Abstract
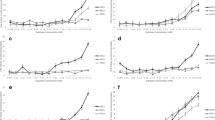
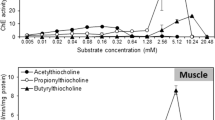
Effects of cadmium on in vitro and in vivo cholinesterase (ChE) activities of brain and muscle tissues of Oreochromis niloticus fingerlings were evaluated, considering its potential use in biomonitoring tropical water pollution. Results show that in vitro ChE activities were depressed significantly by millimolar concentration ranges of Cd2+. The IC50 values of Cd2+ on in vitro ChE activity in brain and muscle tissues were 1.56 and 4.31 mM, respectively. Exposure of fish to environmentally relevant concentrations of Cd2+ (5–30 μg l−l) for 28 days evoked only a transient inhibition (21–34%) of in vivo ChE activities. Prior exposure and co-exposure of fish to 15 μg l−1 of Cd2+ enhanced the extent of inhibition of ChE levels induced by the organophosphorous insecticide chlorpyrifos. As high concentrations of cadmium have the potential to depress ChE activities, monitoring of metal levels in water bodies with suspected high levels of metal inputs is necessary to accurately interpret the fish ChE inhibition data in relation to insecticide contaminations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beauvais SL, Jones SB, Parris JT, Brewer SK, Little EE (2001) Cholinergic and behavioural neurotoxicity of carbaryl and cadmium to larval rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 49(1):84–90
Coppage DL, Bradeich E (1976) River pollution by anti-cholinesterase agents. Water Res 10:19–24
Cunha I, Mangas-Ramirez E, Guilhermino L (2007) Effects of copper and cadmium on cholinesterase and glutathione S-transferase activities of two marine gastropods (Monodonta lineata and Nucella lapillus). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 145(4):648–657
de La Torre FR, Salibian A, Ferrari L (2000) Biomarker assessment in juvenile Cyprinus carpio exposed to waterborne cadmium. Environ Pollut 109(2):277–282
de Souza Dahm KC, Rückert C, Tonial EM, Bonan CD (2006) In vitro exposure of heavy metals on nucleotidase and cholinesterase activities from the digestive gland of Helix aspersa. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 143(3):316–320
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fulton MH, Key PB (2001) Acetylcholinesterase inhibition in estuarine fish and invertebrates as an indicator of organophosphorus insecticide exposure and effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:37–45
Garcia-Santos S, Fontainhas-Fernandes A, Wilson JM (2006) Cadmium tolerance in the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) following acute exposure: assessment of some ionoregulatory parameters. Environ Toxicol 21:33–46
Gill TS, Tewari H, Pande J (1991) In vivo and in vitro effects of cadmium on selected enzymes in different organs of the fish Barbus conchonius ham (Rosy barb). Comp Biochem Physiol C Comp Pharmacol 100(3):501–505
Gruber SJ, Munn MD (1998) Organophosphate and carbamate insecticides in agricultural waters and cholinesterase inhibition in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 132:117–142
Jebali J, Banni M, Guerbej H, Almeida EA, Bannaoui A, Boussetta H (2006) Effect of malathion and cadmium on acetycholinesterase activity and metallothionein levels in the fish Seriola dumerilli. Fish Physiol Biochem 32(1):93–98
Klavins M, Briede A, Rodinov V, Kokorote I, Parele E, Klavina I (2000) Heavy metals in rivers of Lativia. Sci Total Environ 262:175–183
Kozlovskaya VI, Mayer FI, Menzikova OV, Chuyko GM (1993) Cholinesterases of aquatic animals. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 132:117–142
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Méndez-Armenta M, Rios C (2007) Cadmium neurotoxicity. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 23:350–358
Mukherjee S, Bhattacharya S (1974) Effects of some industrial pollutants on fish brain. Cholinesterase activity. Environ Physiol Biochem 4:226–231
Norrgren L, Pettersson US, Bergquist PA (2000) Environmental monitoring of the Kafae river located in the upper belt Zambia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 38:334–341
Pathiratne A, Athauda P (1998) Toxicity of chlorpyrifos and dimethoate to fingerlings of the Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus: Cholinesterase inhibition. Sri Lanka J Aquat Sci 3:77–84
Pathiratne A, Chandrasekara LWHU, Seram PKC De (2008) Effects of biological and technical factors on brain and muscle cholinesterases in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus: implications for biomonitoring neurotoxic contaminations. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54(2):309–317
Payne JF, Mathieu A, Melvin W, Fancey LL (1996) Acetylcholinesterase, an old biomarker with a new future? Field trials in association with two urban rivers and a paper mill in Newfoundland. Mar Pollut Bull 32(2):225–231
Rodriguez-Fuentes G, Gold-Bouchot G (2004) Characterization of cholinesterase activity from differential tissues of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Mar Environ Res 58:505–509
Roesijadi G, Robinson WE (1994) Metal regulation in aquatic animals: mechanisms of uptake, accumulation and release. In: Malins DC, Ostrander GK (eds) Aquatic toxicology: molecular, biochemical and cellular perspectives. Lewis Publishers, CRC Press, pp 387–420
Senarathne P, Pathiratne KAS (2007) Accumulation of heavy metals in a food fish Mystus gulio inhabiting Bolgoda Lake Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka J Aquat Sci 12:61–76
Senger MR, Rosemberg DB, Rico EP, Arizi MDB, Dias RD, Bogo MR, Bonan CD (2006) In vitro effect of zinc and cadmium on acetylcholinesterase and ectonucleotidase activities in Zebra fish (Danio rerio) brain. Toxicol In vitro 20(6):954–958
Sturm A, Wogram J, Segner H. Liess M (2000) Different sensitivity to organophosphates of acetylcholinesterase and butylcholinesterase from three-spined stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus): application in biomonitoring. Environ Toxicol Chem 19(6):1607–1615
Van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149
Wijeyaratne WMDN, Pathiratne A (2006) Acetylcholinesterase inhibition and gill lesions in Rasbora caverii an indigenous fish inhabiting rice field associated waterbodies in Sri Lanka. Ecotoxicology 15:609–619
Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. K. A. S. Pathiratne, Head of the Department of Chemistry, University of Kelaniya for granting permission to analyze the cadmium levels in water by atomic absorption spectrometry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, K.T.U., Pathiratne, A. In vitro and in vivo effects of cadmium on cholinesterases in Nile tilapia fingerlings: implications for biomonitoring aquatic pollution. Ecotoxicology 17, 725–731 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0221-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0221-1