Abstract
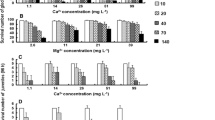
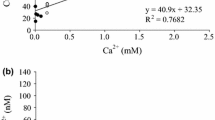
A major question in the field of ecotoxicology is how DOM affects copper accumulation and toxicity in planktonic organisms; copper acute toxicity and bioaccumulation in Ceriodaphnia silvestrii were investigated in the presence and absence of humic substances (HS) under controlled laboratory conditions. Copper was determined as free Cu2+ ions in the media and total copper in the animals; metal ion buffers were used for ion selective electrode calibration, extending the lower detection limit to 10−11 mol l−1. Groups of 20 adult females of similar sizes were exposed (24 h) to a range of nominal copper concentrations. Based on total added copper, LC50 was 4.4 × 10−8 mol l−1 without HS, whereas with 20 mg l−1 HS, it was 25 times higher (1.1 × 10−6 mol l−1). Based on free Cu2+ ions LC50 was statistically similar either with (2.8 × 10−8 mol l−1) or without HS (3.3 × 10−8 mol l−1). The present results showed that natural DOM reduced copper toxicity and that free Cu2+ ions correlates to the bioavailable fraction to zooplankton. Nevertheless, copper bioaccumulation by C. silvestrii was similar either in the presence or absence of humic substances, suggesting that C. silvestrii regulates its body copper content up to 3.0 × 10−8 mol l−1 free Cu2+ ions in the media. The organisms were not able to deal with higher free Cu2+ ions concentrations in the media.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABNT (2005) Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. Avaliação da toxicidade crônica utilizando Ceriodaphnia ssp. (Cladocera, Crustacea) NBR13373. Rio de Janeiro, julho, 14 p
Borgmann U, Norwood WP, Clarke C (1993) Accumulation, regulation and toxicity of copper, zinc, lead and mercury in Hyalella azteca. Hydrobiologia 259:79–89
Bossuyt BTA, Janssen CR (2005) Copper regulation and homeostasis of Daphnia magna and Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata: influence of acclimation. Environ Pollut 136:135–144
Cao J, Lam KC, Dawson RW, Liu WX, Tao S (2004) The effect of pH, ion strength and reactant content on the complexation of Cu+2 by various natural organic ligands from water and soil in Hong Kong. Chemosphere 54:507–514
El-Moor-Loureiro LMA (1997) Manual para a identificação dos Cladocera límnicos brasileiros Universa. Universidade Católica de Brasília, Brasília, 155 p
Fonseca AL, Rocha O (2004) The life-cycle of Ceriodaphnia silvestrii Daday, 1902, a neotropical endemic species (Crustacea, Cladocera, Daphnidae). Acta Limnol Bras 16:319–328
Giesy JP, Newell A, Leversee GJ (1983) Copper speciation in soft, acid, humic waters: effects on copper bioaccumulation by and toxicity to Simocephalus serrulatus (Daphnidae). Sci Total Environ 28:23–36
Gorbi G, Corradi MG, Invidia M, Rivara L, Bassi M (2002) Is Cr(VI) toxicity to Daphnia magna modified by food availability or algal exudates? The hypothesis of a specific chromium/algae/exudates interaction. Water Res 36:1917–1926
Hamilton MA, Russo RC, Thurston RV (1977) Trimmed Spearman–Karber method for estimating median lethal concentration in toxicity bioassays. Environ Sci Technol 11:714–719 Correction (1978), 12, 417
Heijerick DG, Janssen CR, Coen WM (2003) The combined effects of hardness, pH, and dissolved organic carbon on the chronic toxicity of Zn to Daphnia magna: development of a surface response model. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 44:210–217
Kim SD, Ma HZ, Allen HE, Cha DK (1999) Influence of dissolved organic matter on the toxicity of copper to Ceriodaphnia dubia: effect of complexation kinetics. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:2433–2437
King CK, Gale SA, Stauber JL (2006) Acute toxicity and bioaccumulation of aqueous and sediment-bound metals in the estuarine amphipod Melita plumulosa. Environ Toxicol 21:489–504
Lombardi AT, Hidalgo TMR, Vieira AAH, Sartori AL (2007) Toxicity of ionic copper to the freshwater microalga Scenedesmus acuminatus (Chlorophyceae, Chlorococcales). Phycologia 46:74–78
Lorenzo JI, Nieto O, Beiras R (2002) Effect of humic acids on speciation and toxicity of copper to Paracentrotus lividus in seawater. Aquat Toxicol 58:27–41
Lores EM, Pennock JR (1999) Bioavailability and trophic transfer of humic-bound copper from bacteria to zooplankton. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 187:67–75
Lores EM, Snyder RA, Pennock JR (1999) The effect of humic acid on uptake/adsorption of copper by a marine bacterium and two marine ciliates. Chemosphere 38:293–310
Luoma SN (1983) Bioavailability of trace metals to aquatic organisms: a review. Sci Total Environ 28:1–22
Ma HZ, Kim SD, Cha DK, Allen HE (1999) Effect of kinetics of complexation by humic acid on toxicity of copper to Ceriodaphnia dubia. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:828–837
Meador JP (1991) The interaction of pH, dissolved organic carbon, and total copper in the determination of ionic copper and toxicity. Aquat Toxicol 19:13–32
Morel FMM, Hering JG (1993) Principles and applications of aquatic chemistry. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, p 588
Nogueira PFM, Melão MGG, Lombardi AT, Vieira AAH (2005) The effects of Anabaena spiroides (Cyanophyceae) exopolysaccharide on copper toxicity to Simocephalus serrulatus (Cladocera, Daphnidae). Freshw Biol 50:1560–1567
Oikari A, Kukkonen J, Virtanen V (1992) Acute toxicity of chemicals to Daphnia Magna in humic waters. Sci Total Environ 117/118:367–377
Oliveira-Neto A, Botta-Paschoal CM (2000) Sensibilidade do cladocera lacustre planctônico Ceriodaphnia silvestrii (Família Daphnidae) aos metais cádmio, cromo e chumbo. In: Espíndola ELG (ed) Ecotoxicologia—Perspectivas para o século XXI. São Carlos Rima Editora
Paquin PR, Gorsuch JW, Apte S, Batley GE, Bowles KC, Campbell PGC, Delos CG, Di Toro DM, Dwyer RL, Galvez F, Gensemer RW, Goss GG, Hogstrand C, Jansen CR, McGeer JC, Naddy RB, Playle RC, Santore RC, Schneider U, Stubblefield WA, Wood CM, Wu KB (2002) The biotic ligand model: a historical overview. Comp Biochem Physiol C, Toxicol Pharmacol 133:3–35
Rainbow PS, Dallinger R (1993) Metal uptake, regulation and excretion in freshwater invertebrate. In: Dallinger R, Rainbow PS (eds) Ecotoxicology of metal in invertebrate. Lewis publishers, Boca Raton, pp 119–131
Rainbow PS, White SL (1989) Comparative strategies of heavy metal accumulation by crustaceans: Zn, Cu, and Cd in a decapod, an amphipod and a barnacle. Hydrobiologia 174:245–262
Reuter JH, Perdue EM (1977) Importance of heavy metal-organic matter interactions in natural waters. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 41:325–334
Slaveykova VI, Wilkinson KJ (2005) Predicting the bioavailability of metals and metal complexes: critical review of the biotic ligand model. Environ Chem 2:9–24
US Environmental Protection Agency (1991) In: Weber CI (ed) Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms, 4th edn. EPA-600/4–90/027
Winner RW (1985) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of copper as affected by interactions between humic acid and water hardness. Water Res 19:449–455
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge FAPESP (2002/04275-0) and CNPq (130496/2002-2; 472509/2006-3) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, M.A.P.F., Melão, M.G.G. & Lombardi, A.T. The effects of humic substances on copper toxicity to Ceriodaphnia silvestrii Daday (Crustacea, Cladocera). Ecotoxicology 17, 449–454 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0196-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0196-y