, Egan SK, Barraj LM, Smith KM, Tsuji JS, Lowney YW, Schoof RA, Rachman NJ (2004) Estimation of dietary intake of inorganic arsenic in U.S. children. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 10:473–483. doi:10.1080/10807030490452151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, BC., Chen, WY. & Liao, CM. A biotic ligand model-based toxicodynamic approach to predict arsenic toxicity to tilapia gills in cultural ponds. Ecotoxicology 18, 377–383 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0292-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0292-z