Abstract
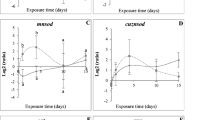
The present study was designed to detect in situ effects of cadmium on marine organisms Cerastoderma glaucum from the gulf of Gabès (Tunisia). Six sampling stations were chosen: one site, relatively far from known local source of pollution, was considered as uncontaminated site and five sites clearly exposed to anthropogenic impact. Metallothionein like protein (MTLP) and sub-cellular metal partitioning were measured in cockles (C. glaucum) gills and digestive gland. Various biomarkers were also measured, including malondialdehyde (MDA) in the digestive gland and acetylcholinesterase activity (AChE) in the remainder. The health status of the cockles was assessed by using the condition index (CI). Significant differences between sites were noted for Cd concentrations, (CI) and also for the three studied biomarkers. Significant higher biomarkers response was measured in cockles from stations located in the northern part of the gulf, which are exposed directly to industrial and urban effluents, whereas the response of most biomarkers was minimal at the reference station. Positive and significant correlations were observed between MTLP and Cd concentrations in the digestive gland and in the gills. However, it must be noted that these correlations were more significant in the digestive gland, suggesting that compared to the gills, the digestive gland of C. glaucum is more suitable for monitoring metal pollution. The subcellular distribution of Cd showed that the soluble fraction was the major compartment for Cd storage, a pattern which is due to the role of MTLP in Cd detoxication. But at the most contaminated site (EH), cadmium in the digestive gland was preferentially accumulated in the insoluble fraction (P1) suggesting that the MTLP capacity in binding metals was not sufficient to avoid the binding of Cd to the insoluble fraction. Furthermore, the MTLP concentrations in the cockles from this site are lower than expected. So in highly polluted sites, MTLP in C. glaucum should not be used as a useful biomarker for metal pollution. The lipid peroxidation as presented by malondialdehyde levels, and MT-like protein concentrations increased in cockles exposed to cadmium contamination. We can, therefore, hypothesize that Cd could induce MTLP synthesis and MDA increase. While AChE had distinct and specific pattern showing that cadmium is not the only factor of the inhibition of cholinesterase activity. There are other polluting inputs engendering this inhibition.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdellaoui D, Jaballi Y (2005) Etude sédimentologique et géochimique des sédiments marins de la zone côtière de Sfax. Mémoire de projet de fin d’études en géologie d’environnement et d’aménagement. Faculté Des Sciences De Sfax
Amiard JC, Amiard-Triquet C, Ballan-Dufrançais C, Berthet B, Jeantet AY, Martoja R, Truchet M (1989) Study of the bioaccumulation at the molecular, cellular and organism levels of lead and copper transferred to the oyster Crassostrea gigas thumbing directly from water or via food. Polish Acad Sci 34:521–529
Amiard JC, Cosson RP (1997) Les métallothionéines. In: Lagadic L, Caquet T, Amiard JC, Ramad F (eds) Biomarqueurs en écotoxicologie. Aspect fondamentaux. Masson, Paris, pp 53–66
Arjonilla M, Forja A, Gomez-Parra A (1994) Sediment analysis does not provide a good measure of heavy metal bioavailability to (Cerastoderma glaucum) (Mollusca: Bivalvia) in confined coastal ecosystems. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 52:810–817
Bebianno MJ, Machado LM (1997) Concentrations of metals and metallothioneins in (Mytilus galloprovincialis) along the South Coast of Portugal. Mar Pollut Bull 34:666–671
Bebianno MJ, Serafim MA (1998) Comparison of metallothionein induction in response to cadmium in the gills of the bivalve molluscs (Mytilus gallopronvincialis) and (Ruditapes decussates). Sci Total Environ 214:123–131
Bocquené G, Galgani F (1998) Biological effect of contaminants: cholinesterases inhibition by organophosphate and carbamate compounds, ICES Tech. Mar Environ Sci 22:1–13
Bocquené G., Galgani F, Walker H (1997) Les cholinestérases, Biomarqueurs de neurotoxicité. In: Lagadic L, Caquet T, Amiard JC, Ramade F (eds) Biomarqueurs en Ecotoxicologie-Aspects Fondamentaux. Masson, Paris, pp 209–240
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Carpené E (1993) Metallothionein in marine molluscs. In: Dalling R, Rainbow PS (eds) Ecotoxicoloy of metal in invertebrate. Lewis Publ, Boca Raton, pp 56–72
Cattani O, Serra R, Isani G, Raggi G, Cortesi P, Carpense E (1996) Correlation between metallothionein and energy metabolism in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) exposed to cadmium. Comp Biochem Physiol 113:193–199
Cavaletto A, Ghezzi B, Burlando B, Evangelisti V, Ceratto N, Viarengo A (2002) Effect of hydrogen peroxide on antioxidant enzymes and metallothionein level in the digestive gland of Mytilus golloprovincialis. Comp Biochem Physiol 131:447–455
Chouba L, Zamouri-Langar N, El Abed A (1998) Le réseau de surveillance des contaminants nocifs: les métaux lourd dans la chaire de la clovisse. INSTM. Actes des Acquis de recherche agronomique et vétérinaire IRESAT, n°5
Cosson RP (2000) Bivalve metallothionein as a biomarker of aquatic ecosystem pollution by trace metals: limits and perspectives. Cell Mol Biol 46:295–309
Cosson RP, Amiard JC (1998) Utilisation des métallothionéines comme biomarqueurs d’exposition aux métaux. In: Lagadic L, Caquet T, Amiard JC, Ramade F (eds) Utilisation des Biomarqueurs pour la Surveillance de la qualité de l’environnement. Lavoisier, Paris, pp 77–109
Cossu C, Doyotte A, Babut M, Exinger A, Vasseur P (2000) Antioxidant biomarkers in freshwater bivalves, Unito tumidus, in response to different contamination profiles of aquatic sediment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 45:106–121
Couillard Y, Campbell PGC, Tessier A (1993) Response of metallothionein concentration in a freshwater bivalve (Anodonta grandis) along an environmental cadmium gradient. Limnol Oceanogr 38:299–313
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andreas V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of AChE activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
El Mnif-Triqui N (1995) La palourde Ruditapes decassatus (Linnee, 1758) des côtes Tunisiennes. Biométrie, reproduction et impact de l’environnement sur la bioaccumulation de métaux traces. Thèse de troisième cycle. Université de Tunis II,Tunisie
Flammarion P, Migeon B, Garric J (1996) Joint effect of copper sulfate and methidathion on rainbow trout (Oncorhyncus mykiss) EROD and AChE activities. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 56:440–445
Food and Drug Administration (1993) Guidance Document for Cadmium in Shellfish. Centre for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition: US/FDA, Washington, pp 31
Galgani F, Bocquené G (1989) A methods for routine detection of organophosphates and carbamates in sea water. Environ Technol Lett 10:311–322
Geret F, Serafim A, Barreira L, Bebianno MJ (2002) Effect of cadmium on antioxidant enzyme and lipid peroxidation in the gills of the clam (Ruditapes decassatus). Biomarkers 7:242–256
Geret F, Serafim A, Bebianno MJ (2003) Antioxidant enzyme activities, metollothioneins and lipid peroxidation as biomarker in (Ruditapes decussates)? Ecotxicol 12:417–426
Giguère A, Couillard Y, Campbell PGC, Perceval O, Hare L, Pinel-Alloul B, Pellerin J (2003) Steady-state distribution of metals among metallothionein and other cytosoic ligand and links to cytotoxicity in bivalves living along a polymetallic gradient. Aquat Toxicol 64:185–200
Guilhermino L, Barros B, Silva MC, Soares AMVM (1998) Should the use of inhibition of cholinesterase as a specific biomarker for organophosphate and carbamate pesticides be questioned? Biomarkers 3:157–163
Hamilton SJ, Mehrle PM (1986) Metallothionein in fish: review of its importance in assessing stress from metal contamination. Trans Am Fish Soc 115:596–609
Hamza-Chaffai A, Cosson R.P., Amiard-Triquet C, El Abed A (1995) Physico-chemical form of storage of metal (Cd, Cu and Zn) and metallothionein-like proteins in gills and liver of marine fish from the Tunisian cost: ecotoxicological consequences. Comp Biochem Physiol 111:329–341
Hamza-Chaffai A, Amiard-Triquet C, El Abed A (1997) Metallothionein-Like protein: is it an efficient biomarker of metal contamination? A case study based on fish from the Tunisian coast. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 33:53–62
Hamza-Chaffai A, Roméo M, Gnassia-Barelli M, El Abed A (1998) Effect on copper and lindane on some biomarkers measured in the clam (Ruditapes decussatus). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 61:397–404
Hamza-Chaffai A, Amiard JC, Pellerin J, Joux L, Berthet B (2000) The potential use of metallothionein in the clam (Ruditapes decassatus) as a biomarker of in situ metal exposure. Comp Biochem Physiol 127:185–197
Hamza-Chaffai A, Pellerin J, Amiard JC (2003) Health assessment of marine bivalve Ruditapes decassatus from the gulf of Gabès (Tunisia). Environ International 28:609–617
Illou S (1999) Impact des rejets telluriques d’origines domestiques et industrielles sur les environnements côtières : cas du littoral Nord de la ville de Sfax (Tunisie). Doctorat de spécialité, Université de Tunis II, Tunisie
Langston WJ, Zhou M (1986) An evaluation of the significance of metal binding proteins in the gastropod, Littorina littorea. Mar Biol 92:505–515
Langston WJ, Bebianno MJ, Burt JR (1998) Metal handling strategies in molluscs. In: Langston WJ, Bebianno MJ (eds) Metal metabolism in aquatic environment. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 219–283
Machreki-Ajmi M (2002) Etude d’une contamination par le cadmium et le plomb chez le mollusque bivalve (Cerastoderma glaucum) issus de la région de Sfax: Etude in situ et in vivo. Diplôme d’études approfondies d’écologie générale. Faculté Des Sciences De Sfax
Machreki-Ajmi M, Hamza-Chaffai A (2006) Accumulation of cadmium and Lead in (Cerastoderma glaucum) originating from the Gulf of Gabès (Tunisia). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 3:529–537
Mouneyrac C, Amiard JC, Amiard-Triquet C (1998) Effect of natural factor (salinity and body weight) on cadmium, copper, zinc and metallothionein-like protein levels in resident populations of oysters (Crassostrea gigas) from a polluted estuary. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 162:125–135
Mougraud Y, Martinez E, Geffard A, Andrai B, Stanisière JY, Amiard JC (2002) Metallothionein concentration in the mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) as a biomarker of response to metal contamination: validation in the field. Biomarker 7:479–490
Najimi S, Bouhaimi A, Daubèze M, Zekhnini A, Pellerin J, Narbonne JF, Moukrim A (1997) Use of acetylcholinestérase in (Perna perna) and (Mytilus galloprovincialis) as a biomarker of pollution in Agadir Marine Bay (South of Marocco). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 58:901–908
Phillips DJH (1990) Use of macroalgae and invertebrates as monitors of metal levels in estuaries and coastal water. In: Furness RW, Rainbow PS (eds) Heavy Metals in the Marine Environment. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 102–119
Roesijadi G (1992) Metallothionein in metal regulation and toxicity in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol 22:81–114
Roesijadi G (1996) Metallothionein and its role in toxic metal regulation. Comp Biochem Physiol 113:117–123
Serbaji MM (2000) Utilisation d’un SIG multi-sources pour la compréhension et la gestion intégrée de l’écosystème côtier de la région de Sfax (Tunisie). Doctorat de spécialité, Université de Tunis II, Tunisie
Smaoui-Damak W, Hamza Chaffai A, Berthet B, Amiard JC (2003) Preliminary study of the clam (Ruditapes decassatus) exposed in situ to metal contamination and originating from the Gulf of Gabès, Tunisia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 71:961–970
Smaoui-Damak W, Hamza Chaffai A, Bebianno MJ, Amiard JC (2004) Variation of metallothioneins in gills of the clam (Ruditapes decassatus) from the Gulf of Gabès (Tunisia). Comp Biochem Physiol 139:181–188
Sokolova IM, Ringwood AH, Johnson C (2005) Tissue-specific accumulation of cadmium in subcellular compartments of eastern oysters Crassostrea virginica Gmelin (Bivalvia: Ostreidae). Aquat Toxicol 74:218–228
Sunderman FW, Marzouk A, Hopfer SM, Zaharia O, Reid MC (1985) Increased lipid peroxidation in tissues of nickel chloride-treated rat. Ann Clin Lab Sci 15:229–236
Szefer P, Szefer K (1985) Occurrence of ten metals in (Mytilus edulis) L. and (Cardium glaucum) from Gdansk Bay. Mar Poll Bull 16:446–450
Szefer P, Wolowcz M (1993) Occurrence of metal in the cockle (Cerastoderma glaucum) from different geographical regions in view of principal component analysis. Mar Poll 64:253–246
Szefer P, Wolowcz M, Kusak A, Deslous Poli JM, Czarmowski WK, Frelek MJ, Berlzunce M-J (1999) Distribution of mercury and other trace metals in the cockle (Cerastoderma glaucum) from the Mediterranean Lagoon Etang de Thau. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 36:56–63
Tort L, Kargacin B, Torres P, Giralt M, Hidalgo J (1996) The effect of cadmium exposure and stress on plasma cortisol, metallothionein levels and oxidative status in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) liver. Comp Biochem Physiol 114:29–34
Viarengo A (1989) Heavy metals in marine invertebrates: mechanisms of regulation and toxicity at the cellular level. In: CRC Reviews in Aquatic Science, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 295–317
Viarengo A, Ponzano E, Dondero F, Fabbari R (1997) A simple spectrophotometric method for metallothionein evaluation in marine organisms: an application to Mediterranean and Antarctic molluscs. Mar Environ Reas 44:69–84
Viarengo A, Burlando B, Ceratto N, Panfoli I (2000) Antioxidant role of metallothioneins: a comparative overview. Cell Mol Biol 46:407–417
Widdows J, Nasci C, Fossato VU (1997) Effect of pollution on the scope for growth of mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) from the Venice Lagoon, Italy. Mar Environ Res 43:69–79
Zairi M, Rouis MJ (1999) Impacts environnementaux du stockage du phosphogypse à Sfax (Tunisie). Bull Lab Ponts Chaussées 219:29–40
Acknowledgments
We thank Bouassida M, Lazzez M, Hantati B and Mansour R for their help. Rebai A (Center of Biotechnology of Sfax) is acknowledged for his assistance in statistical analysis. We also thank Ben ftéma S and Kebsi S for their assistance in English revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Machreki-Ajmi, M., Ketata, I., Ladhar-Chaabouni, R. et al. The effect of in situ cadmium contamination on some biomarkers in Cerastoderma glaucum . Ecotoxicology 17, 1–11 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-007-0166-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-007-0166-9